* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module – 6 Unit – 6 Power Amplifiers
Survey
Document related concepts
Instrument amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Negative-feedback amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
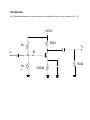
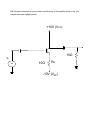
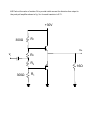
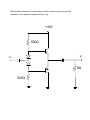
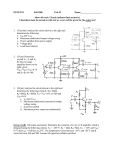
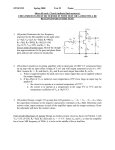
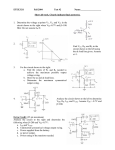
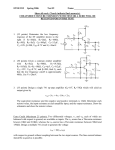
Module – 6 Unit – 6 Power Amplifiers Review Questions: 1. In what way the design features of power transistors different from small signal transistors? 2. What is the basis for the classification of power amplifiers? Mention different types of power amplifiers? 3. Draw the circuit for commonly used class A – amplifier. If the amplifier draws 10W of dc power, what is the maximum ac power available to the load? 4. Draw the circuit for a push-pull amplifier and discuss its working. 5. Derive an expression for the efficiency of class B – power amplifiers. 6. What is harmonic distortion? How does it arise in Class B-operation? And, how can it be corrected in push-pull circuit? 7. What do you understand by cross-over distortion? How can it be eliminated in Class B-operation? 8. What reasons will you assign for higher conversion efficiency of Class B-amplifier as compared to Class A –amplifier? 9. Draw a circuit for Class C- amplifier and discuss its working? 10. Among all the power amplifiers, Class C-amplifier has the maximum efficiency but its use is restricted. Give reasons. Problems: 6.1 Calculate maximum ac output power in the amplifier shown in fig. (Assume V BE = 0) +20V 50Ω 1k vi vo B 1k k 50Ω 100Ω Solution:The ac power in class A-operation, P0 is given by the relation, VCEQ . I CQ P0 2 Where VCEQ and ICQ are voltage across collector – emitter of transistor at operating point and collector current respectively. First we need the value of ICQ. Now in fig above, the voltage between base and ground (point B and ground, see fig.) VBB, is 10 V. Then, I CQ VBB IE VBE RE 10V 100 VBB RE 100 mA VCEQ can be obtained by summing voltage (dc voltages, capacitors taken open) VCC = VCEQ + IE(RC + RE) Or, VCEQ = VCC – IE(RC + RE) = 20 – 100mA (50 + 100)Ω = 20 -15 Or, VCEQ = 5V Therefore, maximum ac power, PO, P0 VCEQ . I CQ or P0 2 250 mW 5 100 mA 2 6.2 Calculate maximum ac output power and efficiency of the amplifier shown in fig. V BE may be assumed negligibly small. +10V (VCC) 10Ω vi ~ 10Ω RE -10V (VEE) Solution:The operating point current and voltages in the circuit are: I CQ VEE RE IE 10V 10 1A And, VCEQ = VCC = 10V Therefore, maximum ac output power is, P0(max) VCEQ . I CQ 2 10 1 2 5W To calculate the efficiency, η , the dc power drawn by collector-emitter circuit is, PDC VCC VEE I CQ (10 10) 1 20W Therefore efficiency, P0(max) PDC or 25% 5W 100 20W 6.3 Find out the value of resistor R2 to provide trickle current for distortion free output in the push pull amplifier shown in fig. VBE for each transistor is 0.7V. +30V 300Ω R1 vo vi R2 R2 300Ω R1 16Ω Solution:Trickle current which flows through resistors R2 and produces a voltage drop of 0.7 V across base – emitter junction over comes cross – over distortion in push – pull amplifier. For analysis purposes, it is sufficient to consider only half of the circuit for reasons of symmetry, and VCC of half (= VCC/2 = 30/2 = 15V) is to be taken for one transistor. The current through resistors R1 and R2 is, I 15V R1 R2 15V 300 R2 But, I X R2 = 0.7V (desired voltage) or , I 0.7 V / R2 ............( B) Combining Eqs (A) and (B), 0.7V R2 15V 300 R2 or , R2 14.7 ....................( A) 6.4 Calculate maximum ac output power and the minimum power rating of the transistors in the push-pull amplifier shown in fig. +40V 500Ω vo vi 8Ω 500Ω Solution:The maximumac power (output). P0(max) as per the discussion on the topic is, VCEQ P0(max) ic ( sat ) 2 Where ic(sat) is maximum (saturated) collector current. Now, VCEQ 1 VCC 2 1 2 40V 20V And, ic(sat) is expressed as, ic ( sat ) VCEQ rC rE 20V 0 8 2.5 A Here, rC is effective ac resistance seen by the collector and rE is effective resistance seen by the emitter. Therefore, P0(max) VCEQ iC ( sat ) 2 20 2.5 2 25 W The maximum power rating, PD(max) is one-fifth of maximum ac power. That is, 1 . P0(max) 5 or , PD (max) 5W PD (max) 25W 5 6.5 In fig. a basic Class C-amplifier is shown. It uses supply voltage of + 20V and load resistance of 100Ω. The operating frequency is 3MHZ and VCE(sat) = 0.3 V. Calculate and efficiency. If peak current is 500 mA, find the conduction angle also. +20V(VCC) 100pf 3μH vi 100Ω Solution:The peak voltage, Vp, as was discussed is, Vp = VCC – VCE(sat) = 20 – 0.3 Or, Vp = 19.7V The ac power P0, is P0 2 V p2 1.97 2 RL 2 100 or , P0 1.69W And, dc power drawn by the circuit is, Pdc VCC I dc Where, I dc P0 Vp 1.69W 19.7 V 0.0857 A Therefore, Pdc = 20 X 0.0857 or, Pdc = 1.714 W And the efficiency, η, is P0 Pdc 1.69W 1.714W 100 98.5% Now, we proceed to find out the conductance angle θ. For the frequency of 3MHZ, the period of the wave, T, is T 1 3 106 0.33 s And transistor’s on- time is, t P0 T I p Vp 1.69W 0.33 10 6 500 10 3 19.7 V 56.6 10 9 s 56.6 ns or , t or , t And, the conduction angle, θ, is t T or , 360 61.7 56.6 10 9 0.33 10 6 360