* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth, Moon, Space, Solar System and Sun Study Guide Vocabulary
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
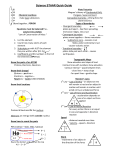
Earth, Moon, Space, Solar System and Sun Study Guide Vocabulary1. Rotation- The spinning of a planet or moon on its axis. Ex- Earth rotates once every 24 hours on its axis. Earth rotates from west to east. 2. Revolution- One complete trip of a planet around the sun. The closer you are to the sun the shorter amount of time it takes to get around. Earth takes 365 days. 3. Orbit- The path that one object in space takes around another object in space. Earth orbits or revolves around the sun. 4. Sun- is a medium size star made up of gases. 5. Photosphere- the layer of the sun we see. 6. Chromosphere- is a red circle around the outside of the sun and can sometimes be seen during an eclipse. 7. Corona- The outermost layer of the sun. 8. Sunspots- are dark spots on the photosphere. 9. Solar Flares- are sparks of energy that shoot out from the sun. 10. Gravity- is the pull that all objects exert on each other. 11. Lunar Cycle- The moon goes through the same sequence of phases as it revolves around the Earth once every month. It takes 28 days for the moon to complete its cycle. 12. Waxing- When the lighted part of the moon we see is becoming larger. 13. Waning- When the lighted part of the moon we see is becoming smaller. Important facts: The Earth has three main layers: Core, Mantle and the Crust. The crust is the surface we live in and where the rock cycle takes place. The mantle is the next layer and is made up of melted rock, or magma. The core is divided into two sections: Inner Core and Outer Core- The outer core is made of liquid and the inner core because of all of the pressure on it is solid even though it is extremely hot. Tides occur twice daily- 2 High tides and two low tides. They are caused by the moon’s gravity pulling on the Earth. Earth’s seasons are caused by the earth revolving around the Sun. Day and Night are caused by the Earth rotating on its axis. Planets- Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune (Pluto is known as a dwarf planet). Hemispheres Tides Our Solar System