* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteria: Staining Techniques
Survey
Document related concepts
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Quorum sensing wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
Microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Horizontal gene transfer wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
Bacterial cell structure wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
3/20/2015
Microscopy
Most microorganisms are in
the micrometer size range
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
m = 1 meter
cm = centimeter = 1/100m = 10-2 meters
mm = millimeter = 10-3 meters
μm = micrometer = 10-6 meters
nm = nanometer = 10-9 meters
1 Angstrom = 10-10 meters
pm = picometer = 10-12 meters
1
3/20/2015
Size Comparisons Among Atoms, Molecules, and Microorganisms
FISH
TAPEWORM
2
3/20/2015
Light microscopy
Magnification vs. resolution
• Magnification = increase in apparent size
of an object
• Resolution = ability to distinguish two
objects as separate from each other
3
3/20/2015
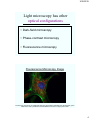
Light microscopy has other
optical configurations
• Dark-field microscopy
• Phase-contrast microscopy
• Fluorescence microscopy
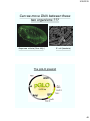
Flourescence Microscopy Image
Fluorescence microscopy of endothelial cells using three labels. Red labels the mitochondria, green
labels the F-actin cytoskeleton and blue labels the nucleus. Image by Steve Karl
4
3/20/2015
Electron Microscopy
Electron Microscope
5
3/20/2015
Electron
Microscope
Images
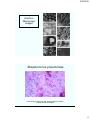
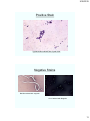
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Gram-positive diplococci with capsule (haloe) formation,
located outside neutrophils.
http://www.fujita-hu.ac.jp/~tsutsumi/case/case071.htm
6
3/20/2015
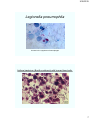
Legionella pneumophila
As seen in the cytoplasm of macrophages
Anthrax bacterium (Bacillus anthracis) with human blood cells.
7
3/20/2015
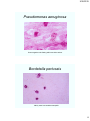
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Gram-negative rods floating within mucoid matrices.
Bordetella pertussis
Mainly seen here outside neutrophils
8
3/20/2015
Bacteria: Staining Techniques
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Positive Stain (basic)
Negative Stain (acidic)
Gram Stain
Acid-Fast Stain
Capsule Stain
Spore Stain
Flagella Stain
Why Stain ???
• A) Achieve Contrast
• B) View Size, Shape, + Cellular Structures
(cell wall, flagella, glycocalyx, spores, etc.)
• C) Classify/Partially identify organisms
9
3/20/2015
Staining: Smear Preparation
• Smear = a slide with microbes on it, ready to be stained
1) Label slide
2) Add water drop to the slide
3) Add the microbe to the water drop
4) Air-dry 5-10 minutes
5) Heat-fix (basic stains only, not acidic stains or
the capsule stain)
Simple Staining Reactions in Microbiology
Positive Stain
10
3/20/2015
Positive Stain
Typical Bacillus stained with Crystal Violet
Negative Stains
Bacillus stained with negrosin
Cocci stained with Negrosin
11
3/20/2015
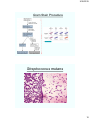
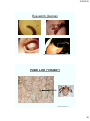
Gram Stain Procedure
Streptococcus mutans
12
3/20/2015
E. coli gram stain
Gram Stain
• 2 slides/group:
• 1 bacterium (tube)
• 1 gum-line sample
•
•
•
•
•
Procedure:
Make Smear
Heat-Fix
Gram-Stain
View with Microscope
• Materials
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Gloves
Slides
Pen
Loop
Toothpick
Sparker/Bunsen Burner
Bacteria
Test Tube Rack
Clothespin
Staining Kit
Transfer Pipette
Drying/Bibulous Paper
Microscope/Oil/Lens Paper
13
3/20/2015
Bacillus cereus with neutrophils
Acid-fast Stain
Designed to identify Mycobacteria
-- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
-- Mycobacterium leprae
Mycobacteria have a special wax
layer in their cell wall (made of
mycolic acid)
Wax helps these bacteria to resist
acid-alcohol de-staining step
(“acid-fast” = have ability to retain
the primary stain in spite of acidalcohol treatment)
Can be used on sputum
Mycobacterium (acid-fast positive)
14
3/20/2015
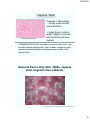
Capsule Stain
Capsule = Glycocalyx
-- sticky layer around
some bacteria
Klebsiella Pneumonia
-- helps them to retain
water, attach to tissues,
and avoid the immune
system
COMBINATION STAIN: two stains on top of each other; one
is acidic (stains background), other is basic (stains the cell);
capsule resists both stains and appears as a white “halo”
around cells.
