* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Use a Venn diagram to compare and contrast sexual and asexual
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Biology and sexual orientation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Life history theory wikipedia , lookup
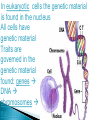
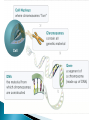
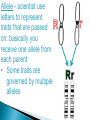
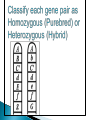
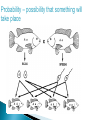
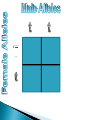
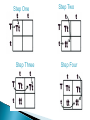
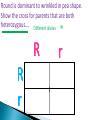
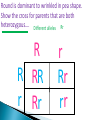
Use a Venn diagram to compare and contrast sexual and asexual reproduction Offspring Diverse Uniform Trait Asexual Type of Reproduction Identical Different Both Budding 1 parent 2 parents Flowers Sexual Use a Venn diagram to compare and contrast sexual and asexual reproduction Offspring Diverse Uniform Trait Asexual Uniform Identical Budding 1 parent Type of Reproduction Identical Different Both Offspring Trait Type of Reproduction Budding 1 parent 2 parents Flowers Sexual Diverse Different 2 parents Flowers Task ◦ Heredity Notes ◦ Heredity Practice Goal ◦ I can define heredity. ◦ I can explain the location of genetic material. ◦ I can use vocabulary to describe how traits are passed on from parent to offspring. Genetics – Study of how traits are inherited by offspring Offspring – result of reproduction; children or young of a parent Heredity – the passage of genetic instructions from one generation to the next Generation – parents are a generation, their offspring are the next generation Define heredity. ◦The passing of genetic material from generation to generation Genetic Material – are instructions for inherited traits Trait – characteristic passed from parent to offspring; eye color, face shape Gene – a section of DNA that codes for a specific trait DNA – (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) • Looks like a twisted ladder, scientist call it a “double helix” • Makes up a chromosome Chromosomes – are made up of DNA • In asexual reproduction a parent cell makes an exact copy of their chromosomes to pass on: offspring are uniform • In sexual reproduction each parent cell copies their chromosomes, but only donates half of the chromosomes to pass on: offspring are diverse • Humans have 46 or 23 pair of chromosomes In eukaryotic cells the genetic material is found in the nucleus All cells have genetic material Traits are governed in the genetic material found: genes DNA chromosomes nucleus Explain where genetic material is located in eukaryotic cells. ◦Genes DNA Chromosome Nucleus Gregor Mendel – known as the “father of genetics” because during his research with pea plants he wrote the Law of Dominance Allele - scientist use letters to represent traits that are passed on: basically you receive one allele from each parent • Some traits are governed by multiple alleles Genotype – the actual genetic makeup found on a chromosome; scientist represent genotype as letters; can be RR, Rr, rr Dominant – represented by a capital letter and are ALWAYS shown because they mask other traits: always written first: RR or Rr Recessive – represented by a lowercase letter and can only be seen when they are all that is present: rr Homozygous / Purebred – alleles in a gene pair are the same RR or ee Heterozygous / Hybrid – alleles in a gene pair are different Ee Phenotype – physical characteristic shown: round, wrinkled, green Probability – possibility that something will take place Punnett Square – model created by Reginald Punnett, used by scientist to predict traits of an offspring Step One Step Three Step Two Step Four Round is dominant to wrinkled in pea shape. Show the cross for parents that are both heterozygous…. Different alleles Rr R R r r Round is dominant to wrinkled in pea shape. Show the cross for parents that are both heterozygous…. Different alleles Rr R R r r Round is dominant to wrinkled in pea shape. Show the cross for parents that are both heterozygous…. Different alleles Rr R R RR r Rr r Rr rr Cross Bb (top) with bb (side). List the % of offspring.