* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Coastal systems and low- lying areas
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Future sea level wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on oceans wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of the IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
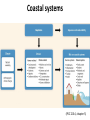
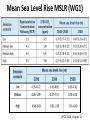
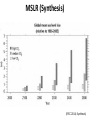
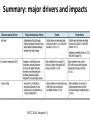
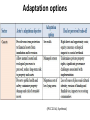
th 5 IPCC Assessment Report : Coastal systems and lowlying areas University of Adelaide, Australia 20 November 2014 Poh Poh Wong Coordinating Lead Author [email protected] IPCC Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) • Created in 1988 by WMO and UNEP. Has 195 governments that commission assessments performed by the international community on the state of human knowledge of climate & climate change. • Role : to assess on a comprehensive, objective, open & transparent basis the scientific, technical & socio-economic information relevant to understanding scientific basis of risk of human-induced climate change, its potential impacts & options for adaptation & mitigation. • IPCC assessments : scientific basis for governments at all levels to develop climate related policies, & they underlie negotiations at the UN Climate Conference (UNFCCC, United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change). Three Working Groups (WGs) and Task Force • WGI : assesses physical scientific aspects of climate system & climate change. • WGII : assesses vulnerability of socio-economic & natural systems to climate change & options for adapting to it. • WGIII : assesses options for mitigation climate change through limiting or preventing GHG emissions & enhancing activities to remove them. • Task Force : to develop & refine internationally-agreed methodology & software for calculation & reporting GHG emissions. AR5 – WGII • Scoping meeting in July 2009 to outline 30 chapters : involving climate change experts from relevant disciplines, users, govt. reps. • 1217 author nominations from 92 countries. • 242 Lead Authors (about 60 are CLAs) & 66 Review Editors from 70 countries : selection criteria include expertise, differing viewpoints & perspectives, geographic balance, gender balance, & ensuring involvement of new experts in accordance to agreed-upon IPCC guidelines. Supplemented by 436 Contributing Authors from 54 countries. • Undergone two extensive reviews : totaling over 50,000 comments from 1729 expert reviewers from 84 countries & 49 governments. • Over 12,000 scientific references. AR5 - Risk assessment • Focus on risks to support decision making. • Risks = interactions of CC hazards (incl. hazardous events) with vulnerability & exposure of human & natural systems. (IPCC 2014, SPM) WGII - Larger knowledge base • Substantial larger knowledge base : from 20 to 30 chapters; 4 on adaptation; 4 on livelihoods & poverty, human security, urban & rural areas; 2 on oceans. • Two parts; part 1 on global & sectorial aspects; part 2 on regions. Coasts Post-AR4 – key/new issues • Higher GMSLR; serious implications for coastal systems, both physical & human. • Ocean acidification of increasing concern; serious implications for shellfish & commercial aquaculture. • Advances in both vulnerability assessments & identification of potential actions, costs, benefits & trade-offs. • More coastal adaptation with wider range of approaches & frameworks. Coastal systems (IPCC 2014, chapter 5) Three key drivers related to Climate Change • Sea level, ocean temperature & ocean acidity. • Long term commitment to experience sea level impacts because of delay in its response to temperature. • Coral bleaching & species ranges can be attributed to temperature change & ocean acidity. Mean Sea Level Rise MSLR (WG1) (IPCC 2014, chapter 5) MSLR (Synthesis) (IPCC 2014, Synthesis) Regional Sea Level Rise RSLR • RSLR can be much larger than projected GMSLR. • Non-climate change local processes include subsidence, glacial isostatic adjustment, sediment transport, coastal development. • Changes in storms & associated storm surges may further contribute to sea level extremes. • Under present levels of global warming, already committed to higher future SLR above current levels. Adverse impacts • Coastal systems & low-lying areas will be increasingly subject to submergence, coastal flooding & erosion. • Beaches, sand dunes, cliffs continued to be eroded under increasing sea level. Acidification and warming • Acidification continues with large & uncertain regional & local variations. • Warming & acidification will lead to coral bleaching, mortality & decreased constructional ability. • Coral reefs will be most vulnerable marine ecosystem with little scope for adaptation. Summary: major drivers and impacts (IPCC 2014, chapter 5) Detection & attribution (IPCC 2014, chapter 5) Human pressures on coastal systems • Increase significantly in future due to population growth, economic development, & urbanization. • Humans have been primary drivers of change in coastal aquifers, lagoons, estuaries, deltas & wetlands. • Further exacerbation on coastal ecosystems from excess input, changes in runoff & reduced sediment delivery. Benefits of protection • Benefits of protection against coastal flooding and land loss at global scale are larger than social & economic costs of inaction. • Without adaptation, hundreds of million will be affected by coastal flooding & displaced due to land loss by 2100; majority from East, Southeast & South Asia. • Protection against flooding & erosion is economically rational for most developed coastlines in many countries for all socioeconomic & SLR scenarios. Relative costs of coastal adaptation • Costs of coastal adaptation expected to vary strongly among & within regions & countries. • Some low-lying countries (Bangladesh, Vietnam) & small islands expected to face high impacts. Associated damage & adaptation costs could be several % of GDP. Coastal adaptation • Increasingly, coastal adaptation options include those based on ICZM, local community participation, EBA & DRR mainstreamed into relevant & management plans. • More proactive responses made & based on technology, policy, financial & institutional support. • Flexible & reversible options are favoured. • Should note that protection further attracts population & development which in turn increases risk of potential catastrophic consequence in case of defence failure. Adaptation among countries • Coastal adaptation progressed more significantly in developed countries than in developing countries. • Innovative approaches, e.g. Dutch approach in “working with nature”, “room for river” rather than dikes and structures. Adaptation options (IPCC 2014, Synthesis) Conclusion Risk and adaptation over timeframe (IPCC 2014, chapter 30) Risks impacted by Sea Level Rise (IPCC 2014, Synthesis) Thank you