* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - Vijay Education Academy
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Acid strength wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
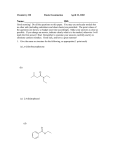
Page 0 CHEMISTRY – REVISION SHEET XII : CBSE SOLID STATE Subjective Type Questions Each Question carries 1 Mark 1. Which point defect in crystal does not alter the density of relevant solid? 2. Name the element with which silicon can be doped to give an n-type semiconductor. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Name one solid in which both frenkel and schottky defect occurs. Which element may be added to Silicon to make electrons available for conduction an electric current? Why does Frenkel defect not change the density of AgCl crystal? Why is Frenkel defect not found in metal halides? What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by (i) ZnS and (ii) CsCl? [Hint: (i) Frekel defect (ii) Schottky defect] If the formula of a compound is A2 B, which sites would be occupied by A ions? [Hint: Number of A atoms is double to B, so it occupied tetrahedral void] What is the coordination number for (a) an octahedral void (b) a tetrahedral void. [Hint: (a) 6; (b) 4] 10. How many octahedral voids are there in 1 mole of a compound having cubic closed packed structure? 11. Write dimensions and bond angles of match-box type of unit cells. [Hint: Orthorhombic crystal system]. 12. Calculate the number of atoms in a cubic unit cell having one atom on each corner and two atoms on each body diagonal. [Hint: No. of atoms 8 1/ 8 4 2 9 ] 13. Fe3 O4 is ferrimagnetic at room temperature but becomes paramagnetic at 850 K. Why? [Hint: Due to randomization of spins at high temperature] 14. Solid A is very hard, electrical insulator in solid as well as in molten state and melts at extremely high temperature. What type of solid is it? [Hint: Covalent solid] Each Question carries 2 Marks 15. Why does table salt (NaCl) sometimes appear yellow in colour? 16. A compound is formed by two elements X and Y. Atoms of the element Y (as anions) make ccp and those of the element X (as cations) occupy all the octahedral voids. What is the formula of the compound? 17. In corundum, oxide ions are arranged in hexagonal close packing and aluminium ions occupy two-third of the octahedral voids. What is the formula of corundum? 18. Why is the window glass of old buildings thick at the bottom? 19. “Crystalline solids are anisotropic in nature”. What does this statement mean? 20. Define paramagnetism with an example. 21. What is the non-stoichiometric defect in crystals? Page 1 22. What happens when a ferromagnetic substance is heated to high temperature? 23. What do you understand by the following types of stacking sequences: (a) AB AB ……… (b) A B CABC ……… What kind of lattices do these sequences lead to? 24. How can you calculate the density of a crystal whose length of the edge of the unit cell is know? [Hint: d 25. ZM ] a NA 3 In a fcc arrangement of A and B atoms. A are present at the corners of the unit cell and B are present at the face centres. If one atom of A is missing from its position at the corners, what is the formula of the compound? 26. A compound made up of elements „A‟ and „B‟ crystallises in a cubic close packed structure. Atom A are present on the corners as well as face centres, whereas atoms B are present on the edgecentres as well as body centre. What is the formula of the compound? 27. Explain how vacancies are introduced in a solid NaCl crystal when a compound containing cation of higher valence is added to it. 28. Define the term „point defects‟ Mention are main difference between stoichiometric and nonstoichiometric point defects. Each Question carries 3 Marks 29. Write and explain three differences between Schottky and Frenkel defects under the heads : (i) Effect on density (ii) Effect on electrical conductivity (iii) Effect on stability of the crystal 30. What is a semiconductor? Describe the two main types of semiconductors on the basis of their conductance mechanism. 31. Explain the following with one examples each: (a) Ferrimagnetism (b) Antiferromagnetism (c) 13-15 compounds 32. Examine the defective crystal lattice given below and answer the following questions: (a) Name of defect present in ionic solid. (b) Out of AgCl and NaCl, which is most likely to show this type of defect and why? (c) Why this defect is also known as dislocation defect? Each Question carries 5 Marks + 33. KCN has a rock salt type structure. What is the distance between K and CN in KCN, if the density is 2.32 g cm-3 . [At masses : K = 39, C = 12, N = 14, N A = 6.022 1023 mol-1 ] 34. How will you distinguish between the following pair of terms? (i) Hexagonal close packing and cubic close packing. (iii) Tetrahedral void and octahedral void. (ii) Crystal lattice and unit cell. Page 2 35. Out of NaCl and CsCl, which one is more stable and why? + 36. A compound consisting of the monovalent ions A , B crystallizes in the body centred cubic lattice. (i) What is the formula of the compound? (ii) If one of A+ ions from the corner is replaced by a monovalent ion C +, what would be the simplest formula of the resulting compound? 37. Maneesh, a student of class XII, watched a programme on TV where it was being shown how use of polythene bags blocked the sewer system and how sometimes the polythene bags thrown as garbage into the streets were swallowed by the animals resulting into their death. Maneesh was highly upset and he discussed the problem with the class teacher to create an awakening among his classmates. After reading the above paragraph, answer the following questions : (a) What values do you attach to Maneesh‟s observation on TV and discussion with his class teacher? (b) What is the basic reason which leads to the harmful effects of use of polythene bags? What alternative do you suggest? 38. Aneesh, a student of class XII, went to a hospital along with his mother. There he saw a woman patient whose neck was highly swollen. He asked his mother what had happened to this woman. She told him that this woman had a problem of thyroid disorder which was due to deficiency of iodine. After reading the above paragraph, answer the following questions : (a) What values do you attach to the information conveyed by Aneesh‟s mother to him? (b) What is the simplest way to follow to save ourselves from this disease? 