* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Moons of the Planets
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Io wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
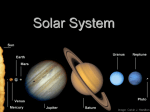
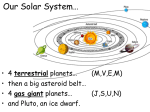
Space Physics THE MOONS OF THE PLANETS Neeke Katharina Rothe 2010/10/18 1 Kjell Rönnmark, Umeå Universitet, fysik 1 Contents 1 Planets 2 2 Natural Satellite 2 3 The 3.1 3.2 3.3 3 3 3 4 4 6 6 7 3.4 3.5 3.6 moons Earth-Moon . . Mars moons . . Jupiter . . . . . 3.3.1 Galilean Saturn moons . Uranus moons . Neptune moons . . . . . . . . . . . . Moons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4 Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7 1 1 Planets A planet is a astronomical object with an orbit around the sun and is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity and stay there in a equilibrium. It also must have cleaned his neighbor region from other objects. If they have not cleaned their orbits they are dwarf planets like Pluto. In our solar system they are eight planets Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Mercury and Venus are the only planets in our systems which have no moons. Figure 1: The planets of the solar system 2 Natural Satellite Moons are also called natural satellites. Natural satellites are natural arose astronomical objects, which are on an orbit around bodies in the space. That can be galaxies, planets, as well as other small objects like asteroids. The interest is now only on the natural satellites surrounding the planets in the solar system, the moons. The moons are classified in two main groups, regular moons and irregular moons. The surrounding direction from regular moons is in the same direction like the mother planet. From irregular moons this direction is going the other way round. Than a moon can be bound or not bound to the mother planet. A bound moon shows every time the same side to his plant, the side from a not bound moons which is shown to the planet is rotating. 2 3 The moons 3.1 Earth-Moon Properties: • diameter: d = 3476 km • mass: m = 7, 349 · 1022 kg • period of circulation: t = 27, 3217 d • Orbital velocity: v = 1, 023 km s Figure 2: Earth with the Moon The earth has only one moon, it is the best known moon. We send a lot of satellites from the earth into the space to discover the space and the objects in it. We also had send missions to the moon, but how the Earth-Moon arose is not clear. The Earth-Moon is the biggest moon in contrast to his planet. The distance between the Earth and the Moon is 384401 km. 3.2 Mars moons The Mars has two moons Phobos and Deimos. Phobos is on the inner orbit. For the moons are two main theories how they arsoe. The first one is that they were asteroids and were bound on the orbits around the mars. The second theory comes from a colliding process, where one bigger moon was destroyed by an asteroid. • Phobos Properties: – diameter: d = 26, 8x22, 4x18, 4 km – mass: m = 1, 072 · 1016 kg – period of circulation: t = 0, 3189 d 3 – Orbital velocity: v = 2, 139 km s It is the moon with the smallest distance to his mother planet. Phobos has changing orbit, when the shift continuos, Phobos will fall into the Mars in 40 Million years. • Deimos Properties: – diameter: d = 15, 0x12, 2x10, 4 km – mass: m = 1, 8 · 1015 kg – period of circulation: t = 1, 262 d – Orbital velocity: v = 1, 351 km s Deimos is one of the darkest bodies in the space. 3.3 Jupiter Jupiter has a the moment 63 moons, but the number of moons rise. The populars moons of the Jupiter are the Galilean Moons. All the moons are categorize in Groups, the regular moons are two groups (inner group and Galilean moons), the irregular moons are six groups (Themisto, Himalia group, Carpo, Ananke group, Carme group and Pasiphaë group). The smallest of the Jupiter moons is Metris. It is the moon with the highest Orbital velocity (v = 31, 55 km s ) 3.3.1 Galilean Moons The four moons are the biggest moons you can see them with a telescope. That why Galilei could discover all of them. Figure 3: The four Galilean Moons (Io, Europa, Ganymed and Calisto) • Io Properties: – diameter: d = 3643, 2 km – mass: m = 8, 49 · 1022 kg 4 – period of circulation: t = 1, 769 d – Orbital velocity: