* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Universial Design for Learning
Survey
Document related concepts
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Rolling resistance wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
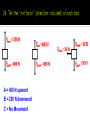
A force is a push or pull on an object. A “Spring Scale” is used to measure force. Newton's A upward force from an object sitting on a surface. This force is always perpendicular to the surface. A force from pulling on an object. When the net forces on an object are unbalanced. When the net forces on an object are balanced. The force that opposes motion of objects that touch as they move past each other. 1. Type of surface or material 2. The force pushing the surfaces together Static Friction Friction of objects that are not moving Sliding Friction A force that opposes motion as it slides over a surface Rolling Friction The friction force that acts on rolling objects Fluid Friction Opposes the movement of an object through a liquid or a gas 1. 2. 3. 4. Fluid (Weakest) Rolling Sliding Static (Strongest) • A force that acts on an object as it moves through the air. • Air resistance is fluid friction • Gravity pulls the object down • Air resistance pushes up A force that acts downward toward the center of the earth The force of gravity acting on an object A constant velocity when the gravitational force and the air resistance force is equal Aristotle Galileo Law of Inertia An object in motion wants to stay in motion and an object at rest will stay at rest unless acted on by an outside force. The tendency of an object to resist a change in motion Law of Acceleration. The Force of any object is a product of its mass and acceleration (F = m x a). Law of Interaction For every action there is an opposite and equal reaction. Weight : The force of gravity acting on an object Weight = m x 9.8 m/s2 Mass: Measured by the inertia of an object A = 400 N upward B = 200 N downward C = No Movement Look thru your packet and understand how to do force problems using the formulas. Any Questions!!!! Quiz Tomorrow! Good Luck and Study !!