* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE ROLE OF DENTAL TECHNOLOGY IN ORAL HEALTH CARE
Survey
Document related concepts
Water fluoridation in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Scaling and root planing wikipedia , lookup
Amalgam (dentistry) wikipedia , lookup
Forensic dentistry wikipedia , lookup
Impacted wisdom teeth wikipedia , lookup
Periodontal disease wikipedia , lookup
Tooth whitening wikipedia , lookup
Calculus (dental) wikipedia , lookup
Remineralisation of teeth wikipedia , lookup
Dental implant wikipedia , lookup
Focal infection theory wikipedia , lookup
Crown (dentistry) wikipedia , lookup
Special needs dentistry wikipedia , lookup
Dentistry throughout the world wikipedia , lookup
Dental hygienist wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
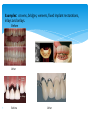
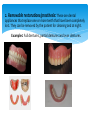
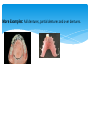
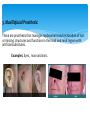
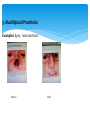
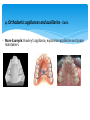
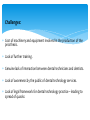
THE ROLE OF DENTAL TECHNOLOGY IN ORAL HEALTH CARE Introduction: Dental laboratory technology is the art and science of designing, manufacturing and customizing corrective devises and replacement for natural teeth and associated tissues. A Dental Technologist is a member of the dental team who, upon prescription from a dental clinician, constructs custom made restorative and dental appliances. WHY Dental prostheses? Mastication; as chewing ability is improved Aesthetics; teeth gives a natural appearance to the face, and wearing a denture to replace missing teeth provides support for the lips and cheeks. Pronunciation; because replacing missing teeth, especially the anteriors, enables patients to speak better. Self-esteem; because improved looks and speech boost confidence in the ability to interact socially There are four major disciplines within dental technology: 1. Fixed restorations/prosthesis: These are restorations to replace a tooth/teeth that may have been lost or damaged. These restorations once placed by a dentist, the patient cannot remove them. Examples: crowns, bridges, veneers, fixed implant restorations, inlays and onlays. Before After Examples: crowns, bridges, veneers, fixed implant restorations, inlays and onlays. Before After Before After 2. Removable restorations/prosthesis: These are dental appliances that replace one or more teeth that have been completely lost. They can be removed by the patient for cleaning and at night. Examples: Full dentures, partial dentures and over dentures. More Examples: Full dentures, partial dentures and over dentures. 3. Maxillofacial Prosthesis: These are prosthesis that manages replacement and restoration of lost or missing structures and functions in the head and neck region with artificial substitutes. Examples: Eyes, nose and ears. 3. Maxillofacial Prosthesis: Examples: Eyes, nose and ears. Before After 4. Orthodontic appliances and auxiliaries: These are removable appliance made of wires, springs and screws incorporated in acrylic resin, to move teeth to form a more harmonious occlusion and aesthetics appearance of teeth and maintain the position of previously moved teeth. Example: Hawley’s appliance, expansion appliances and space maintainers. 4. Orthodontic appliances and auxiliaries – Cont. More Example: Hawley’s appliance, expansion appliances and space maintainers. Challenges: Cost of machinery and equipment involved in the production of the prosthesis. Lack of further training. Genuine lack of interaction between dental technicians and dentists. Lack of awareness by the public of dental technology services. Lack of legal framework for dental technology practice – leading to spread of quacks Conclusion: Training opportunities in specialized areas The Dental Technologists as part of the dental team play a key role in dental treatment cycle. There is need for dentists/dental surgeons to collaborate closely with dental technologists in the treatment and design of prostheses. Provision of relevant equipment/machines and laboratory work instruments Procurement of key materials in specialized areas like maxillo-facial prosthetics THANK YOU!!