39. Solid A is very hard, electrical insulator in solid as well as in molten state and melts at extremely high temperature. What type of solid is it? 40. Give the significance of a „lattice point‟. 41. Name the parameters that characterize a unit cell. 42. Distinguish between : (i) Hexagonal and monoclinic unit cell. (ii) Face centred and end centred unit cell. 43. A compound forms hexagonal close packed structure. What is the total number of voids in 0.5 mol of it? How many of these are tetrahedral voids? 44. A compound is formed by two elements M and N. The element N foms ccp and atoms of M occupy 1 rd 3 of tetrahedral voids. What is the formula of the compound? 45. Explain how vacancies are introduced in an ionic solid when a cation of higher valence is added as an impurity in it. 46. Ionic solids, which have anionic vacancies due to metal excess defect develop colour. Explain with the help of a suitable example. 47. What type of substances would make better permanent magnets ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic? Justify your answer. 48. What makes a glass different from a solid such as quartz? Under what conditions could quartz be converted into glass? 49. How can you determine the atomic mass of an unknown metal if you know its density and the dimension of its unit cell? Explain. Page 3 50. Calculate the efficiency of packing in case of a metal crystal for: (a) Simple cubic (b) face centred cubic (c) body centred cubic (with the assumption that atoms are touching each other) 51. If the radius of the octahedral void is r and radius of the atoms in close packing is R, derive relation between r and R. 52. Analysis shows that nickel oxide has formula Ni0.98 O1.00 . What fractions of the nickel exist as Ni2+ and Ni3+ ions? 53. Non-stoichiometric cuprous oxide, Cu2 O can be prepared in laboratory. In this oxide, copper to oxygen ratio is slightly less than 2 : 1. Can you account for the fact that this substance is a p-type semiconductor? 54. Explain the following terms with suitable examples: (i) Schottky defect (ii) Frenkel defect (iii) Interstitials (iv) F-centres 55. Aluminium crystallises in a cubic close-packed structure. Its metallic radius is 125 pm. (a) What is the length of the side of the unit cell? (b) How many unit cells are there in 1.00 cm3 of aluminium? 56. Explain the following with suitable examples: (i) Ferromagnetism (ii) Paramagnetism (iii) Ferrimagnetism (v) 12-16 and 13-15 group compounds. (iv) Antiferromagnetism 57. In a crystalline solid anions „C‟ are arranged in cubic close packing, cation „A‟ occupy 50% of tetrahedral voids and cations „B‟ occupy 50% of octanedral voids. What is the formula of the solid? 58. Magnetite, a magnetic oxide of iron used on recording tapes, crystallises with iron atoms occupying of the tetrahedral holes and 1 8 1 of the octahedral holes in a closed packed array of oxides ions. What is 2 the formula of magnetite? -1 59. An element of atomic mass 98.5 g mol occurs in fcc structure. It its unit cell edge length is 500 pm and its density is 5.22 g cm-3 . Calculate the value of Avogadro constant. 60. A fcc unit cell containing atoms of element (molar mass 60.4 g mol-1 ) has cell edge 4 108 cm. Calculate the density of unit cell. 61. Analysis shows that a metal oxide has a empirical formula M0.96O . Calculate the percentage of M2+ and M3+ ions in this crystal. AgCl is doped with 10-2 mol% of CdCl2 , find the concentration of cation vacancies. 3 63. KF has NaCl structure. It‟s density is 2.48 g/cm . Calculate edge length of crystal lattice. (Given At. Mass of K = 39 g mol-1 , F = 19 g mol-1 and N A = 6.002 1023 mol-1 ) 62. 64. The density of copper metal is 8.95 g cm-3 . If the radius of copper atom is 127 pm, is the copper unit cell a simple cubic, a body-centred cubic or a face centred cubic structure? (Given at. mass of Cu = 63.54 g mol-1 and N A = 6.02 1023 mol-1 ) [Hint: d ZM calculate Z/a3 by putting the values given in the question. a NA 3 Calculate P.E. by Z 4 / 3 r3 100 using value of Z/a3 , 74% results the fcc unit cells]. 3 a Page 4 CHEMISTRY – REVISION SHEET XII : CBSE ALCOHOLS, PHENOLS AND ETHERS Each question carries 1 mark 1. Write IUPAC name of the following compound: H3C CH CH 2 CH CH CH 2OH CH3 2. OH CH3 Write IUPAC name of the following : CH3 O CH 2 CH CH 2 CH3 CH3 CH3 3. Write IUPAC name of OH CH3 4. Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pair of compounds: Phenol and benzoic acid. 5. Give the structural formula and name of the product of following reaction : phenol is treated with excess of aqueous bromine. 6. Which of the following will have higher boiling point and why ? CH3NH2 or CH3OH 7. Write IUPAC name of aspirin. Each question carries 2 marks 8. Give reason for the following : Orthonitro phenol is more acidic than orthomethoxy phenol. 9. How is tertiary butyl alcohol obtained from acetone? 10. How is phenol obtained from aniline? 11. Account for the following : o-nitrophenol has lower boiling point than p-nitrophenol. 12. Describe the mechanism of alcohols reacting both as nucleophiles and as electrophiles in their reactions. 13. How would you account for the following : (i) Phenols are much more acidic than alcohols. (ii) The boiling points of ethers are much lower than those of the alcohols of comparable molar masses? 14. Give an illustration of Reimer-Tiemann reaction. 15. Give the structures and IUPAC names of monohydric phenols of molecular formula C 7 H8 O. Page 5 16. Give the equation of reaction of preparation of phenol from cumene. 17. Explain, why ortho-nitrophenol is more acidic than ortho-methoxyphenol? 18. Explain how does the –OH group attached to a carbon of benzene ring activates it towards electrophilic substitution. 19. While separating a mixture of ortho and paranitrophenols by steam distillation, name the isomer which will be steam volatile. Give reasons. 20. Diethyl ether does not react with sodium. Explain. 21. Write the structural formula and IUPAC name of the following compounds : (i) Neo-pentyl bromide 22. (ii) Methyl tert-butyl ether. Write the equations involved in the following reactions : (i) Hydroboration oxidation (ii) Reimer-Tiemann equation Each question carries 3 marks 23. The following is not an appropriate reaction for the preparation of tert-butylethyl ether. 