* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download KINGDOM PROTISTA
Survey
Document related concepts
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Mating in fungi wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Arbuscular mycorrhiza wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
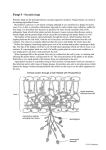
2/24/2011 OVERVIEW KINGDOM FUNGI Cell type: Eukaryotic Cell type: uni- or multicellular Nutrition: Heterotrophic ALWAYS (they absorb nutrients) Habitat: moist environment Cell walls made of chitin (a tough polysaccharide) STRUCTURE Hyphae—hair-like filaments of fungi that can group together to form larger structures called mycelium— a cluster of hyphae USES OF FUNGI Decomposers for the environment Make foods & medicine Edible mushrooms, truffles Bleu cheese Breads and alcohols are made with yeast (a single celled fungus) Medicines (ex: antibiotic Penicillin) HOW THEY EAT 1. 2. Saprophyte—lives on dead organic (carbon-containing) matter Parasite—absorbs nutrients from living cells OBTAINING NUTRIENTS 3. Mutualistic—lives in a symbiotic (mutually beneficial) relationship with another organism ex: Lichens—organisms made of both an algae (protist) and a fungus. Algae - provides energy through photosynthesis Fungi - provides moisture/place to grow 1 2/24/2011 FUNGUS REPRODUCTION 1. Asexually A. Fragmentation—part of hyphae breaks off and grows into a new mycelium B. Budding—cells replicate their DNA, split into two identical cells Ex: yeast C. Spores—reproductive cells that can develop into new organisms (are NOT true seeds, but they act in a similar way) FUNGAL INFECTIONS/ DISEASES 1. Lungs: can cause allergies and severe respiratory illnesses Body: hair, skin, nails 2. Sexually Can happen occasionally; when hyphae from two different fungi meet and fuse together to make spores FUNGAL INFECTIONS/DISEASES 2. Aspergillosis Most humans inhale Aspergillus spores every day so it develops mainly in individuals who are immunocompromised; it’s a leading cause of death in acute leukemia Also make aflatoxin, the most toxic mycotoxin known which is also a potent carcinogen (liver cancer) are largely associated with products from the tropics and subtropics, such as cotton, peanuts, spices, and pistachios Athlete's foot, jock itch, and ringworm are caused by the same fungus that can grow in various locations FUNGAL INFECTIONS/ DISEASES 3. Death Cap Scientific name: Amanita phalloides It has been involved in the majority of human deaths from mushroom poisoning FYI: This possibly includes the deaths of Roman Emperor Claudius and Holy Roman Emperor Charles VI. FUNGAL INFECTIONS/DISEASES 4. Plants Some “blights” are caused by fungi Almost all chestnut trees have been infected with a blight 2