v = 17, 3 km s Io is the moon with the biggest density and is is one of the most active volcanic astronomical objects in the space. He is the inner and third greatest moon of the Galilean moons. • Europa Properties: – diameter: d = 3121, 6 km – mass: m = 4, 80 · 1022 kg – period of circulation: t = 3, 551 d – Orbital velocity: v = 13, 74 km s The ice-moon is smallest of the four moons and scientist think that under the crust might be an 90 km deep ocean. • Ganymed Properties: – diameter: d = 5262, 4 km – mass: m = 1, 482 · 1023 kg – period of circulation: t = 7, 155 d – Orbital velocity: v = 10, 88 km s Ganymed is not only the biggest and heaviest moon of the Galilean moons he is also the the the biggest and heaviest moon in our solar system. The mass is 2, 5% of the mass from the Earth. • Callisto Properties: – diameter: d = 4820, 6 km – mass: m = 1, 076 · 1023 kg – period of circulation: t = 13, 689 d – Orbital velocity: v = 8, 20 km s Third largest of our moons and second largest of the Galilean moons. 5 3.4 Saturn moons There are 62 moons around Saturn. The satellite Cassini was send some years ago up to Saturn to discover new moons and explore the others. The inner moons in the near of the Saturn rings called shepherd moons. They influence the rings by her mass. Janus and Epimethus have nearly the same orbit, because of that they change they orbits regularly. The bigger moons Saturn are Iapetus, Phoebe and Hyperion they all have a big distance to Saturn. Iapetus is the two color moon. He have a white and a dark layer. The dark one is over the white layer and came later. At the equator is a mountain chain with 12 km heigh. Hyperion is the only satellite which has a chaotic rotation and the crater on it are build by himself. And Phoebe is the only bigger regular moon with a not bound rotation. Enceladus is not so far away like the other bigger moons. It is a ice-moon with a new face, so the layer was build not so long ago, but the reason is not clear yet. The largest of the saturn moons is Titan: • Titan Properties: – diameter: d = 5150 km – mass: m = 1, 345 · 1023 kg – period of circulation: t = 15, 945 d – Orbital velocity: v = 5, 57 km s Figure 4: Atmosphere from Titan The orange star is a moon with an atmosphere. Titan have a methane atmosphere, so there can be something like methane rain on it. 3.5 Uranus moons Around the Uranus there are not so many moons like Jupiter and Saturn. Uranus have 27 moons, the five main moons are Miranda, Ariel, Umbriel, 6 Oberon and Titania.Like Saturn Uranus have rings and so there are also shepherd moons. Miranda is the smallest of the five main moons, the layer shows a big broken area. Maybe the moon was broken and fixed again together. 3.6 Neptune moons Neptune the broadest Planet of our system have 13 moons. The six inner moons are all regular ones and the other seven are irregular moons. • Triton Properties: – diameter: d ≈ 2706 km – mass: m = 2, 147 · 1022 kg – period of circulation: t = 5, 877 d – Orbital velocity: v = 4, 39 km s Triton is the biggest of the Neptune moons and the biggest irregular moon. The temperature on it is −235◦ C. So it is not far away from the absolute zero. The Nitrogen is available as fluid and solid. Only the gravitation force hold the hole moon together. 4 Summary Figure 5: Solar System In the solar system are eight planets with 168 moons. Mercury and Venus are without moons. Saturn is the planet with the most moons. Some of the moons are captured asteroids or arose after a collision with asteroids. The bigger moons are regular moons accept Triton. Only smaller moons are irregular or not bound. The biggest moon is Ganymed then comes Titan and Callisto. From two of them Jupiter is the mother planet. 7 Referenzes • http://lexikon.astronomie.info • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki • http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki • http://astronomie.klaus-moedinger.de • http://eclipse.astronomie.info • http://www.monde.de/index3.html 1. http://sse.jpl.nasa.gov/planets/index.cfm 2. http://lexikon.astronomie.info/mond/img/erde-und-mond.jpg 3. http://catholicsensibility.files.wordpress.com/2008/06/galilean-moons.jpg?w=510&h=173 4. http://lexikon.astronomie.info/saturn/titan/img/atmosphaere.jpg 8