24. Write the structure of the major products expected from the following reactions : (a) Mononitration of 3-methylphenol (b) Dinitration of 3-methylphenol (c) Mononitration of phenyl methanoate 25. Arrange the following sets of compounds in order of their increasing boiling points : (a) Pentan-1-ol, butan-1-ol, ethanol, propan-1-ol, methanol. (b) Pentan-1-ol, n-butane, pentanal, ethoxyethane. 26. Give the structures and IUPAC names of the products expected from the following reactions : (a) Catalytic reduction of butanol. (b) Hydration of propene in the presence of dilute sulphuric acid. (c) Reaction of propanone with methylmagnesium bromide followed by hydrolysis. 27. Account for the following : (i) The boiling point of alcohols decreases with increase in the branching of alkyl chain. (ii) Phenol does not give protonation reaction readily. (iii) Phenylmethyl ether reacts with HI to give phenol and methyl iodide and not iodobenzene and methyl alcohol. 28. Show how the following alcohols are prepared by the reaction of a suitable Grignard reagent on methanol. (i) H3C CH CH 2OH CH3 CH 2 OH (ii) Page 6 29. Write structures of the products of the following reactions : (i) H O/H 2 CH3 CH CH2 O NaBH4 CH 2 C OCH3 (ii) O NaBH4 (iii) H3C CH 2 CH CHO CH3 30. 31. Give structures of the products you would expect when each of the following alcohol reacts with (a) HCl ZnCl2 , (b) HBr and (i) Butan-1-ol (ii) 2-Methylbutan-2-ol Write the equations involved in the following reactions : (i) Reimer Tiemann reaction 32. (c) SOCl2 . (ii) Kolbe‟s reaction Give major products that are formed by heating each of the following ethers with HI. CH3 (i) CH3 H3C CH 2 CH CH 2 O CH 2CH3 (ii) CH 3CH 2 CH 2 OCCH 2 CH3 CH3 (iii) 33. CH 2 O Predict the products of the following reactions : (i) CH3 CH2 CH2 O CH3 HBr (ii) HI (CH3 )3 C OC2H5 OC2 H5 (iii) 34. OC2 H5 HBr (iv) conc.H SO 2 4 conc.HNO 3 Name the reagents used in the following reactions : (i) oxidation of a primary alcohol to carboxylic acid. (ii) oxidation of a primary alcohol in an aldehyde. (iii) bromination of phenol to 2, 4, 6-tribromophenol. (iv) benzyl alcohol to benzoic acid. (v) dehydration of propan-2-ol to propene. (vi) butan-2-one to butan-2-ol. 35. Write the names of reagents and equations for the preparation of the following ethers by Williamson synthesis: (i) 1-propoxypropane (ii) Ethoxybenzene (iii) 2-methyl-2-methoxypropane (iv) 1-methoxyethane Page 7 36. When 3-methylbutan-2-ol is treated with HBr following reaction takes place. Br HBr H 3C C CH 2 CH 3 H3C CH CH CH 3 CH3 CH3 CH3 Give a mechanism for this reaction. Each question carries 5 marks 37. (a) Complete the following reactions : OH COOH (i) LiAlH 4 (CH3 )2 CO (ii) CH 3CO O CH 3CO (b) Write the structural formulae of the organic compounds „A‟, „B‟, „C‟ and „D‟ in the following sequence of reactions : HO Br Conc. alc.KOH 2 CH CH CH CH 'A' CH2MgBr 'B' 2 'C' 'D' 3 2 3 H SO 2 38. 4 (a) (i) Give chemical test to distinguish between phenol and ethanol is seemingly conditions. (ii) Write the reaction equation for what happens when tertiary butyl alcohol is heated with reduced copper at about 573 K. (b) Give equations only to distinguish between primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols by Victor Meyer‟s test. 39. (a) Explain giving reasons why: (i) Phenol has a smaller dipole moment than methanol. (ii) It undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions. (b) Giving equations and reaction conditions, describe how methyl alcohol is obtained from water gas. Give two uses of methyl alcohol. 40. Wurtz reaction fails in case of tert-alkyl halides. Explain. 41. Explain why alkyl halides are generally not prepared in the laboratory by free radical halogenation of alkanes. 42. An organic compound X which is manufactured by heating a mixture of chloral and chlorobenzene in the presence of concentrated H2 SO 4 is used as an insecticide. The use of compound X is banned in many countries. The compound is very effective against mosquitoes which spread malaria. Answer the following questions based on above information : (a) Name the compound X. Give its structural formula and IUPAC name. (b) Why the use of compound X is banned in many countries? Should we also advocate the ban of this compound though it is banned in many countries? (c) Which value is reflected in its ban? Should our country follow exactly the same rules and regulations in such matters as those being followed in other countries? Page 8 43. Classify the following as primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols : CH 3 (i) H 3C C CH 2OH (ii) H2C CH CH2OH CH3 OH CH CH 3 (iii) H3C CH2 CH2 OH (iv) CH3 CH 2 CH CH 3 (v) 44. OH CH CH C OH (vi) Give IUPAC names of the following compounds : (i) H3C CH CH CH CH 2OH Cl (ii) (iii) CH3CH O CH 2CH3 CH 3 CH3 CH3 OH 45. CH3 H 3C NO 2 CH3 (iv) OC 2 H 5 Give the structures and IUPAC names of products expected from the following reactions : (a) Catalytic reduction of butanal. (b) Hydration of propene in presence of dilute sulphuric acid. (c) Reaction of propanone with methyl magnesium bromide followed by hydrolysis of the adduct. 46. Write short notes : (i) Kolbe reaction (ii) Reimer-Tiemann reaction (iii) Williamson ether synthesis (iv) Unsymmetrical ether SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS 47. Write IUPAC names of the following compounds : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Page 9 (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) (ix) (x) [Hint: 2-Bromo-5hydroxybenzene-nitrile]. (xi) 48. Write the structures of the compounds whose names are given below : (i) 3,5-Dimethoxyhexane-1, 3, 5-triol (ii) Cyclohexylmethanol (iii) 2-Ethoxy-3-methylpentane (iv) 3-Chloromethylpentan-2-ol (v) p-Nitroanisole 49. 50. Describe the following reactions with example : (i) Hydroboration oxidation of alkenes (ii) Acid catalysed dehydration of alcohols at 443K (iii) Williamson synthesis (iv) Riemer Tiemann reaction. (v) Kolbe‟s reaction (vi) Friedel-Crafts acylation of Anisole. Complete the following reactions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) (ix) (x) (xi) (xii) Page 10 (xiii) (xiv) 51. What happens when : (i) aluminium reacts with t-butylalcohol (ii) phenol is oxidised with chromic acid (iii) cumene is oxidised in the presence of air and the product formed is treated with dilute acid. (iv) phenol is treated with conc. HNO 3 . (v) phenol is treated with chloroform in presence of dilute NaOH. 52. How will you convert (i) propene to propan-l-ol. (ii) anisole to phenol (iii) butan-2-one to butan-2-ol (iv) ethanal to ethanol (v) phenol to ethoxybenzene (vi) 1-Phenylethene to 1-Phenylethanol (vii) formaldehyde to cyclohexylmethanol (viii) butylbromide to pentan-1-ol. (ix) toluene to benzyl alcohol (x) 1-Propoxypropane to propyliodide (xi) ethylbromide to 1-ethoxyethane (xii) methyl bromide to 2-methoxy-2-methylpropane (xiii) ethylbromide to ethoxybenzene (xiv) ethanol to benzylethyl ether. 