Bacteria from a dirty dish; 1600x, capsule
stain (negrosin then safranin)
http://picasaweb.google.com/marc.murison/BestMicro/photo#5114441791829109154
15
3/20/2015
Spore Stain
Resistant structures formed by
some bacterial species
Examples: bacteria that cause
anthrax, botulism, tetanus,
gangrene, diarrhea (“C. diff.”)
Difficult to stain, need to use
steam and lots of stain to
visualize them
Can have “endospores” or
“free spores”
Anthrax spore stain
16
3/20/2015
Flagella Stain
Provide motility (movement)
-Long, thin proteins that are
fragile, break easily
-Difficult to stain and visualize
-Other methods exist to look at
motility (wet mount technique)
Also go to wet mount video at http://www-micro.msb.le.ac.uk/video/motility.html
Bacteria: Culturing and Counting Techniques
• How to grow microbes: Types of media
• How to isolate microbes: Throat swab / “Streak” plate
• How to count microbes: Serial dilution / “Spread” plate
17
3/20/2015
Culture media
PEA Agar for GramPositive bacteria
Mannitol Salt agar
for pathogenic
staphylococci
Selective Media
Phenylethanol Agar, selective for Gram-positive organisms.
18
3/20/2015
Differential Media Example
Used when Trying to examine “Staph” bacteria
S. Aureus – potential pathogen
S. Epidermidis – harmless resident of skin
Plate contains a dye that turns yellow at low pH
(if the bacteria are producing acid)
S. Aureus can eat the sugars in the media
(mannitol) and produces acid as a “waste”
product
S. Epidermidis cannot eat the sugar at all
Mannitol Salt Agar
Selective and Differential: McConkey Agar
19
3/20/2015
Enriched Media
Neisseria Gonorrhea
on Chocolate Agar
CHECK YOUR
UNDERSTANDING
THIS IS
EMB AGAR (Eosin-Methylene Blue)
IT CONTAINS DYES THAT INHIBIT
GRAM POSITIVE BACTERIA.
IT CONTAINS LACTOSE THAT ALLOWS
LACTOSE-FERMENTERS TO HAVE A
GREEN/METALLIC COLOR
THIS IS AN EXAMPLE OF which type of
media:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
F.
G.
SELECTIVE
DIFFERENTIAL
ENRICHED
ALL OF THE ABOVE
A AND B
B AND C
I DON’T KNOW
20
3/20/2015
Streak Plate Technique
GOAL: separate different
bacterial species from
each other when they are
in a mixture
ISOLATION of colonies:
a colony represents a
single bacterium and its
overnight descendants
Streak Isolation on Nutrient Agar
Materials needed: Gloves/swab/loop/tongue depressor/plate/sparker/alcohol/tape/pen
Hemolysis
Alpha = partial
breakdown of the
red blood cells
(greening)
Beta – total
destruction of
RBCs
(white/clear zone)
Gamma – no
destruction of
RBCs
Alpha,
Beta, and
Gamma hemolysis
21
3/20/2015
Hemolysis
http://gold.aecom.yu.edu/id/micro/hemolysisabg-72.jpg
Serial dilution of cultures
22
3/20/2015
Biochemical Tests
• Bacteria and other microbes can be
classified/identified according to the
types of enzymes they possess
{and thus the types of biochemical
reactions they can perform}.
