* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes–Maxwell`s Equations
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
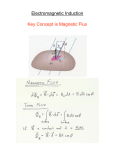
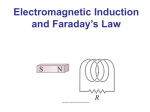
Equation 𝒒𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑙 ∮ 𝑬 ∙ 𝑑𝑨 = 𝜀𝑜 ∮ 𝑩 ∙ 𝑑𝑨 = 0 ∫ 𝑬 ∙ 𝑑𝑟 = − 𝑑Φ𝐵 𝑑𝑡 Maxwell’s Equations of Electromagnetism Name Meaning Gauss’ Law for Electricity Relates net electric flux Φ𝐸 = ∮ 𝑬 ∙ 𝑑𝑨, to enclosed charge Gauss’ Law for Magnetism Faraday’s Law (with Lenz’ negative sign) also ℇ=− 𝑑Φ𝐵 𝑑𝑡 Relates net electric flux Φ𝐵 = ∮ 𝑩 ∙ 𝑑𝑨, to enclosed magnetic system. Mathematically denies the existence of a magnetic monopole. Relates induced electric field (voltage, induced current, etc.) to changing magnetic flux. The negative sign indicating direction of Emf opposes the change in Bflux. Notice also the definition of electric potential (V) on the left hand side of the top equation. ∮ 𝑩 ∙ 𝑑𝑙 = 𝜇𝑜 𝜀𝑜 𝑑Φ𝐸 + 𝜇𝑜 𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑙 𝑑𝑡 ∫ 𝑩 ∙ 𝑑𝑙 = 𝜇𝑜 𝑖𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑙 Ampere-Maxwell Law Ampere’s Law Relates induced B-field to changing electric flux and current. This is the full version of the equation, we only use the Ampere’s Law part When to Use Normally used to determine the electric field due to some geometry of charge. If a “Gaussian Surface” is picked carefully such that the E-field has uniform intensity at all points, E comes out of the integral. Implies that if qencl = 0, the E-field must also be zero. Never, unless to prove no Bmonopoles. Not to be confused with a simple calculation of B-flux for use in Faraday’s Law. Φ𝐵 = ∫ 𝑩 ∙ 𝑑𝑨 When finding the induced Emf (voltage), induced current that results (Emf/Resistance), or the Efield inside the conductor/wire (usually V=Ed). To mathematically utilize Faraday’s Law you probably need to fund a function of the Bflux: Φ𝐵 = ∫ 𝑩 ∙ 𝑑𝑨. The solutions to this flux integral are usually: B*A(t) B(t)*A B(t)*A(t) Ampere-Maxwell: Never for this class. Ampere’s Law: To find the B-field due to a current. Applies with Biot-Savart equation.