* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Student 2
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
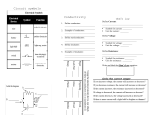
Student 2: High Merit AS 90941 Student 2 From my results I noticed that: Voltage being received by the resisters in the circuits was the same as the total voltage supplied. This is typical of parallel circuits even though current increases across the parallel branches. The energy carried by the electrons is the same. Current, unlike voltage raised between circuits. The current drawn by a resistor depends on its resistance (Ohms Law states that resistance is inversely proportional to current) Low resistance has high current and vice versa. The order of circuits has no effect on the results. Ohms law states that the heat in wires is directly proportional to the current flowing. More current hotter wires. If current is very high insulation can melt and start a fire. Application of results to a house hold environment: In a house circuits are wired in parallel so as all branches of a circuit get 240V. It also means a single branch can operate independent of the other branches. All components get the max voltage. In NZ this is 240V. The problem comes with current. In parallel circuits as more appliances are added to a circuit then more current flows and more current means a hotter environment. If enough appliances are added to a parallel circuit then the wires get hot enough to melt the insulation then start a fire. (1) To stop this we add circuit breakers to the circuit at the start and this circuit breaker is wired in series. If too much current flows then the circuit breaker trips taking out all the parallel circuits until the problem is fixed. (2) The use of multiboxes today compounds this issue so the safest multiboxes are those with inbuilt circuit breakers. They stop people overloading the multiboxes.