* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2nd 6 Weeks - Forms of Energy, Circuits and Force
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
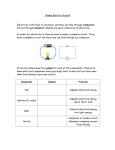
2nd Six Weeks - Vocabulary Forms of Energy Energy – what is needed to do work or cause change Mechanical energy – energy produced by a machine or moving part Sound energy – energy produced from vibration that you can hear Thermal energy – energy that causes a transfer of heat between materials Electrical energy – energy produced by the movement of electrons Light energy – radiant energy that our eyes can see from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum Electricity Electricity - a form of energy that is produced when electrons move from one place to another Electric circuit - a complete pathway that electrons flow through Open circuit - circuit that is not connected in come area, so electrons do not flow through Closed circuit - complete circuit that allows electrons to flow through completely Electric current - the constant flow of electrons Conductor - a material that allows electricity or heat energy to pass through easily Insulator - a material that does not allow electricity or heat energy to pass through easily Electromagnet - a temporary magnet formed by passing an electric current through a wire coiled around an iron core Series circuit - the electrical devices are connected in one continuous loop Parallel circuit - an electric circuit in which each device has its own separate loop Force Force - a push or pull that acts on an object Inertia - the tendency of an object to resist change Push - a force that moves something away Pull - a force that moves something closer Friction - force that opposes the movement of an object Work - using force to move an object Magnetism - a force that pulls magnetic materials across a distance. Gravity - the force that pulls things towards earth Motion - change in position of an object Kinetic energy - energy of movement Potential energy - energy at rest