Catalase Test
Staphylococcus
aureus
Enterococcus
faecalis
23
3/20/2015
COAGULASE TEST
An enzyme produced by
some, but not all, bacteria
Positive reaction = clump or
clot formation in the media
within 2-6 hours
Negative reaction – no clot
Media is rabbit plasma broth
Makes bacs more dangerous
because unwanted clots are
produced and the clot itself
shields them from phagocytes
UREASE TEST
An enzyme produced by
some, but not all, bacteria
Urea – a toxic compound,
kills bacteria (in stomach, in
bladder, kidneys, etc.)
Some bacteria can break
down urea to carbon
dioxide and ammonia
(basic, can neutralize
stomach acid)
Dye is pink
when pH is
basic
H. pylori is urease +
24
3/20/2015
OXIDASE TEST
CITRATE TEST
25
3/20/2015
INDOLE TEST
BILE ESCULIN AGAR
26
3/20/2015
Dichotomous key
• a map for the identification of organisms
based on a series of choices between
alternative characters
• can be stains, biochemical tests,
antibiotic susceptibility, or other
Dichotomous Key -- a simple example
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
27
3/20/2015
Partially complete example…..
ALL 13 Organisms
Gram -
Gram +
Cocci,
clusters
Cocci,
Chains
Large
Rods
ML, SE
EF
BC, BM
F
F
-
LP, BS, BP
FG
F
-
Rods
Short Rods
PF, CV
EC, KP, SM
F
Lactose
SE
Normal Rods
+
Glucose
Lactose
Glucose
-
Indole
ML
EC
BC
BM
BP
LP
BS
CV
KP SM
PF
+
motility
SM
KP
28
3/20/2015
29
3/20/2015
API-20E kit example (A)
Culture ID #8101
{Patient 1 symptoms: severe abdominal
cramps and watery diarrhea. There is little or
no fever, and no vomiting.
Example Data Table
O
A L O C H U T I
G G M I S R S M A A
culture N
V
D D D I 2 R D N
E L A N O H A E M R
no.
P
P
H C C T S E A D
L U N O R A C L Y A
G
8101
+
– + +
– – – – + – –
+ +
–
+
+ + +
–
+
Identification:
Escherichia
coli
5144572
30
3/20/2015
API-20E kit example (B)
Culture ID: 8P14
Patient Symptoms:
PAIN, fever, diarrhea
and abdominal cramps
Example Data Table
O
culture N
no.
P
G
A
L O C H U T I
G G M I S R S M A A
V
D D D I 2 R D N
E L A N O H A E M R
P
C C T S E A D
L U N O R A C L Y A
H
8P14 – – + + – + – – – – –
7-digit ID code = 4501552
+ +
–
+
+ – +
–
+
Identification:
Salmonella
sp.
31
3/20/2015
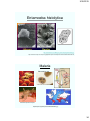
Parasitology
• Parasitology = study of protozoa
and multicellular parasites such as
worms, ticks, lice, and fleas
• Today Examine microscope slide sets
Live “wet mounts” and worm dissection
Introduction: Coccidiosis
Eimeria necatrix
http://www.anri.barc.usda.gov/pbel/images/bigchicklittlechick.jpg
32
3/20/2015
Trypanosomes: African Sleeping Sickness
LIFE CYCLE
OF TSE-TSE
FLY =
VECTOR
http://www.med.uni-marburg.de/stpg/ukm/lt/hygiene/schwarz/Trypanosoma.jpg
Balantidiasis
Balantidium coli
33
3/20/2015
Entamoeba histolytica
http://www.weizmann.ac.il/Biological_Chemistry/images/mirelman.jpg
http://www.microscope-microscope.org/applications/pond-critters/protozoans/sarcodina/entamoeba.htm
Malaria
Plasmodium spp.