53. Identify the missing reactant or product A to D in the following equations : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) 54. Identify X, Y and Z in the following sequence of reactions : (i) (ii) (iii) 55. Describe the mechanism of Chemical reactions in which alcohol acts as a nucleophile or an electrophile. 56. Write the mechanism for following reactions : (i) (acid catalysed hydration of alkenes) Page 11 (ii) (acid catalysed dehydration of alcohols) (iii) (acid catalysed nucleophilic substitution reaction) (iv) (acid catalysed cleavage of ethers) (v) (acid catalysed cleavage of ethers) 57. Give reason for the following : (i) The C O C bond angle in dimethylether is (111.7°) (ii) Alcohols have higher boiling points than ethers of comparable molecular mass. (iii) Phenols are more acidic than alcohols. (iv) Nitrophenol is more acidic than o-methoxyphenol. (v) Phenol is more reactive towards electrophilic substitution reaction than benzene. (vi) Preparation of ether by treatment of alcohol with dilute H2 SO4 is not a suitable method for the preparation of diisopropylether or ditert butylether. (vii) The following is not an appropriate method for the preparation of t-butyl ethyl ether : (viii) The following is not an appropriate method for the preparation of 1-methoxy-4-nitrobenzene; (ix) o-Nitrophenol is steam volatile but p-nitrophenol is not. (x) Phenol is less polar than ethanol. (xi) The phenylmethylether reacts with HI of form phenol and iodomethane and not iodobenzene and methanol. (xii) Methanol is less acidic than water. (xiii) Alcohols can act as weak base as well as weak acids. (xiv) Phenols do not give protonation reaction readily. Page 12 (xv) Alcohols undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions but phenols do not undergo nucleophilic substitution at C-1 carbon. (xvi) Absolute ethanol can not be obtained by factional distillation of ethanol water mixture. 58. 59. 60. Arrange the following in the increasing order of property shown : (i) Methanol, Ethanol, Diethylether, Ethylene-glycol. (Boiling points) (ii) Phenol, o-nitrophenol, m-nitrophenol, p-nitrophenol. (Acidic strength) (iii) Dimethylether, ethanol, phenol. (Solubility in water) (iv) n-butanol, 2-methylpropan-1-ol, 2-methylpropan-2-ol. (Acidic strength) Give a chemical test to distinguish between the following pair of compounds. (i) n-Propylalcohol and isopropylalcohol (ii) Methanol and ethanol (iii) Cyclohexanol and phenol. (iv) Propan-2-ol and 2-methylpropan-2-ol. (v) Phenol and anisole (vi) Ethanol and diethylether Which of the following compounds gives fastest, reaction with HBr and why? (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) 61. What is the function of ZnCl2 (Anhyd) in Lucas test for distinction between 1°, 2° and 3° alcohols. 62. An alcohol A(C 4 H10 O) on oxidation with acidified potassium dichromate gives carboxylic acid B(C4 H8 O2 ). Compound A when dehydrated with conc. H2 SO 4 at 443 K gives compound C. Treatment of C with aqueous H2 SO4 gives compound D. (C 4 H10 O) which is an isomer of A. Compound D is resistant to oxidation but compound A can be easily oxidised. Identify A, B, C and D and write their structures. 63. An organic compound A having molecular formula C 6 H6 O gives a characteristic colour with aqueous FeCl3 . When A is treated with NaOH and CO 2 at 400 K under pressure compound B is obtained. Compound B on acidification gives, compound C which reacts with acetyl chloride to form D, which is a popular pain killer. Deduce the structure of A, B, C and D. What is the popular name of Drug D? 64. An ether A(C 5 H12 O) when heated with excess of hot concentrated HI produced two alkyl halides which on hydrolysis from compounds B and C. Oxidation of B gives an acid D whereas oxidation of C gave a ketone E. Deduce the structures of A, B, C, D and E. 65. Phenol, when it first reacts with concentrated sulphuric acid forms Y. Y is reacted with concentrated nitric acid to form Z. Identify Y and Z and explain why phenol is not converted to Z by reacting it with conc. HNO 3 . Page 13 CHEMISTRY – REVISION SHEET XII : CBSE HALOALKANE & HALOARENES Each Question carries 1 Mark 1. What is meant by enantiomers? 2. What is meant by racemic mixture? 3. An alkyl halide having molecular formula C 4 H9 Cl is optically active. What is its structure? 4. State the IUPAC name of the following compound: H3C H H H H H 5. Br Peroxide Complete the following chemical equation: CH3CH2CH CH2 HBr Each Question carries 2 Marks 6. Explain as to why haloarenes are much less reactive than haloalkanes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions. 7. How are enantiomers different from diastereomers? Give one example of each. 8. Write the reactions involved in (a) the isocyanide test (b) iodoform test. 9. Identify the compounds A, B, C and D in the following sequence of reaction : Conc. H2SO4 HBr KOH(aq) C2H5OH A B C D 443 K I2 , NaOH yellow ppt 10. Does the presence of two chiral carbon atoms always make the molecule optically active? Explain giving an example. 11. Describe laboratory preparation of chloroform. Why is it stored in dark coloured bottles? Give four main uses of chloroform. 12. How many methyl bromide be preferentially converted to methyl cyanide and methyl isocyanide? 13. Why are haloarenes more stable than haloalkanes and undergo electrophilic substitution reaction at ortho and para positions? 14. Why is sulphuric acid not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI? 15. The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in presence of alcoholic KOH alkenes are major products. Explain. Page 14 Each Question carries 3 Marks 16. (i) Explain the following with the help of suitable examples: (a) Carbylamine reaction (b) Finkelstein reaction (c) Give one chemical test to distinguish between ethanol and 1-propanol. 17. (i) Describe the following with the help of suitable examples: (a) Kolbe‟s electrolytic reaction (b) Ullmann‟s reaction. (c) Fittig reaction. 