* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Physics Lecture #22
Survey
Document related concepts
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
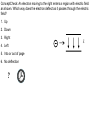
Mon. Jan. 26 – Physics Lecture #22 The Electric Field 1. Forces & Fields 2. Superposition 3. Electric Field due to Continuous Charge Distributions Example: An electron placed in a gravity field experience a gravity force of 6.1 x 10–10 N. a) What is the magnitude of the gravity field? b) A proton is placed in that same gravity field. What is the magnitude of the gravity force on that proton? Example: An electron placed in an electric field experience an electric force of 6.1 x 10–10 N. a) What is the magnitude of the electric field? b) A proton is placed in that same electric field. What is the magnitude of the electric force on that proton? ConceptCheck: An electron moving to the right enters a region with electric field as shown. Which way does the electron deflect as it passes through the electric field? 1. Up 2. Down 3. Right 4. Left 5. Into or out of page 6. No deflection ? E PhET Interactive Simulations – Charges and Fields http://phet.colorado.edu/en/simulation/charges-and-fields Example: The sketch shows two point charges located in the x-y plane: q1 at the origin and q2 at (0 m, 4 m). Also consider a field point at (3 m, 0 m) a) Determine the unit vector from q1 to the field point. b) Determine the unit vector from q2 to the field point. c) Determine the electric field at the field point due to q1 and q2. d) How does your answer change if q2 is negative? e) A charge q3 is placed at (3 m, 0 m). What is the electric force acting on q3?