Female anopheles mosquito
http://bepast.org/docs/photos/malaria/Malaria.jpg
34
3/20/2015
Eye-worm (loa loa)
http://maven.smith.edu/~sawlab/fgn/pnb/loaloa.html
PUBIC LICE (“CRABS”)
www.visualdxhealth.com
35
3/20/2015
Scabies Mites
http://www.stanford.edu/class/humbio103/ParaSites2004/Scabies/scabies1.jpg
Parasite Lab
Materials
1. Black Box – Protozoa Slides
2. White Box – Multicellular Parasite Slides
3. Green Jar – Preserved worms (for inspection)
4. White Jar – Preserved worms (for DISSECTION)
Precautions/Safety –
-- HANDLE SPECIMENS WITH FORCEPS AND GLOVES
(+USE GOGGLES DURING DISSECTION)
-- DISPOSE DISSECTED WORMS IN BIOHAZARD BIN
36
3/20/2015
Parasite Lab – Week 5 Microbiology
Dissection
-- Use your dissecting tools to make a longitudinal cut in the
roundworm provided (Ascaris). Try to distinguish if your
worm is male or female (see photo below). Note that the
major structures you see will be used for sexual
reproduction and digestion.
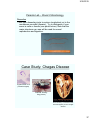
Case Study: Chagas Disease
Trypanosoma cruzi
(causative agent)
Reduviid “Kissing”
Bug (Vector)
Gross anatomy of a heart that has
been damaged by chronic Chagas
disease
37
3/20/2015
PORK TAPEWORM
CYSTS IN THE BRAIN
Top: A pork tapeworm (Taenia solium)
cysticercus, the form in which the
tapeworm is found in an infected brain.
(Colorized image by P. W. Pappas and S.
M. Wardrop, courtesy of P. W. Pappas,
Ohio State University.)
Bottom: T. solium cysticerci in the brain
of a nine-year-old girl who died during
cerebrospinal fluid extraction to diagnose
her headaches. This was in the 1970s—if
it had happened 10 years later,
noninvasive computerized tomography
would have given an accurate diagnosis,
and the parasites could have been killed
with drugs. (Image courtesy of Dr. Ana
Flisser, National Autonomous University
of Mexico.)
Wet Mount Technique
• Method to visualize living microbes
• Uses a cover glass and “depression” slide
• Also known as the “hanging drop” technique
Planaria (flatworm)
Trichomonas vaginalis
38
3/20/2015
Control of Microbes
Measuring Zones of Inhibition
Pour 25mL agar plates
Grow bacteria in liquid culture
to 100,000,000/ml
Spread 150 microliters on plate
Add antibiotic discs to plate
Let bacteria grow overnight
Measure ZOI and compare to
standard table
Antibiotic Disc Diffusion Assay
39
3/20/2015
Using the Spectrophotometer to count bacteria
Absorbance is
proportional to
number of bacteria
GO TO http://www.physics.csbsju.edu/stats/chi_fit.html
Salt
• Used to preserve foods (meats/fish/etc.)
• Works by dehydrating microbes -- (lose water, shrivel)
• Creates hypertonic environment (re: osmotic stress)
• Exception: Halophiles prefer 3% NaCl or ↑
40
3/20/2015
pH
• Measures H+ ion concentration
• ↑ H+ means more acidic (lower pH),
• ↓ H+ means more basic (higher pH)
• Most microbes are neutralphiles (5.5-8.5)
• Some are acidophiles (<5.5)
• A few are basophiles (>8.5)
• Examples: “pickling” with vinegar (acid) or basify shampoos
Filtration
•Method to physically trap
microbes
•Used to purify liquids/air
•Has tiny holes called “pores”
(anything larger than the pore size
gets trapped on the filter itself)
AcetatePlus VP vacuum filtration units with cellulose acetate
41
3/20/2015
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering
42
3/20/2015
Restriction Enzymes and Recombinant DNA
Construction of a Recombinant DNA Molecule
43
3/20/2015
Human genes can be cloned in bacteria
“Artificial” Transformation
44
3/20/2015
Examples of products made by recombinant DNA technology
1. HUMALOG – Human insulin made by E. coli bacteria
2. PROCRIT – Human erythropoietin made by mouse cells
3. NEUPOGEN – helps humans grow more neutrophils,
made by inserting human DNA into E. coli
4. RECOMBIVAX – Hepatitis B vaccine made by inserting
viral DNA into yeast cells and growing up viral proteins !