18. How will you effect the following two steps of conversions? (a) Chlorobenzene to p-nitrophenol. (b) Bromobenzene to diphenyl. (c) Propene to propan-1-ol 19. Write the structure of main products : (a) Chlorination of benzene in presence of UV light. (b) Propene is treated with HBr in presence of benzoyl peroxide. (c) Chlorobenzene is treated with NaOH at 623 K and high pressure. 20. Complete the following : (ii) CH3COCH3 I2 NaOH FeCl3 Cl2 (i) Acetone (iii) CH3CH2CH2Cl NaI heat 21. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of SN1 reactivity. ClCH2CH CHCH2CH3 , CH3C(Cl) CHCH2CH3, CH3CH CHCH(Cl)CH3 (ii) CH3CH2Br, CH2 CHCH(Br) CH3 , CH2 CHBr, CH3CH(Br)CH3 (iii) (CH3 )3 CCl, C6H5C(CH3 )2 Cl, (CH3 )2 CHCl, CH3CH2CH2Cl (i) 22. Write the products of the following reaction : H (i) H (ii) HBr H CH3 CH2 CH CH2 HCl CH 2 C CH 2 (iii) H Peroxide HBr Page 15 23. In the following pairs of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes faster SN1 reaction? Each Question carries 5 Marks 24. A hydrocarbon of molecular mass 72 g mol-1 gives a single monochloro derivative and two dichloro derivatives on photochlorination. Give the structure of the hydrocarbon. 25. Ram is a marketing executive, one day he felt body pain and headache. He goes to a medical store to get aspirin pills without doctor‟s prescription. The chemist is reluctant to give him pills without doctor‟s prescription. (a) Write structure and IUPAC name f aspirin. (b) Mention the chemical reaction involved in the synthesis of aspirin. (c) Mention the values reflected by chemists approach. 26. Rakesh and Digvijay went on a hiking trip. During tracking Digvijay brushed against the plant stinging nettle. It causes severe itching on his leg. Rakesh went to a nearby shop and bought a soap cake. He rubbed the soap cake on the leg of Digvijay after wetting it with water. It helped Digvijay and the itching stopped within a very short time. (a) Name the organic substance caused itching on Digvijay‟s skin. (b) Why itching stopped when some soap is rubbed on it? (c) Name the values shown by Rakesh by this act. 27. Write the products of the following reaction : H (i) H (ii) HBr H CH3 CH2 CH CH2 HCl CH 2 C CH 2 (iii) 28. H Peroxide HBr Identify chiral and achiral molecules in each of the following pair of compounds. Page 16 29. Identify A, B, C, D, E, R and R1 in the following : 30. Explain why (a) the dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride? (b) alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water. (c) Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions? 31. How the following conversions can be carried out? 1. 1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane 2. Ethanol to but-1-yne 3. Benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene 4. Toluene to benzyl alcohol 5. Ethanol to propanenitrile 6. Aniline to chlorobenzene 7. Chlorobenzene to p-nitrophenol 8. Isopropyl alcohol to iodoform 9. Chloroethane to butane 10. Benzene to diphenyl PREVIOUS YEAR BOARD QUESTIONS + HOTS 1. Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds. I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Page 17 2. VII. VIII. IX. X. Write the structure of following halogen compounds 3. (i) D D T (ii) Freon - 12 (iii) 1-Bromo 4-Sec, butyl-2-methylbenzene. (iv) p-Bromo toluene. (v) Methylene chloride (vi) Chloral Complete the following reactions : I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. VIII. IX. X. XI. XII. XIII. XIV. XV. XVI. Page 18 4. How will you bring about the following conversions? (i) Benzene to 3-Bromonitrobenzene (ii) Ethanol to But-1-yne (iii) 1-Bromopropane to 2-Bromopropane (iv) Benzene to 4-Bromo-1-nitrobenzene (v) Aniline to chlorobenzene 5. (vi) 2-Methyl-1-propene to 2-chloro-2-methylpropane (vii) Ethyl chloride to propanoic acid (viii) But-1-ene to n-butyliodide (ix) Benzene to Phenyl chloromethane. (x) Tert-butylbromide to isobutylbromide. Identify the products formed in the following sequence : I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. 6. Explain the following reactions with suitable example : (i) Finkelstein reaction. (ii) Swarts reaction. (iii) Wurtz reaction. (iv) Wurtz Fitting reaction (v) Friedel Craft‟s alkylation reaction. (vi) Friedel Craft‟s acylation reaction (vii) Sandmeyer reaction. 7. What is the difference between (i) enantiomers and diastereomers (ii) retention and inversion of configuration. (iii) electrophilic and nucleophilic substitution reactions. Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in SN2 reaction with OH- and why? 8. (i) CH3 Br or CH3 l (ii) (CH3 )3 CCl or CH3 Cl 9. In the following pairs which halogen compound undergoes faster SN1 reaction? I. III. II. IV. V. Page 19 10. Give reasons for the following : (i) The bond length of C Cl bond is larger in haloalkanes than that in haloarenes. (ii) Although alkyl halides are polar in nature but are not soluble in water. (iii) t-Butyl bromide has lower boiling point than n-butyl bromide. (iv) Haloalkanes react with KCN to form alkyl cyanide as main product while with AgCN alkylisocyanide is the main product. (v) Sulphuric acid is not used in the reaction of alcohol with KI. (vi) Thionyl chloride is the preferred reagent for converting ethanol to chloroethane. (vii) Haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction easily but haloarenes do not undergo nucleophilic substitution under ordinary conditions. (viii) Chlorobenzene on reaction with fuming sulphuric acid gives ortho and para chlorosulphonic acids. (ix) 2,4-Dinitro chlorobenzene is much more reactive than chlorobenzene towards hydrolysis reaction with NaOH. (x) Grignard reagent should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. (xi) The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride. (xii) Neopentyl bromide undergoes nucleophilic substitution reactions very slowly (xiii) Vinyl chloride is unreactive in nucleophilic substitution reaction. (xiv) An optically inactive product is obtained after the hydrolysis of optically active 2- bromobutane. [Hint: The hydrolysis reaction is proceeding by S N1 pathway. The carbocation is formed first which gives a mixture of (±) butan-2-ol in the second step]. I. II. (xv) Methyliodide is hydrolysed at faster rate than methyl chloride. 11. An optically active compound having molecular formula C 7 H15 Br reacts with aqueous KOH to give C7 H15 OH, which is optically inactive. Give mechanism for the reaction. 