* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Roman Republic
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
History of science in classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman temple wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
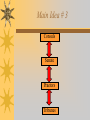
December 9, 2014 I will be able to explain what happened when the Etruscans & Greeks came in contact with the Latins of Italy. I can describe the difference between a Republic and a Democracy? Homework: Our Activity For Sections 3 to 8 describe the Etruscan and Greek influences on Rome, which you must understand before beginning the activity. Pick out of the bin the section that you will learn about first. For each section, begin by reading that section of the Student Text. In the box for that section, summarize the Etruscan or Greek influence on Rome. Repeat…. Section 3 The Romans used Etruscan arches to build bridges, stadiums, and aqueducts. They adopted the cuniculus from the Etruscans and used it to irrigate land, drain swamps, and carry water to their cities. The Keystone State Section 4 Romans enjoyed watching the dangerous Etruscan sport of chariot racing. Slave fighting was also adapted from the Etruscans. Some Roman slaves that fought against each other or animals were called gladiators. Section 5 The Romans used Greek columns and designs to add to the beauty of their buildings. They constructed buildings that resembled Greek temples and used concrete to create even large structures, such as the Pantheon. Section 6 The Romans used a modified Etruscan alphabet, which was an adaptation of the Greek alphabet. Like the Greeks, they write in all-capital letters and carved important documents into walls and columns for all to see. Greek poetry also inspired Roman writers. Section 7 Romans copied the Greek technique for making pottery. Wealthy Romans collected Greek art and built monuments in the Greek style. Roman sculptors and painters used Greek art as a model, but their figures were more realistic. Section 8 Roman religion was highly influenced by Greek religion. The Romans made Greek gods as their own, but gave them Roman names. The Romans were more concerned with following the correct rituals than with stories about their gods. Shoes Caligae Putting your knowledge to use This is an artist painting of a typical street in Rome. From what you learned yesterday what can be seen and inferred. Putting your knowledge to use… Influences that might be seen: – Etruscan engineering (arches), Etruscan sporting events (chariot), Greek architecture (monumental public buildings), Greek art (sculptures on fountain), and Greek writing (on wall) Influences that might be inferred: – Etruscan engineering (water from cuniculi being drawn from a fountain) Using your knowledge, again… Putting your knowledge to use… Influences that might be seen: – Etruscan engineering (arches), Etruscan sporting events (chariot race), Greek architecture (stadium), Greek art (sculptures and monuments), Greek religion (statues of gods and goddesses) Influences that might be inferred: – Etruscan engineering (water for the horses and spectators), Greek writing (accounts of payment and posted scores of the races) The Roman Republic The Growth and Expansion Key Topic: The Roman Republic Main Idea # 1 : How the original Republic was formed Main Idea # 2 : Rome’s republic was shaped by a struggle between wealthy nobles and regular citizens. Main Idea # 3 : How the Roman Republic works Main Idea # 1 How the original Republic was formed Main Idea # 1 1. Who ruled Rome before the Romans? The Etruscans (Tarquins) . 2. What type of rulers were the Etruscans? CRUEL 3. Romans rebel in 509 B.C.E. 4. Create a Republic 5. Republic = form of government where citizens have the power and pick their leaders. Okay so now I’m confused….. What is the difference between a Republic and a Democracy? Okay so now I’m confused….. What is the difference between a Republic and a Democracy? A Democracy is where all the people have a say and have no one to report to. Each person votes on each law. A Republic is a democracy, but each person is responsible to someone else since they are picked by the people to represent them. Main Idea # 1 Make a timeline with these events 509 B.C.E. Rome = small city. Slowly expands. 338 B.C.E. defeat the other Latins 284 B.C.E. defeat Etruscans 267 B.C.E. defeat the Greeks The Republic is growing! Main Idea # 1 1. How did the Romans take over Italy? By force 2. How did they keep those people they conquered under their control Made them citizens able to take part in the government OR Made them allies with their own government, but they had to pay taxes and supply an army to Rome December 10, 2014 I can compare and contrast Plebeians and Patricians. I can describe the difference between a Republic and a Democracy? Homework: Key Topic: The Roman Republic Main Idea # 1 : How the original Republic was formed Main Idea # 2 : Rome’s republic was shaped by a struggle between wealthy nobles and regular citizens. Main Idea # 3 : How the Roman Republic works Main Idea # 2 Rome’s republic was shaped by a struggle between wealthy nobles and regular citizens. Patricians Plebeians Main Idea # 2 Patricians Plebeians Slaves Main Idea # 2 Patricians Plebeians 1. Wealthy land owners 2. Nobles that made up the ruling class 3. Citizens (male)– 1. Majority of the population 2. Artisans, shopkeepers, small farm owners 3. Citizens (male)– could vote, pay taxes, serve in army 4. Could not marry a Patrician 5. Could not serve in could vote, had to pay taxes and serve in the army 4. Could not marry a Plebian 5. Could serve in government government Main Idea # 3 How the Roman Republic works Main Idea # 3 Consuls Senate Praetors Tribunes Main Idea # 3 Consuls 1. Top government official (Like our President) 2. Two chosen every year 3. Headed the army and ran the government 4. Served short term….avoided risk of abusing power 5. Veto The right of the consul to reject the other’s decision. Latin for “I forbid” Main Idea # 3 Senate 1. 300 men 2. Chosen for life 3. Advise Consul 4. Deal with other countries 5. Proposes laws 6. Approve public works 7. Deal with daily government problems (Congress) Main Idea # 3 Praetors 1. Government officials 2. Interpreted law and judged court cases (Supreme Court & IRS) 3. Kept tax records 4. Handled public finances 5. Supervised public festivals Main Idea # 3 Tribunes 1. Elected by all citizens (Plebeians have a large majority so they really elect the official) 2. Bring Plebeian concerns to the government (Lobbiest) 3. Right to veto actions taken by the government First steps towards democracy in Rome! December 11, 2014 I understand and can operate a Roman Republic and fix the problems the Romans couldn’t. Homework: – List 5 different ways to be a good citizen. Example: Voting! Warm Up: (in your passport) The plebeians/patricians (pick one) control the majority of the government (who controlled the pop quiz yesterday). The commoners are the plebeian/patrician (pick one), they are not allowed to take part in the ______________________. What is the difference between a republic and democracy? Main Idea # 3 Keeping it Fair! How do you know what a law says? How do you know how someone should be punished if they do something wrong? Draco of Greece was the first person to do this! Write the laws down so the patricians couldn’t be unfair to the plebeians!!!! Main Idea # 3 Keeping it Fair! 451 BCE The Twelve Tablets were made on bronze tablets Where would you put them in Rome so everyone (both rich and poor) could see them? The forum (marketplace) Main Idea # 3 Keeping it Fair! Finish these sentences…. Innocent until______________________. You have the right to _____________ in court. 1. Laws of Nations – laws to settle disputes between all people Do we still use this today??? Main Idea # 3 Keeping it Fair! Is it fair to punish one person for stealing but not another person? Why or why not? 1. Rule of Law – the idea that all laws should apply to every person equally and all people should be treated the same by the legal system 2. We base all our laws today off of this idea made by the Romans!