* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download First Hour Exam Answers
Survey
Document related concepts
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Clastic rock wikipedia , lookup
Geology of the Pacific Northwest wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Igneous rock wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Geology 141(A)
Spring, 2017
atÅx
3 March, 2017
CORRECT ANSWERS are in RED
GE141(A): Earth and Environment
First Hour
Examination
INSTRUCTIONS :
PLEASE read the instructions and questions
CAREFULLY and completely. If you do not understand a question as it
appears on the exam, PLEASE ASK FOR CLARIFICATION!! It is to
YOUR benefit to do so. This examination is worth 150 points, or 15% of
your overall semester grade. Exams will be graded as quickly as possible;
your individual point total will be entered on the last page to ensure that only
you know how well you did on the exam, unless you choose to divulge that
information to others.
“Problems will always torment us, because all important problems
are insoluble: that is why they are important. The good comes from
the continuing struggle to try to solve them, not from the vain hope
of their solution.”
- Arthur M. Schlesinger, Jr., historian (1917-2007)
Geology 141(A): Spring, 2017
First Hour Examination
... Page 2 ...
Section I: Multiple-choice. Please read each question and possible answer
carefully, and circle the letter of the correct or best response to each question. Do NOT
under any circumstances circle the entire response or write the answer in the margin! Doing so
suggests to me that you are attempting to assist someone else on the exam, which is
definitely a bad idea! !Any question answered in that manner will automatically be
marked incorrect!
Each question here is worth 4 points; the section as a whole is worth 100 points of the
150 for the exam.
1. Which of the following is not one of the "Big Ideas" of Geology?
a. The Earth is a "water planet."
b. Humans depend on the Earth for resources.
c. Earth is a complex system of rock, water, air and life.
d. Earth is continuously changing.
e. Human activities change the Earth.
f. trick question – all are "Big Ideas" in Geology.
2. The study of meteorites is important in geology because
a. they represent solid fragments of material formed early in the history of our Solar
System.
b. they are fragments of earlier solar systems, much older than the Earth, that have
traveled through countless light-years of space to land on Earth.
c. they help give us insight into the inner composition of the Earth itself.
d. all of the above
e. only (a) and (c) above.
f. none of the above
3. The Earth, and our Solar System, are believed by scientists to be about how old?
a. 13.5-14.0 billion years
c. 4.6-4.7 billion years
b. 13.5-14.0 million years
d. 4.6-4.7 million years
4. The "trans-ferric elements" – i.e., those above iron in the Periodic Table of the Elements –
are evidence of our solar system being a "second-generation" star system because
a. these have to have been brought to Earth from outside our own galaxy, because none
of them are found naturally in the Milky Way.
b. these elements can only form in a supernova – the explosion of a large star
nearing the end of its lifetime.
c. these elements are not found on Earth naturally, but only in meteorites.
d. these elements were only formed in the Big Bang, and had been part of a giant nebula
before our star system started to condense.
5. The most abundant two elements in the Earth's crust, by weight, are
a. iron and aluminum
c. oxygen and silicon
b. iron and magnesium
d. iron and oxygen
6. Approximately 95% of the Earth's crust is composed of minerals in what group?
a. native elements
d. silicates
b. oxides and hydroxides
e. sulfates
c. sulfides
f. carbonates
7. The only mineral group other than that in #6, that is important more for its bulk in the
crust (~3%) than for its economic value, is the
a. native elements
d. silicates
b. oxides and hydroxides
e. sulfates
c. sulfides
f. carbonates
Geology 141(A): Spring, 2017
First Hour Examination
... Page 3 ...
8. Oxide, hydroxide, and sulfide minerals are most important
a. for their abundance in the mantle.
b. as ores of industrially essential metals, like iron, aluminum, copper and zinc.
c. because of their incredible age, since they all formed during the Big Bang.
d. as demonstrating that the Earth is a second-generation star system.
9. Island-arc systems are created by
a. spreading along the mid-oceanic rise and ridge system (MORRS).
b. lines of mantle plumes or "hot spots."
c. subduction of oceanic lithosphere beneath younger, less dense oceanic lithosphere.
d. faults on the sea floor that extend down into the mantle, providing open gaps where
magma rises to the surface.
10. Almost all new oceanic crust is being created by
a. spreading along the mid-oceanic rise and ridge system (MORRS).
b. lines of mantle plumes or "hot spots."
c. subduction of oceanic lithosphere beneath younger, less dense oceanic lithosphere.
d. faults on the sea floor that extend down into the mantle, providing open gaps where
magma rises to the surface.