12. An organic compound C 8 H9 Br has three isomers A, B and C. A is optically active. Both A and B gave the white precipitate when warmed with alcoholic AgNO3 solution in alkaline medium. Benzoic acid, Terephthalic and -Bromobenzoic acid were obtained on oxidation of A, B and C respectively. Identify A, B and C. 13. An organic compound (A) having molecular formula C 3 H7 Cl on reaction with alcoholic solution of KCN gives compound B. The compound B on hydrolysis with dilute HCl gives compound C and C on reduction with H2 /Ni gives l-aminobutane. Identify A, B and C. Page 20 CHEMISTRY – REVISION SHEET XII : CBSE ALDEHYDE, KETONE AND CARBOXYLIC ACID Subjective Type Questions Each Question carries 1 Mark 1. Arrange the following compound in increasing order of their acid strengths. CH3CHCOOH, CH3CHCH(Br) COOH, CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH. 2. 3. 4. 5. Write Draw Draw Write the the the the chemical equation to convert Benzonitrite to acetophenone. structure of hex-2-en-4-ynaic acid. structure of the compound whose IUPAC name is 4-chloropentan-2-one. IUPAC name of the compound : CH3 CH CO CH CH3 CH3 6. 7. CH 3 How are formalin and trioxane related to methanal? Write IUPAC name of O C OC 2 H 5 Cl O 8. Write IUPAC name of CH3 9. Mention a chemical property in which methanoic acid differs from acetic acid. 10. What is Tollen‟s reagent? 11. Write the chemical name and structure of Rochelle salt. 12. What product is obtained when ethylbenzene is oxidized with alkaline KMnO4 . 13. Name of the product obtained by heating of calcium acetate? Each Question carries 2 Marks 14. Describe the following reactions : (i) Cannizzaro‟s reaction (ii) Cross aldol reaction 15. Write chemical tests to distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid. 16. State reasons for the following situations : (i) Monochloroethanoic acid is a weaker acid than dichloro ethanoic acid. (ii) Benzoic acid is a stronger acid than ethanoic acid. 17. Write chemical equations to illustrate each of the following reactions : (i) Acylation reaction (ii) Rosenmund reduction 18. Complete the following reactions : (i) H2O CH3COCH3 CH3MgBr NaBH4 (iii) CH3COCH2CH3 H2O Boil. Alkali (ii) CH3CH2CHCl2 H2O (iv) R COCl H2 PdBaSO4 Page 21 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. Give chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds : (i) Propanoyl chloride and propanoic acid (ii) Benzaldehyde and acetophenone How are the following conversions carried out? (i) Ethanol to 1, 2-Ethanediol (ii) Phenol to Acetophenone Write the names of the reagents and equations in the conversion of (i) phenol to salicylaldehyde (ii) anisole to p-methoxyacetophenone Give one test each to distinguish between : (i) Aqueous solution of acetaldehyde and acetone (ii) Aqueous solution of phenol and benzoic acid (iii) Aqueous solution of formaldehyde and acetaldehyde Account for the following : (i) Ethers possess a dipole moment even if the alkyl radicals in the molecule are identical. (ii) Sodium bisulphite is used for the purification of aldehyde and ketones. Describe trans-esterification reaction, giving an example. State : (i) Why benzaldehyde does not undergo aldol condensation? (ii) How an acid amide may be converted to the parent acid? Complete the following reaction equation : (i) 27. (ii) CH3CONH2 HNO2 Zn/HCl RCHO An organic compound „A‟ (molecular formula C3H6O) is resistant to oxidation but forms a compound „B‟ (C3H8O) on reduction. „B‟ reacts with HBr to form a bromide „C‟ which on treatment with alcoholic KOH forms an alkene „D‟ (C3H6 ). Deduce the structure of A, B, C and D. Each Question carries 3 Marks 28. Complete the following reaction statements by giving the missing starting material, reagent or product as required. (i) O3 ............... 2 Zn H 2 O O (ii) CHO 2 ..................... CHO CH2OH (iii) KMnO4 ............... KOH, heat 29. How would you account for the following : (i) Aldehydes are more reactive than ketones towards nucleophiles. (ii) The boiling points of aldehydes and ketnes are lower than those of corresponding acids. (iii) Aldehydes and ketones undergo a number of addition reactions. 30. Conversions : (i) 2-Bromopropane to acetone (ii) Propanal to Propyne (iii) Ethanal to 2-hydroxy but-3-enoic acid 31. Arrange the following in increasing acid strength order : (i) HCOOH, CH3COOH, (CH3 )2 CHCOOH, CH3CH2COOH, (CH3 )3 C COOH. (ii) CH3COOH, ClCH2COOH, Cl2CHCOOH, Cl3CCOOH (iii) ClCH2COOH, BrCH2COOH, ICH2COOH, FCH2COOH. Page 22 32. How would you bring about the following conversions : (i) Propanal to butanone? (ii) Benzaldehyde to benzophenone? (iii) Benzoyl chloride to benzonitrile? 33. Give reasons for the following : (a) Carboxylic acids do not give characteristic reactions of carbonyl group (b) Treatment of benzaldehyde with HCN gives a mixture of two isomers which cannot be separated even by careful fractional distillation. (c) Sodium bisulphite is used for the purification of aldehydes and ketones. Each Question carries 5 Marks 34. (i) Describe the preparation of acetic acid from acetylene. (ii) How can the following be obtained from acetic acid : (a) Acetone? (b) Acetaldehyde? (iii) In what way can acetic acid be distinguished from acetone? (iv) Why do carboxylic acids not give the characteristic reactions of carbonyl group? 35. (a) Explain the mechanism of a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl group of an aldehyde or a ketone. (b) Identify A, B and C in the following sequence of reactions : C2H5MgCl Conc. H2SO4 HBr Peroxide CH3CHO A B C H2O (c) Predict the structure of the product formed when benzaldehyde is treated with (i) Conc. NaOH 36. (ii) HNO3 / H2SO4 (at 273 383 K) Write chemical reactions to affect the following transformations : (i) Butan-1-ol to butanoic acid (ii) Benzyl alcohol to phenylethanoic acid (iii) 3-Nitrobromobenzene to 3-nitrobenzoic acid (iv) 4-Methyl acetophenone to benzene 1, 4-dicarboxylic acid (v) Cyclohexene to hexane-1, 6-dioic acid (vi) Butanol to butanoic acid 37. PCl5 reacts with ethanol to form chloroethane. However, with phenol, it does not give chlorobenzene but gives triphenylphosphate. Example. 38. Although both allyl alcohol and 1-propanol are primary alcohols, they can still be distinguished by Lucas reagent. Explain how? 39. In Brazil, there are no longer any light vehicles in Brazil running on pure gasoline. Since 1976 the government made it mandatory to blend anhydrous ethanol with gasoline. Since July 1, 2007 the mandatory blend is 25% of anhydrous ethanol and 75% gasoline. (a) Why do you think Brazil has made it mandatory to blend gasoline with ethanol? (b) Write the chemical reactions involved in the synthesis of ethanol by sugarcane. (c) What are the values involved in use of ethanol substitute for gasoline? 