* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrical energy flows around a path called a “circuit”
Survey
Document related concepts
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
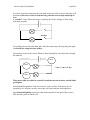
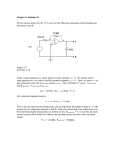
S2 Curriculum for Excellence may 2012 Electricity Summary Egyptian scientists are thought to have been the first to invent batteries or “cells” using jars containing a pair of different metal “electrodes” and soaked in acidic liquid “electrolyte”. The technique was re-discovered around 2 hundred years ago by an Italian scientist Alessandro Volta. A battery, or other “voltage” supply, provides the energy for electrically charged electrons to carry around a circuit. The bigger the voltage the more energy that is carried around the circuit and any bulbs in the circuit will get brighter, motors will run faster. . There are two types of electric circuit: “series” and “parallel”. A series circuit allows the electrical energy to flow along a single path. + Voltage supply Resistor lamp / bulb The energy is measured by a device called a “voltmeter”. The voltmeter is not part of the circuit and is connected across the components. + 10 Volts 6 V + 4 V = 10 V 6V 4V The voltage is measured in units called “Volts” or smaller units called “milliVolts”. There are 1000 milliVolts in 1.0 Volt. The voltages in the circuit must always add up to the voltage of the supply. (All the fractions must add up to the whole.) When more bulbs are added to a series circuit the current decreases and the bulbs get dimmer. The energy is carried by an electric “current” measured in units called “Amps” or smaller units called “milliAmps”. Current is measured using a device called an “Ammeter”. S2 Curriculum for Excellence may 2012 In a series circuit the current has only one path so the size of the current is the same at all positions. If the series circuit is broken at any point the current stops and drops to zero. A “parallel” circuit allows the energy (carried by the electric charges) to flow along more than one path. + switches In a parallel circuit, with more than path, when the current stops flowing along one path it can still flow along the other path(s). The ammeter is part of the circuit. Whatever flows through the wires also flows through the ammeter. 5mA 2mA 2 mA + 3 mA = 5 mA 3mA When more bulbs are added to a parallel circuit the current increases and the bulbs get brighter. Most household applainces such as microwave ovens, cookers, food mixers etc are operated by two switches in series; one at the wall socket and one at the appliance. Most household lighting circuits are connected in parallel. If one part of the circuit is OFF the other parts can still be ON.