* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Classification
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
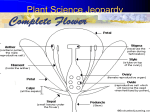
Plant Classification: Six Characteristics of Plants: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Structures of Angiosperms (Flowering Plants) Vascular Tissue (Plumbing) List the TWO types of vascular tissue & what they transport: Where are they found in the plant? Roots What are the THREE functions of a root? What are the TWO root types? Stems What are the THREE functions of a stem? What are the TWO stem types? Leaves What is the function of the leaves? Photosynthesis What are the TWO important products of photosynthesis and why are they important? What is the equation for photosynthesis? Cellular Respiration What are the TWO reasons respiration is important for plants? Flowers What is the function of a flower? What are THREE reasons flowers are important? Sexual Reproduction List the SIX steps of sexual reproduction in angiosperms? Basic Photosynthesis Fill in the blanks of the diagram with the following words: Water (H2O) Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Light Energy Food (C6H12O6) Oxygen (O2) Questions: 1. Which two types of atoms (Carbon, Hydrogen, or Oxygen) enter the plant but do not leave the plant? 2. Out of the two atoms that you selected in question 1, which one do you think allows the plant to grow? Explain your reasoning: Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is a process unique to the pant world. Photo means “light” and synthesis means “putting together”. Through this process, plants are able to make their own food. Use the terms in the word box to complete each sentence. Photosynthesis Oxygen Glucose Chloroplast Carbon Dioxide Cellulose Carbohydrates Sunlight Leaves Water Chlorophyll 1. Water, carbon dioxide, and ________________________________ are the three ingredients needed for photosynthesis to occur. 2. Through photosynthesis, plants convert these ingredients into ________________________________, a food used by the plant. 3. ________________________________ is the material in green plant cells that trap energy from the sun. 4. The plant take in a gas called ________________________________ from the air. 5. Chlorophyll is found in the ________________________________, structures within the cell where photosynthesis will take place. 6. ________________________________ is a material the plant takes up through its roots and stems. 7. During photosynthesis, ________________________________ is a waste product released by the plant into the air. 8. Plants produce more glucose than they need. The excess glucose is stored by the plant as ________________________________ or starches. 9. Plants also change glucose into ________________________________, the structural material used in their cell walls. 10. While chlorophyll is found in most above-ground parts of green plants, most photosynthesis takes place in a plant’s ________________________________. 11. In many regions, there is not enough sunlight or water during winter for ________________________________ to occur. Journal Title: Plant Cells Plant Name: Elodea (aquatic plant) Color Drawing & Label - cell wall & chloroplasts ___________________________________________________________ Journal Title: Nonvascular (seedless) Plants Plant Name: Moss Color Drawing & Label - Leaf like structure; stalk; spore capsule; rhizoid Question: 1. Why doesn’t moss have true roots, leaves and stems? Journal Title: Vascular Seedless Plant Plant Name: Fern (Parts of a Fern) Label the parts of a fern using the word bank: Rhizome Root Frond Fiddlehead Plant Name: Fern (Frond and Spores) Color Drawing & Label - frond (leaf); spores and fiddlehead (if available) Question: What is different between the stem of a fern and the stem on a pine tree? Journal Title: Gymnosperm – Conifer Needles and Cones Comparing Conifer Needes: Observe the conifer needles of an Arborvitae tree and the needles of a Douglas Fir tree using a dissection microscope. In the space below describe the difference in the two types of conifer needles. Female Pine Cone: Color Drawing & Label - female cone; seed inside the cone Question: What is the difference between a gymnosperm seed and an angiosperm seed? Journal Title: Angiosperm Root Types Color Drawing Tap Root System Fibrous Root System Question: What advantages does each root type have in different environmental conditions? Taproot System – Fibrous Root System – Journal Title: Angiosperm Stem Types and Parts Woody Stem Label the following cross section of a woody stem. Use the woody stem diagram provided to help label the parts. NOTE: The cambium is where new xylem and phloem cells form each year. Questions: 1. Using the actual woody stem cross section, try to locate the five parts of the stem labeled above. 2. How old is your actual woody stem cross section (count the rings)? ___________________ 3. Which do you count to determine the age of the tree? (xylem or phloem) ______________ 4. Why is the spring xylem thicker than the summer xylem? ___________________________ Herbaceous Stem Color Drawing & Label - vascular tissue (tubing) Celery Cross Section Question: Is the stained vascular tissue in the celery stalk the xylem or phloem? Explain why. Journal Title: Angiosperm Leaves (Parts and Function) Leaves Color and label the following cross section of a leaf. Use the word bank and textbook to help label the parts. Epidermis Guard cell vein palisade layer stoma spongy layer cuticle Questions: 1. What part of the leaf labeled above contains the xylem and the phloem? _________________________ 2. What is the function of the stomata? ______________________________________________________ 3. In most leaves, the stomata are found only on the lower epidermis. Why do you think it is not a successful adaptation to have the stomata on the upper epidermis (top side of the leaf)? ___________________________________________________________________________________ Stomata & Guard Cells Color Drawing & Label – stomata; guard cells Lower Epidermis of a Leaf Journal Title: Angiosperm Flower (Parts) Stamen & Pistil Remove the petals and sepals to expose the female and male reproductive parts of the flower. Color Drawing & Label – stamen & pistil Questions: Pistil (female) Stamen (male) 1. How many petals? 2. How many stamen(s)? 3. Which is taller the pistil (female) or stamen (male)? 4. Can this flower self-pollinate without insects or birds? Using the list of flower parts label the two diagrams #1-12. Also color the flower parts. 4 . C a n t h i s Sepal Petal Pistil Anther Ovary Ovule Stamen f l o w e r s e l f p o l l i n a Journal Title: Angiosperm Sexual Reproduction List the SIX steps of angiosperm sexual reproduction: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Journal Title: Angiosperm Fruits (comparison) Silver Maple (fruit) Tomato (fruit) Draw & Color Fruit; Label Seed Draw & Color Fruit; Label Seeds Questions: 1. How are the seeds within each of the fruits above dispersed within their environment? 2. How have these fruits adapted to their method of dispersal? Journal Title: Angiosperm Seed Parts & Germination Lima Bean Seed Pea Plant (Germinating) Color Drawing & Label - Draw Germinating Pea Plant seed coat, young plant & cotyledon Journal Title: Tropisms & Limiting Factors The following are the types of tropisms you need to know: Gravitropism (AKA geotropism): response to ___________ Thigmotropism: response to ____________ Hydrotropism: response to ____________ Negative Tropism: growth ___________ from the stimulus Phototropism: response to ____________ Positive Tropism: growth ____________ the stimulus Data Table: Example Type of Tropism + or - List SIX Limiting Factors that you observe outdoors. Sketch