40. Ethyl alcohol in the form of alcoholic beverages is used for drinking. The alcohol used for drinking is heavily taxed in the form of excise duty. However, alcohol used for industrial purposes is not taxed. To prevent the misuse, ethanol gets denatured by adding some chemical substance. A chemist always suggests not to use such industrial ethanol for drinking purpose. (a) Name the chemical substances used for denaturation of ethanol, (b) Mention the composition of methylated spirit. (c) Mention the values shown by chemist. Page 23 41. Tarun was watching news on T.V. with his family. Reporters were reporting about the special drive launch by government to curb the crimes and accidents related to „drunken driving‟. The news showed some policemen stopping vehicles and asking the drivers to blow air into an instrument. Finding, Tarun confused, his father told him to police were testing whether a driver consumed alcohol or not. (a) What instrument is used by the police? (b) What values are the police trying to inculcate in drivers and general public. (c) How does the instrument test whether a driver has consumed alcohol or not? Write the reaction. 42. Give names of the reagents to bring about the following transformation : (a) Hexan-1-ol to hexanal (b) Cyclohexanol to cyclohexanone (c) p-Fluorotoluene to p-fluorobenzaldehyde (d) Ethanenitrile to ethanol (e) Allyl alcohol to propanal (f) But-2-ene to ethanol 43. Write the structures of products of the following reactions : O (a) Anhyd. AlCl3 CS2 C (b) (C6H5CH2 )2 Cd 2CH3COCl C2 H 5 Cl CH3 (c) 2 Hg H2SO4 H3C C C H 1. CrO 2 Cl 2 2. H O (d) 3 NO 2 44. Would you expect benzaldehyde to be more reactive or less reactive in nucleophilic addition reactions than propanal? Explain your answer. 45. An organic compound (A) with molecular formula C8H8O forms an orange-red precipitate with 2, 4DNP reagent and gives yellow precipitate on heating with iodine in the presence of sodium hydroxide. It does not reduce Tollen‟s or Fehling‟s reagent, nor does it decolourize bromine water or Baeyer‟s reagent. On drastic oxidation with chromic acid, it gives a carboxylic acid (B) having molecular formula C7H6O2 . Identify the compound (A) and (B) and explain the reactions involved. 46. Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions. (a) Ethanal, Propanal, Propanone, Butanone (b) Benzaldehyde, p-Tolualdehyde, p-Nitro-benzaldehyde, Acetophenone 47. Predict the products of the following reactions : O (a) O H HO NH 2 O2 N NH 2 NH (b) NO 2 O (c) H R CH CH CHO NH 2 C NH NH 2 O (d) C H CH 3 CH 3CH 2 NH 2 Page 24 48. Write chemical reactions to effect the following transformations : (a) Butan-1-ol to Butanoic acid (b) Benzyl alcohol to Phenylethanoic acid (c) 3-Nitrobromobenzene to 3-nitrobenzoic acid (d) p-Methylacetophenone to Benzene-1, 4-dicarboxylic acid (e) Cyclohexane to Hexane-1, 6-dioic acid (f) Butanal to Butanoic acid 49. Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger? (a) CH3COOH or CH2FCOOH (c) CH2FCH2CH2COOH or CH3CHFCH2COOH (d) F3C (b) COOH or H3C CH2FCOOH or CH2ClCOOH COOH 50. What is meant by the following terms? Give an example in each case. (a) Cyanohydrin (b) Semicarbazone (c) Hemiacetal (d) Ketal (e) 2, 4-DNP-derivative (f) Acetal (g) Aldol (h) Oxime (i) Imine (j) Schiff‟s base 51. Write the IUPAC names of the following ketones and aldehydes. Wherever possible, give also common names. (a) CH3CO(CH2 )4 CH3 (b) CH3 (CH2 )5 CHO (d) CH3CH2CHBrCH2CH(CH3 )CHO CHO (c) 52. 53. 54. 55. Ph CH CH CHO (e) (f) PhCOPh Draw structures of the following derivatives. (a) The 2, 4-dinitrophenyllydrazone of benzaldehyde (b) Cyclopropanone oxime (c) Acetaldehydedimethylacetal (d) The semicarbazone of cyclobutanone (e) The ethylene ketal of hexan-3-one (f) The methyl hemiacetal of formaldehyde Which of the following compounds would undergo aldol condensation, which the Cannizzaro reaction and which neither? Write the structure of the expected products of aldol condensation reaction. (a) Methanal (b) 2-Methylpentanal (c) Benzaldehyde How will you convert acetaldehyde into the following compounds? (a) Butane-1, 3-diol (b) But-2-enal (c) But-2-enoic acid An organic compound with the molecular formula C9H10O forms 2, 4-DNP derivative, reduces Tollens‟ reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro reaction. On vigorous oxidation, it gives 1, 2benzenedicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound. 56. An organic compound (A) (Mol. For. C8H16O2 ) was hydrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C). Oxidation of (C) with chromic acid produced (B). Write possible structures of (A) and give their IUPAC names. Also write equations for the reactions involves. 57. Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds. (a) Propanal and Propanone (b) Phenol and Benzoic acid (c) Ethanal and Propanal (d) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate (e) Acetophenone and Benzophenone (f) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one (g) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone Page 25 58. How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps? (a) Propanone to Propene (b) Ethanol to 3-Hydroxybutanal (c) Benzaldehyde to Benzophenone (d) Benzaldehyde to 3-Phenylpropan- l-ol (e) Benzaldehyde to α-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid (f) Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde (g) Benzene to m-Nitroacetophenone (h) Bromobenzene to 1-Phenylethanol (i) Benzoic acid to m-Nitrobenzyl alcohol 59. Give plausible explanation for each of the following : (a) Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2, 2, 6-trimethylcyclohexanone does not. (b) There are two – NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones. (c) During the preparation of esters from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst, the water or the ester should be removed as soon as it is formed. 60. An organic compound contains 69.77% carbon, 11.63% hydrogen and rest oxygen. The molecular mass of the compound is 86. It does not reduce Tollen‟s reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium bisulphite and give positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation it gives ethanoic and propanoic acid. Write the possible structure of the compound. ALDEHYDES, KETONES AND CARBOXYLIC ACIDS Previous Year Board Questions + HOTS 1. 