Applications of Genetic engineering
45
3/20/2015
The Genetic Code
Bt crop concerns
http://www.biology-blog.com/images/blogs/10-2007/genetically-engineered-corn.jpg
46
3/20/2015
Golden Rice
“THE GENE GUN”
47
3/20/2015
Can we move DNA between these
two organisms ???
Aequorea victoria (Sea Jelly )
E. coli (bacteria)
The pGLO plasmid
48
3/20/2015
THE
PROCEDURE
Expected Results
LB/AMP/pGLO
LB/AMP/ARA/pGLO
LB/AMP
LB
49
3/20/2015
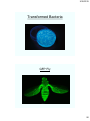
Transformed Bacteria
GFP Fly
50
3/20/2015
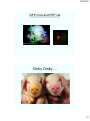
GFP mice and RFP cat
Oinky Oinky….
51
3/20/2015
Fun on a plate
Living bacteria expressing 8 different colors of fluorescent proteins.
BIOTERRORISM – “THE BIG 6”
• ANTHRAX
• SMALLPOX
• TULAREMIA
(“rabbit fever”)
• HEMMORHAGIC
FEVER VIRUSES
(EBOLA/MARBURG)
• PLAGUE
• BOTULISM
52
3/20/2015
Epidemiology
• Study of disease “determinants” in populations
(infectious, environmental, genetic, and lifestyle)
• Includes measurements of incidence,
prevalence, distribution, and control of diseases
• Usually involves collecting and analyzing data
(heavy statistics!).
Epidemiological terms
• Epidemic: An outbreak of disease that attacks a
large percentage of the population simultaneously
and may spread through one or several
communities.
• Pandemic: When an epidemic spreads throughout
the world.
• Endemic: a disease that exists permanently in a
particular region or population. Usually a small
percentage of persons are affected.
• Outbreak: a short epidemic (contained)
53
3/20/2015
Smoking vs. lung cancer per capita per year (country)
Hungary
2515
Japan
2510
USA
2020
South Africa
1950
UK
1700
France
1690
USSR
1650
Brazil
1200
Philipines
1150
Venezuela
950
Zaire
150
India
100
The Oxford Atlas of the World, ISBN 0-19-520955-9, published in 1992
From Parkin, D. M. et al. CA Cancer J Clin 2005;55:74-108.
Extras
54
3/20/2015
Genetic Vaccine Questions
• What are some of the disadvantages of inactivated,
subunit, and attenuated viral vaccines?
• What are the potential advantages of genetic
vaccines?
• In what genetic form and how are genetic vaccines
delivered to the body cells?
• How can the positive effects of the vaccines be
amplified/increased ?
• What human genetic vaccine tests are currently
being performed/attempted?
RNA interference questions
1.
How is RNA interference more precise than the interferon response?
2.
What are some of the ultimate goals of “directed” RNA interference ?
3.
What type of RNA proved most useful in RNAi, single or double
stranded RNA ??
4.
What are siRNAs? MicroRNAs?
5.
How does RNA interference help in learning about the functions of
genes ?
6.
What is the most difficult challenge facing human RNAi therapies ?
55
3/20/2015
Making Yogurt
• Heat milk (450ml) to 83°C while stirring
• Allow to cool to 43°C degrees
• Put starter culture (1/2 cup) in separate
mixing bowl
• Slowly add milk to starter culture w/ stirring
• Cover with foil and punch holes in foil
• Incubate 2-6 hours at 30°C
• Add fruit (optional)
• Try it (if you are brave………)
Questions for Food Poisoning Film
• Who is getting sick, and why ??
• Where did physical control of microbes
break down ???
• Why do some victims recover quickly,
while others take 10+ years ???
56