* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
History of supernova observation wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Brown dwarf wikipedia , lookup
Astrophysical X-ray source wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
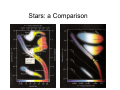
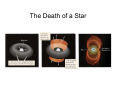
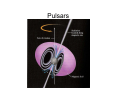
White Dwarfs and Neutron Stars Stellar Corpses Stars: a Comparison • As astronomers collected and compared data from individual stars, a trend became apparent • Spectral type, surface temperature, luminosity and magnitude are closely related • Adding in mass and size, we get a correlation on a chart called a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram Stars: a Comparison The Life of a Star • Nuclear fusion inside the cores of stars creates energy • What happens when all of the nuclear fuel (hydrogen) is used up? The Life of a Star The Life of a Star The Death of a Star White Dwarfs • Small Carbon and Oxygen inert core of once active main sequence stars White Dwarfs White Dwarfs • By accumulating mass (hydrogen), periodic bursts of fusion can occur on the surface called a nova • If too much mass is accumulated, the explosion may take place within the star blowing it apart in a supernova • Supernovae can also happen if two white dwarfs collide CfA press release • Evidence of merging white dwarfs exploding: supernova 2006gz • SN 2006gz shows strong spectral signature of unburned carbon – pushed away by the merger • Spectrum also shows silicon – created during the explosion • Brighter than most white dwarf supernovae, suggesting more mass than the Chandrasekhar limit (1.4 solar masses) would allow • • Dwarf “Sibling Rivalry” Explodes into Supernova. Release Number 2007-29. http://www.cfa.harvard.edu/news/2007/pr200729.html White Dwarf Fact Sheet • Composed of Carbon and Oxygen • Is no longer actively creating energy through thermonuclear fusion • Peak emission in Ultraviolet • Radius comparable to Earth’s • Mass limit of about 1.4 solar masses • Can explode into novae and supernovae High Mass Stars • Above 8 solar masses (less massive stars will blow off their outer layers into planetary nebulae and the core remains as a white dwarf) High Mass Stars • Additional stages of fusion in the core • Stops at iron (more energy input required) High Mass Stars • Core rapidly contracts and heats to around 5 billion degrees • Previously large core shrinks to less than 20 kilometers in diameter • Core becomes so dense that the protons and electrons fuse into neutrons • Inner part of the core bounces and produces a shockwave that triggers a supernova explosion Neutron Stars • The remnants of the core after a supernova has blasted the rest of the star into space Neutron Stars • Have an upper mass limit of around 3 solar masses (heavier cores of very massive stars collapse forming a black hole) • Hypothesized to exist long before the discovery of pulsars (rapidly spinning neutron stars that emit beams of radiation) Pulsars Neutron Stars • By accumulating mass (helium), periodic bursts of fusion can occur on the surface and create an X-ray burster • Can collide or merge with each other (or black holes), creating a gamma ray burst (the most powerful explosions in the universe) Spitzer press release • Neutron stars can form powerful jets of matter and energy • Previously only thought possible with black holes • Binary system with neutron star gaining matter from white dwarf companion’s atmosphere in an accretion disk • Neutron star is tiny compared to white dwarf but is very dense and about 14 times as massive Spitzer press release • • Staff Writers. May 22, 2006. Stellar Jets. Spitzer. http://gallery.spitzer.caltech.edu/Imagegallery/image.php?image_name=sig06-014 Neutron Star Fact Sheet • Composed largely of neutrons, with some protons and possibly exotic states of matter • Is no longer actively creating energy through thermonuclear fusion • Peak emission in X-ray (not always from the star itself) • Radius comparable to Winnipeg’s • Mass limit of about 3 solar masses Sources and Links • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Freedman RA, Kaufmann III WJ, 2005. Universe: New York: W. H. Freeman and Company. 693pp. 7th ed. Staff Writers. September 24, 1997. Hubble Sees a Neutron Star Alone in Space. Release Number STScI-1997-32. http://hubblesite.org/newscenter/archive/releases/1997/32/ Staff Writers. May 22, 2006. Stellar Jets. Spitzer. http://gallery.spitzer.caltech.edu/Imagegallery/image.php?image_name=sig06-014 Staff Writers, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. November 1, 2007. White Dwarf “Sibling Rivalry” Explodes into Supernova. Release Number 2007-29. http://www.cfa.harvard.edu/news/2007/pr200729.html link to the paper: http://arxiv.org/PS_cache/arxiv/pdf/0709/0709.1501v1.pdf Staff Writers, Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. January 31, 2006. Neutron Star Swaps Lead to Short Gamma Ray Bursts. Release Number 2006-12. http://www.cfa.harvard.edu/news/2006/pr200612.html link to the paper: http://www.nature.com/nphys/journal/v2/n2/full/nphys214.html List of Images Used • • • • • • • • • • • • 1) Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram 1 – Universe 7th ed. page 428 2) Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram 2 – Universe 7th ed. page 428 3) Fusion of Hydrogen into Helium – Universe 7th ed. page 381 4) Main Sequence to Red Giant – Universe 7th ed. page 471 5) Red Giant Sun – Universe 7th ed. page 470 6) Mass Ejection – Universe 7th ed. page 494 7) Sirius B White Dwarf Star – Universe 7th ed. page 495 8) White Dwarf Mass Radius Relation – Universe 7th ed. page 495 9) Fusion Layers in a Supergiant Star – Universe 7th ed. page 498 10) Neutron Star Section – Universe 7th ed. page 520 11) Neutron Pulsar – Universe 7th ed. page 516 12) White Dwarf and Neutron Star Jets – Spitzer press release, NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt (SSC)