* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Questions to Chapter 1 of book Quantum Computation and Quantum
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Topological quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Double-slit experiment wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Bell test experiments wikipedia , lookup
Bohr–Einstein debates wikipedia , lookup
Basil Hiley wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot cellular automaton wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Delayed choice quantum eraser wikipedia , lookup
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Scalar field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum decoherence wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Density matrix wikipedia , lookup
Measurement in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Quantum fiction wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum computing wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Quantum cognition wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
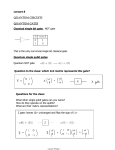
Questions to Chapter 1 of book Quantum Computation and Quantum Information by Michael Nielsen and Isaac Chuang Short answers. Do not provide details. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is quantum electrodynamics? What would happen if cloning were possible. Give one example. What is Universal Turing Machine? Give an example of Turing machine. Formulate Church-Turing Thesis What is Moore’s Law and how it is related to quantum computing? What are efficient and inefficient algorithms – link to P=NP problem. Give examples. 7. Formulate the strengthened versions of Church-Turing thesis 8. What kinds of results were shown by Robert Solovay and Volker Strassen in 1970s? Why are they important? 9. What was the question that David Deutsch asked himself in 1985 related to Church-Turing Thesis? 10. What was the question that Richard Feynman asked related to simulating quantum mechanical systems? 11. What are the most famous quantum algorithms? Why are they important? 12. What are error-correcting codes? Give one example. 13. What was the achievement of Calderbank, Shorr and Steane in 1996? Explain importance 14. What is superdense coding? 15. What is networked information theory? 16. What is cryptography? 17. Compare definitions of private key cryptosystems and public key cryptosystems. 18. What is RSA? Why is it important? 19. Why RSA is in danger? 20. What is quantum entanglement? 21. What is a qubit? 22. Give three realizations of qubit in physics 23. What is Bloch sphere? Show an example. 24. What is hidden information of quantum computing? 25. What is EPR pair? 26. Give examples of five one-qubit gates and their unitary matrices. 27. What is a unitary matrix? 28. Visualize one-qubit gates on Bloch sphere 29. Universal decomposition of one-qubit systems. Present the gates and their interpretation on Bloch sphere 30. Feynman or CNOT gate as an example of a controlled 2-qubit gate. Explain. 31. Show other examples of 2-qubit quantum gates. 32. Give at least one set of 2-qubit and 1-qubit gates that is universal. 33. What is a link between quantum and reversible logic? 34. How to realize a swap gate using quantum primitives? 35. (difficult) Invent ternary gates that generalize the binary quantum gates from chapter 1. Design a ternary Toffoli gate, ternary Feynman gate etc. Build a ternary swap gate using these primitives. First define the unitary matrix for each ternary quantum gate, including swap. 36. The role of measurement in quantum computing. 37. What is no-cloning theorem. Explain intuitively (no proof) why cloning is not possible, use Figure 1.11. 38. What are Bell states and how to generate them? 39. Realization of binary Toffoli gate. 40. Quantum parallelism. 41. Hadamard transform for 2 qubits 42. Be able to explain the Deutsch Algorithm for one qubit. Why is it very important although it is practically useless? 43. What is the essence of Deutsch – Jozsa results? 44. Describe briefly quantum algorithms based on Fourier Transform 45. Grover’s quantum search problem, what is speedup, why it is important? 46. What is quantum simulation and why is it important? 47. Mutual relations of quantum simulation and Moore’s Law. 48. Give definitions of the following complexity classes: P, NP, PSPACE, BPP, BQP. Give examples of algorithms in each. 49. What was proved by Stern-Gerlach and cascaded Stern-Gerlach experiments? 50. What are the prospects for practical quantum information processing?