* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download atomic number.
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
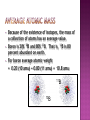
An atom consists of a • nucleus – • (of protons and neutrons) electrons in space about the nucleus. Electron cloud Nucleus • John Dalton (1766-1844) proposed an atomic theory • While this theory was not completely correct, it revolutionized how chemists looked at matter and brought about chemistry as we know it today instead of alchemy • Thus, it’s an important landmark in the history of science. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. matter is composed, indivisible particles (atoms) all atoms of a particular element are identical different elements have different atoms atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements. 1. matter is composed, indivisible particles Atoms Can Be Divided, but only in a nuclear reaction 2. all atoms of a particular element are identical Does Not Account for Isotopes (atoms of the same element but a different mass due to a different number of neutrons)! 3. different elements have different atoms YES! 4. atoms combine in certain whole-number ratios YES! Called the Law of Definite Proportions 5. In a chemical reaction, atoms are merely rearranged to form new compounds; they are not created, destroyed, or changed into atoms of any other elements. Yes, except for nuclear reactions that can change atoms of one element to a different element All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons in the nucleus, Z 26.981 Al 13 AVERAGE Atomic Mass Atom symbol Atomic number • C atom with 6 protons and 6 neutrons is the mass standard = 12 atomic mass units • Mass Number (A) • • = # protons + # neutrons NOT on the periodic table…(it is the AVERAGE atomic mass on the table) A boron atom can have: A = 5 p + 5 n = 10 amu A 10 Z 5 B • • • Atoms of the same element (same Z) but different mass number (A). Boron-10 (10B) has 5 p and 5 n Boron-11 (11B) has 5 p and 6 n 11B 10B Isotopes: Are two forms of an element (atom) with the same atomic number but different mass number (atomic weight). All atoms contain three kinds of basic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. The protons and neutrons in an atom are found in the atomic nucleus, while the electrons are found in the space around the nucleus. The number of protons in a nucleus defines an atom. Hydrogen atoms all have one proton in their nucleus; helium atoms all have two protons in their nucleus; lithium atoms all have three protons in their nucleus; and so on. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus is called its atomic number. Hydrogen has an atomic number of 1; helium, an atomic number of 2; and lithium, an atomic number of 3. But atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons. Some helium nuclei, for example, have two neutrons; others have only one. The mass number (atomic weight) of an atom is the total number of protons and neutrons in the atom's nucleus. The two-neutron atom of helium has a mass number of four (two protons plus two neutrons) The one-neutron atom of helium has a mass number of three (two protons plus one neutron). Isotopes are commonly represented in one of two ways: First: they may be designated by writing the name of the element followed by the mass number of the isotope. The two forms of helium are called helium-4 and helium-3. Second: isotopes may be designated by the chemical symbol of the element with a superscript that shows their mass number. The designations for the two isotopes of helium are 4He and 3He. Naturally occurring carbon consists of three isotopes, 12C, 13C, and 14C. State the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in each of these carbon atoms. 12C 13C 14C 6 6 6 #p+ _______ _______ _______ #no _______ _______ _______ #e- _______ _______ _______ 12C 6 13C 6 14C 6 #p+ 6 6 6 #no 6 7 8 #e- 6 6 6 An atom has 14 protons and 20 neutrons. A. Its atomic number is 1) 14 2) 16 3) 34 B. Its mass number is 1) 14 2) 16 3) 34 C. The element is 1) Si 2) Ca 3) Se D. Another isotope of this element is 1) 34X 2) 34X 3) 36X 16 14 14 • • • Because of the existence of isotopes, the mass of a collection of atoms has an average value. Boron is 20% 10B and 80% 11B. That is, 11B is 80 percent abundant on earth. For boron average atomic weight = 0.20 (10 amu) + 0.80 (11 amu) = 10.8 amu 11B 10B • Because of the existence of isotopes, the mass of a collection of atoms has an average value. • 6Li – = 7.5% abundant and 7Li = 92.5% Avg. Atomic mass of Li = ______________ • 28Si – = 92.23%, 29Si = 4.67%, 30Si = 3.10% Avg. Atomic mass of Si = ______________ A radioactive isotope is an isotope that spontaneously breaks apart (decay), changing into some other isotope. As an example, potassium has a radioactive isotope with mass number 40, 40K. This isotope breaks down into a stable isotope of potassium, 39K . Radioisotope, have an unstable nucleus that decays, emitting alpha, beta, or gamma rays until stability is reached. The stable end product is a nonradioactive isotope of another element, i.e., radium-226 decays finally to lead-206. a) In therapy: Used to kill or inhibit specific malfunctioning cells. Radioactive phosphorus is used to treat abnormal cell proliferation, e.g., polycythemia and leukemia. Radioactive iodine can be used in the diagnosis of thyroid function and in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. b) In Research: Radioactive isotopes used as tracer agents making it possible to follow the action and reaction of organic and inorganic substances within the body. c) In Industry: Used for a number of purposes, including measuring the thickness of metal or plastic sheets by the amount of radiation they can stop, testing for corrosion or wear, and monitoring various processes. Bone scans with radioactive technetium-99. The tritium content of ground water is used to discover the source of the water, for example, in municipal water or the source of the steam from a volcano.