2. Indicate the electrophilic acid nucleophilic centre in acetaldehyde. Write the IUPAC names of the following organic compounds : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) [(CH3 )2 CH CH2CO]2 O (viii) (ix) (x) (xi) (xii) (xiii) (xiv) Page 26 3. Explain the following reactions giving one example in each (i) Rosenmund reduction reaction (ii) Stephen reaction (iii) Etard reaction (iv) Gatterman-Koch reaction (v) Aldol condensation (vi) Cross Aldol condensation (vii) Cannizzaro reaction (viii) Decarboxylation reaction (ix) Kolbe‟s reaction (x) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction (xi) Clemmensen reduction (xiii) Wolff-Kishner reduction (xiv) Haloform reaction. 4. How will you convert : (i) Isopropyl chloride to 2-methylproplonaldehyde. (ii) benzene to benzaldehyde (iii) benzoic acid to acetophenone (iv) propene to propanol (v) butanoic acid to 2-hydroxy butanoic acid (vi) benzoic acid to m-nitrobenzylalcohol (vii) propanol to propene (viii) propanol to butan-2-one. (ix) methyl magnesium bromide to ethanoic acid (x) (xi) acetone to chloroform benzoic acid to benzyl chloride (xii) acetylene to acetic acid (xiii) formaldehyde to 1-propanol (xiv) acetophenone to 2-phenyl-2-butanol. 5. Complete the following reactions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) (vii) (viii) (ix) (x) Br2 /P CH3 CH2 COOH X (X is a dibromo compound) (xi) 6. 2 Hg /H2SO4 CH3 C CH How will you prepare the following derivatives of acetone? (i) 2, 4-DNP derivative (iii) Oxime (ii) Schiff‟s base Page 27 7. 8. Arrange the following in the increasing order of the property indicated (i) CH3 CHO, HCHO, CH3 COCH3 , C6 H5 CHO (Reactivity towards HCN) (ii) Propan-1-ol, propanone, propanal (boiling point) Give the reaction mechanism for following reactions : (i) (ii) CH3COOH C2H5OH CH3COOC2H5 H2O (iii) 9. Give the chemical tests to distinguish between following pair of compounds : (i) Propanol and propanone (ii) Ethyl acetate and methyl acetate (iii) Benzaldehyde and benzoic acid (iv) Benzaldehyde and acetaldehyde (v) Formic acid and acetic acid (vi) Propanal and propanol (vii) Ethanoic acid and ethylethanoate 10. Give reason for the following : (i) The reactivity of aromatic aldehydes and ketones is less than that of aliphatic carbonyl compounds towards nucleophilic addition reactions. (ii) (iv) Benzaldehyde does not give Fehling test. (iii) The α-H atoms in ethanal are acidic in nature. p-Nitrobenzaldehyde is more reactive than benzaldehyde towards nucleophilic addition reactions. (v) Acetic acid does not give sodium bisulphite addition product. (vi) For the formation of ethylacetate from acetic acid and ethanol in presence of sulphuric acid, the reaction mixture is heated to remove water. (vii) Chloroacetic acid has lower pka value than acetic acid. (viii) Monochloroethanoic acid is a weaker acid than dichloroethanoic acid. (ix) Benzoic acid is stronger acid than ethanoic acid. (x) Aldehyde are more reactive than ketones towards nucleophilic reagents. (xi) Benzaldehyde does not undergo aldol condensation. (xii) Formic acid reduces tollen‟s reagent. (xiii) Electrophilic substitution in benzoic acid takes place at m-position. (xiv) Carboxylic acids do not give characteristics reactions of carbonyl group. (xv) Formaldehyde gives Cannizzaro‟s reaction whereas acetaldehyde does not. (xvi) Tert. butyl benzene can not be oxidised with KMnO4 . (xviii) Bond length of C = O in carboxylic acids is slightly larger than C = O bond length in carbonyl compounds. (xviii) There are two -NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one -NH2 group is involved in the formation of semicarbazones. (xix) Benzoic acid is less soluble in water than acetic acid. (xx) Formic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid. Page 28 11. You are given four different reagents Zn-Hg/HCI, NH2 - NH2 /OH- in Glycol, Hg/Ni and NaBH4 . Select one reagent for the following transformation and give reasons to justify your answer. 12. 13. 14. An organic compound (A) having molecular formula C 5 H10 O gives a positive DNP test. It does not reduce Tollen‟s Reagent but forms an addition compound with Sodium hydrogen sulphite. On reaction with I2 in alkaline medium, it forms a yellow precipitate of compound B and another compound C haming molecular formula C4 H7 O2 Na. On oxidation with KMnO 4 [A] forms two acids D and E haming molecular formula C 3 H6 O2 and C2 H4 O 2 respective. Identity A, B, C, D and E. Formaldehyde and acetaldehyde on treatment with dil. NaOH form A which on heating changes to B. When B is treated with HCN, it forms C. Reduction of C with DIBAL- H yields D which on hydrolysis yields E. Identify the missing reagent/products in the following reactions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) 15. Identify A, B, C, D and E in the following sequences of reactions : HCl A (C H ) B C 6 12 Acydic compound major minor both give tollen's test but (i) O3 A(C6H12 ) D E (ii) Zn/H2O do not give iodoform test conc. NaOH D E HCOONa (CH3 )3 C CH2OH 16. A tertiary alcohol „A‟ on acid catalyzed dehydration gave product „B‟ Ozonolysis of „B‟ gives compounds „C‟ and „D‟. Compound „C‟ on reaction with KOH gives benzyl alcohol and compound E'. Compound 'D' on reaction with KOH gives α. β - unsaturated ketone having the following structure. Identify A, B, C, D and E Page 29 17. Identify A, B, C, D and E in the following sequence of reactions : 18. Arrange the following acids in the increasing order of acidic strength (i) Formic acid, benzoic acid, acetic acid (ii) (iii) 19. CH3CH2COOH, C6H5COOH, CH3COOH,C6H5CH2COOH During the reaction of a carbonyl compound with a weak nucleophile H+ ions are added as catalyst. Why? 20. During reaction of carbonyl compound with 2, 4-DNP reagent the pH of the reaction mixture has to be maintained between 3 and 4. Why? 21. An aromatic compound X with molecular formula C 9 H10 gives the following chemical tests : (ii) Reduced Tollen‟s reagent (i) Forms 2, 4-DNP derivative (iii) Undergoes Cannizzaro reaction (iv) On vigorous oxidation gives 1, 2-benzenedicarboxylic acid. Identify X and write its IUPAC name. Also write the reactions involved in the formation of above mentioned products. Page 30 Page 31