11. Typical island-arc systems in the world include all of the following except
a. the Sumatra-Java arc
d. the Kuril Islands
b. the Hawaiian Islands
e. the Aleutian Islands
c. the Antilles (eastern Caribbean)
12. The mountain range that is currently being uplifted by oceanic plate subduction is the
a. Appalachian Mountains
c. Himalaya
b. Andes Mountains
d. Rocky Mountains
13. The mountain range that is currently being uplifted by continental-continental collision is
the
a. Appalachian Mountains
c. Himalaya
b. Andes Mountains
d. Rocky Mountains
14. Islands that are situated above modern active mantle plumes ("hot spots") include all of
the following except
a. Iceland
c. the Hawaiian Islands
b. Puerto Rico & Cuba
d. the Galápagos Islands
15. The capital city of Montserrat, Plymouth, was destroyed by all of the following except
a. pyroclastic flows
c. thick deposits of volcanic ash
b. rapid basaltic lava flows
d. lahars – volcanic mudflows
16. When did the Soufriere Hills volcano erupt on Montserrat to destroy the capital city?
a. 1912-15
b. 1947-49
c. 1979-82
d. 1995-98
e. 2015-16
17. The lavas from a volcano that will have the lowest viscosity will be those with
a. high silica, high gas, and high temperature.
b. low silica, low gas, and low temperature.
c. high silica, high gas, and low temperature.
d. low silica, high gas, and high temperature.
e. low silica, low gas, and high temperature.
18. Flood basalts, such as those of eastern Washington and Oregon, India, and Siberia, were
produced by volcanic eruptions of lavas with
a. high silica, high gas, and high temperature.
b. low silica, low gas, and low temperature.
c. high silica, high gas, and low temperature.
d. low silica, high gas, and high temperature.
e. low silica, low gas, and high temperature.
Geology 141(A): Spring, 2017
First Hour Examination
... Page 4 ...
19. The minerals at the top of Bowen's Reaction Series are those
a. with low silica contents and high melting temperatures.
b. that are usually dark-colored in igneous rocks.
c. that have relatively simple structures but are subject to easy chemical weathering.
d. are the minerals that make up mafic igneous rocks like basalt and gabbro.
e. all of the above.
f. none of the above.
20. Most plutonic rock bodies on the continent are felsic (high silica) in character, but many
dikes and sills are mafic (low silica) in composition. This is because
a. the mafic magmas have much lower viscosity and so are able to intrude
other rocks to form these narrow tabular bodies.
b. mafic magmas are much more common in continental regions than felsic magmas are.
c. mafic magmas originate from multiple sources to infill pre-existing voids in the rocks.
d. the mafic magmas are formed in place from melting of the country rocks.
21. Geologic dikes are
a. naturally occurring ridges found on the coast of the Netherlands (Holland).
b. intrusive igneous rock bodies that cut across pre-existing rocks and structures.
c. volcanic features created by lava flows that enter bodies of standing water like a lake or
the ocean.
d. naturally occurring ridges found along the lengths of many rivers, which is why the
rivers flow in the courses they do.
22. You have been studying the geology of a large peninsula in eastern Greenland that has
recently become ice-free as the margin of the ice sheet has melted. In the course of this
study, you've found a large area of granite that you can show is found over an area of at
least 136 square kilometers (136 km2). Since you've been working out of the same field
camp for three years, which you've named "Camp Colby" for your favorite alma mater,
and knowing that tradition is to name new units for a local geographic feature, you use
this as justification for naming this new rock body the
a. Colby Batholith
c. Colby Stock
b. Colby Xenolith
d. Colby Lithostat
23. Porphyritic textures in igneous rocks is caused by
a. rapid cooling of high-silica magmas.
b. slow cooling of high-silica magmas.
c. rapid cooling of low-silica magmas.
d. slow cooling of low-silica magmas.
e. two-stage cooling of any magmas.
24. Igneous dikes and sills, and volcanic necks, often stand out as high ground on the
landscape because
a. the rocks of which they're composed are tougher and more resistant to
weathering and erosion than the surrounding rocks.
b. the rocks of which they're composed are composed of non-silicate minerals.
c. as they were intruded into the country rock, the country rock was all shattered into
small pieces, making it easy for it to be eroded away.
d. of reasons that geologists don't understand, which is why lots of research is being done
on this subject.
25. Bowen figured out the "reaction series" that bears his name by studying
a. the dike and sill at the Gettysburg Civil War battlefield in Pennsylvania.
b. the Palisades Sill of New York.
c. the Sierra Nevada Batholith of California.
d. the Katahdin Granite of Maine.
Geology 141(A): Spring, 2017
First Hour Examination
... Page 5 ...
Section II: Please respond to each question in the most appropriate fashion. Please make
your responses concise and to the point, but thorough; use sketch diagrams any place
you believe that they may help explain your response. There should be ample space
provided for an adequate response to each question; PLEASE RESTRICT YOUR
RESPONSES TO THE SPACE PROVIDED; materials outside the space allotted will not
be read. PLEASE ALSO try to write legibly; I CANNOT give any credit for responses I
can't read! The number of points for each question is indicated in parentheses after the
question; there are 40 points possible for this entire section.
