* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5250-6-enlargement
Survey
Document related concepts
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
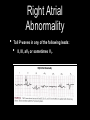
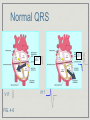
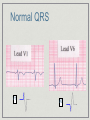
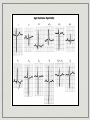
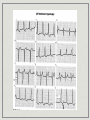
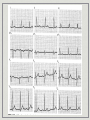
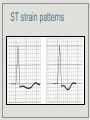
Atrial and Ventricular Enlargement Chapter 6 Cardiac Enlargement dilation stretched congestive heart failure hypertrophy increase size of heart muscle fibers aortic stenosis Cardiac Enlargement Increase amount of cardiac tissue How would this affect amount of depolarization? How could that affect an ECG? Right Atrial Abnormality Overload of the right atria dilation hypertrophy Increase voltage of the P wave Right Atrial Abnormality Normal P wave amplitude is less than 2.5 mm and 0.12 seconds in width. Abnormal P waves are typically taller than 2.5 mm but not longer the 0.12 sec. Right Atrial Abnormality Causes: Pulmonary disease Congenital heart disease Right Atrial Abnormality • Tall P waves in any of the following leads: • II, III, aVF or sometimes V1. Right Atrial Abnormality P pulmonale artial enlargement due to severe pulmonary disease Atrial enlargement can occur in the absence of tall P waves. Left Atrial Abnormality Left atria normally depolarizes after the right atria. Left atrial enlargement should prolong the P wave greater than 0.12 sec. P wave height may be normal or increased Left Atrial Abnormality CAD may produce wide P waves without left atrial enlargement. Left Atrial Abnormality • Leads I and/or II may show notched P waves • • • (second hump due to delayed depolarization of the left atrium) (P mitrale: mitral valve disease) V1 may show a bi-phasic P wave • • negative part is > 0.4 sec. or 1 mm in depth (right atria is anterior to the left atria) Left Atrial Abnormality Causes: Valvular heart disease Hypertensive heart disease Cardiomyopathies CAD Right Ventricular Hypertrophy What do you think will happen to the ECG with ventricular hypertrophy? Normal QRS V6? V6? V1? FIG. 4-6 V1? Normal QRS V1 V6 Right Ventricular Hypertrophy Consider right ventricular hypertrophy and V1 NORMAL HYPERTROPHY Right Ventricular Hypertrophy 1. In V1, R wave is greater than the S wave 2. In V1, T wave inversion (reason unknown) 3. Right axis deviation Right Ventricular Hypertrophy Causes of RVH congenital heart disease atrial septal defects others Emphysema may mask signs of RVH Left Ventricular Hypertrophy With LVH, the electrical balance is tipped even further to the left. Predominate S waves in the right chest leads Tall R waves in the left chest leads Left Ventricular Hypertrophy • If S wave in V + R wave in either V5 or V6 > 35 mm (not specific indicator). 1 • R wave > 11-13 mm in aV • ST segment changes • Left axis deviation • Left atrial abnormality L ST strain patterns Left Ventricular Hypertrophy Causes: Hypertension Aortic stenosis Risks of LVH congestive heart failure arrhythmias Left Ventricular Hypertrophy High voltage can be seen in normal people, especially athletes Hypertrophy in both ventricles the ECG will show more evidence of LVH