* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 19 - Napa Valley College
Survey
Document related concepts
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Angiosperms
§ Division/Phylum Anthophyta
(anthe = flower; phyto = plant)
§ flower, a cluster of highlyspecialized leaves which
participate in reproduction.
§ 300,000 to 450,000 species
§ Monophyletic
True secondary growth, with vascular cambium rarely present True secondary growth, with vascular cambium commonly present complete flowers
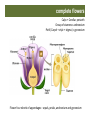
Calyx + Corolla= perianth Group of stamens= androecium Pis9l (Carpel + style + s9gma) = gynoecium corolla calix Stamen Flower four whorls of appendages : sepals, petals, androecium and gynoecium The flower
Lacandonia schismatica
Lacandonia is most famous for being the only flower that typically produces its androecium above the gynoecium rather than below. Nutrition. Saprophyte
Monotropa uniflora cannot photosynthesize Fungal root-‐associa9on (mycorrhiza) Nutrition. Parasitic
Cuscuta § Haustoria § Tiny seeds with hard coa9ng, survive in the soil for 5–10 years § Some photosynthe9c species § Some species en9rely dependent on the host plants for nutri9on Nutrition. Parasitic
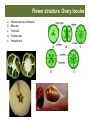
§ Rafflesia arnoldii ("corpse flower”) § The largest individual flower on earth § Distribu9on: Sumatra, Borneo in the Indonesian Archipelago. § Lacks any observable leaves, stems or roots Tetras+gma vine Flower structure. Ovary locules
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
Monolocular or unilocular Bilocular Trilocular Tetralocular Pentalocular Flower structure. Placentation
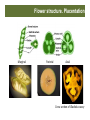
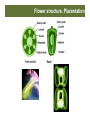
Marginal Parietal Axial Cross sec9on of Gladiolus ovary Flower structure. Placentation
Flower structure. Sex of the flower
Carpellate or pis9llate flower Perfect flower Monoecious (one house or plant) Narcissus Staminate flower Imperfect flower Dioecious (two houses or plants) Pterygota alata, Buddhas coconut flowers Incomplete flowers lack one of their whorls Not all the incomplete flowers flower are imperfect Flower structure. Sex of the flower
Acorns from carpellate or pis9llate flowers Grevillea robusta (Silky Oak) Tanbark oak (Lithocarpus densiflora) flowers: Staminate flower Quercus Flower structure. Position of ovary
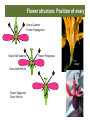
Ovary Superior Flower Hypogynous Ovary Half-‐Superior Ovary Half-‐Inferior Flower Epigynous Ovary Inferior Flower Perigynous ovary Flower structure. Fusion of the whorls
adna9on (epipetaly) conna9on (synfilamentous) Adnna9on: fusion of dissimilar organs. Conna9on: developmental fusion of organs of the same type. Flower structure. Symmetry
Life cycle
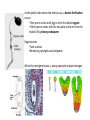
ü Pollina9on ü Fer9liza9on Small female gametophyte (7 cells) • Does not produce an archegonium • Does not provide nutri9on to the embryo Small male gametophyte (3 cells) Double fer9liza9on • One produce an embryo • One produce the endosperm The ovary wall develops into the fruit wall (pericarp) Microsporogenesis and microgametogenesis
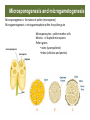
Microsporogenesis = forma9on of pollen (microspores) Microgametogenesis = microgametophyte within the pollen grain Microsporocytes = pollen mother cells Meiosis = 4 haploid microspores Pollen grains • exine (sporopollenin) microsporangium • In9ne (cellulose and pec9ns) microspores tapetum stem Megasporogenesis and megagametogenesis
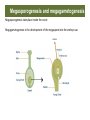
Megasporogenesis take place inside the ovule Megagametogenesis is the development of the megaspore into the embryo sac chalaza As the pollen tube enters the embryo sac, a double fer:liza:on occurs • One sperm unites with egg to form the diploid zygote • Other sperm unites with the two polar nuclei to form the triploid (3n) primary endosperm Degenera9on • Tube nucleus • Remaining synergids and an9podals When the seed germinates, a young sporophyte plant emerges 3n