☛ (And PLEASE remember as well that, as promised on the syllabus,
I WILL deduct a point
each time I see "volcanoe" or "techtonic" in any response!)"
26. Please identify three of the independent lines of evidence, other than the apparent fit
of continental margins, that support the combined theories of continental drift and
plate tectonics, and indicate how each line of evidence supports these concepts. Avoid
circular reasoning (i.e., don't use plate tectonics as evidence for plate
tectonics!). (10 points: 4-3-3)
(1) Identical plant and terrestrial animal fossils on different continents, despite
the fact that modern plants and animals are totally different. This does not make
logical sense unless the continents at one time were connected, so plants and
animals could migrate (or spread) from one part to another.
(2) Matching geology - the same rock types in the same arrangement - across the
areas where it looks like the continents “fit together.” This would be incredibly
unlikely unless the continents were actually at one time connected across that
area - because you’re otherwise requiring identical geologic history in different
places.
(3) Matching structural geology - mountain ranges, folds and faults - across the
areas where it looks like the continents fit together. Again, all but impossible
unless they had a shared geologic history.
(4) Ancient glacier flow lines indicate that ice sheets came out of the ocean to
push up onto land, which is totally nonsensical (since glacial ice flows downhill!)
unless you reconnect the continents the way they look like they fit together.
Then, you have a single, coherent pattern of a large ice sheet flowing outwards
from a central core.
(5) Curves showing the apparent wandering of the north magnetic pole are
different when developed from rocks on different continents, but become the
same when the continents are allowed to move over time.
(6) Direct GPS measurements now allow us to measure both the speed and
direction of plate velocities around the world.
Geology 141(A): Spring, 2017
First Hour Examination
... Page 6 ...
27. The cartoon below is a sketch of a cross-section of the Earth. Please label (name) each of
the constituent layers, and in the spaces below, indicate the composition of each. (10
points: 2-2-1-1-1-1-1-1)
Layer (a) is composed mostly of
silicate minerals / rocks
Layer (b) is composed of
iron & magnesium silicates and oxides
Layer (c) is composed of
molten iron
Layer (d) is composed of
solid iron
28. To be considered a mineral, a substance must meet four criteria. These are (5 pts.: 2-11-1):
a.
naturally occurring
b.
inorganic solid
c.
crystalline structure
d.
constant chemistry (or one that varies within set limits)
29. Rocks are classified into three major groups in what is called a genetic classification.
These three major groups are (3 points):
a.
Igneous
b.
Sedimentary
c.
Metamorphic
Geology 141(A): Spring, 2017
First Hour Examination
... Page 7 ...
30. What is MEANT by a "genetic classification" of rocks? (2 points)
That they are classified according to the way in which they come
into existence (their origins)
31. WHY are shield volcanoes, such as those in Hawaii, characterized by such gentle slopes,
compared to the stratovolcanoes of the Andes, Cascades, or most other parts of the world?
(5 points)
Because the lavas that build shield volcanoes are very low in
viscosity, so they flow easily across the landscape and don’t pile up. The
volcanoes of the Andes and Cascades are the products of much more viscous
magmas - both higher in silica and lower in temperature.
32. The two principle gasses in magmas are (5 points: 3-2):
a.
steam (H2O)
b.
carbon dioxide (CO2)
and
Geology 141(A): Spring, 2017
First Hour Examination
... Page 8 ...
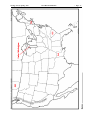
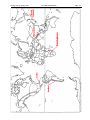
Section III: Geography. On the maps on the following page (the maps are printed backto-back), please locate precisely each of the following localities or features. FOR
SMALL FEATURES OR LOCALITIES, please use a sharp arrow drawn from your
label to the feature, so there can be no doubt about what you are labeling. PLEASE
remember that IT IS TO YOUR BENEFIT that your label is clear enough that there is
NO question as to your meaning or intent! (10 points, 1 point each)
And YES, ☛ all labels must be correctly spelled for credit!
[ Since all you have to do is copy the name from the list below! ]
On the map of the U.S. & Canada:
Massachusetts (MA)
South Carolina (SC)
Louisiana (LA)
Lake Michigan
Alberta (AB)
On the map of the world:
Zimbabwe
Andes Mountains
Himalaya
Kuril Islands
Cuba
Grade on exam: __________________ out of 150 possible*.
* If this is below 105, please see me within the next week !!!
PLEASE NOTE: After exams are graded, I will return your exam ONLY to you. It will
not be released to friends, roommates, your lab partner, or anyone else. This is to
ensure YOUR security and confidentiality.
Geology 141(A): Spring, 2017
First Hour Examination
... Page 9 ...
Geology 141(A): Spring, 2017
First Hour Examination
... Page 10 ...