* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MATH 2414 - Calculus II Units of Measurement and Some Applications
Survey
Document related concepts
Hooke's law wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Density matrix wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
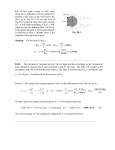
MATH 2414 - Calculus II Units of Measurement and Some Applications distance mass time velocity acceleration force work length density density weight density pressure centimeter/gram/second (cgs) System meter/kilogram/second (mks) System centimeter (c) gram (g) second (s) centimeters/second (c/s) centimeters/second2 (c/s2) dyne (dyn) erg g/cm gram/cm3 dyne/cm3 dyn/cm2 or barye (bar) meter (m) kilogram (kg) second (s) meters/second (m/s) meters/second2 (m/s2) newton (N) joule (J) kg/m kg/m3 N/m3 N/m2 or pascal (Pa) foot/pound/second (fps) System (U.S. Customary System) foot slug second feet/second (ft/s) feet/second2 (ft/s2) pound (lb) foot-pound (ft-lb) slug/ft slug/ft3 lb/ft3 lb/ft2 acceleration due to gravity: 980 cm/sec2 , 9.8 m/sec2 , 32 ft/sec2 weight = mass × acceleration due to gravity w = mg € € € Hooke’s Law: The force F applied to a spring is proportional to the distance x the spring is stretched. In other€words, F = kx , where the constant of proportionality k is called the spring constant. € Density, usually denoted by the Greek letter rho ( ρ ), is mass per volume, such as kg/m3 or slug/ft 3 . The€density of water is 1000 kg/m3. € as N/m3 or lb/ft 3 and is obtained € by multiplying € Weight density is weight per volume, such the density € by the acceleration due to gravity, so ρg . The weight density of water is 9800 N/m3 or approximately 62.5 lb/ft 3 . € € The pressure P at a depth of€d in a liquid is obtained by multiplying € the weight density times the depth, € so P = ρgd . Pressure units will be weight per area, such as N/m2 or lb/ft 2 . The force F on a surface with area A at a depth d in a liquid with density ρ is given by F = PA = ρgdA. € € € € €