* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 0-10V, PWM, TRIAC Dimmable LED panel
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
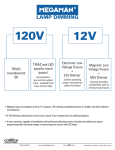
0-10V, PWM, TRIAC Dimmable LED panel 0-10V Dimming 0-10 V is one of the earliest and simplest electronic lighting control signaling systems; simply put, the control signal is a DC voltage that varies between zero and ten volts. The controlled lighting should scale its output so that at 10 V, the controlled light should be at 100% of its potential output, at 1v it should be at minimum output, and at 0 V it should at 0% output (i.e. “Off”). Dimming devices may be designed to respond in various patterns to the intermediate voltages, giving outputcurves that are linear for: voltage output, actual light output, power output, or perceived light output. Advantages and disadvantages The simplicity of the lighting system makes it straightforward to understand, implement and diagnose, and its low current (typically 1 mA) means it can be run along relatively thin cables with little voltage drop. However, since it requires one wire per control channel (plus a common return wire), a sophisticated system could have hundreds of wires, requiring expensive multicore cables and connectors. Over a long cable, the voltage drop requires every channel of the receiving device to be calibrated to compensate for the voltage losses. (This is only a theoretical limitation as the resistance of the thinnest practical wire is around 20 Ω/1000 m.) Interference from nearby ac power cables can affect the signal to the fitting and even cause flickering. Signal wire running parallel to power cables for a fair distance would need to be screened. PWM Dimmable 1/4 0-10V, PWM, TRIAC Dimmable LED panel Pulse-width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a commonly used technique for controlling power to inertial electrical devices, made practical by modern electronic power switches. The main advantage of PWM is that power loss in the switching devices is very low. When a switch is off there is practically no current, and when it is on, there is almost no voltage drop across the switch. Power loss, being the product of voltage and current, is thus in both cases close to zero. PWM also works well with digital controls, which, because of their on/off nature, can easily set the needed duty cycle. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by turning the switch between supply and load on and off at a fast pace. The longer the switch is on compared to the off periods, the higher the power supplied to the load is. The PWM switching frequency has to be much faster than what would affect the load, which is to say the device that uses the power. Typically switchings have to be done several times a minute in an electric stove, 120 Hz in a lamp dimmer, from few kilohertz (kHz) to tens of kHz for a motor drive and well into the tens or hundreds of kHz in audio amplifiers and computer power supplies. The term duty cycle describes the proportion of ‘on’ time to the regular interval or ‘period’ of time; a low duty cycle corresponds to low power, because the power is off for most of the time. Duty cycle is expressed in percent, 100% being fully on. TRIAC Dimming TRIAC, from Triode for Alternating Current, is a genericized tradename for an electronic component that can conduct current in either direction when it is triggered (turned on), and is formally called a bidirectional triode thyristor or bilateral triode thyristor. TRIACs belong to the thyristor family and are closely related to Silicon-controlled rectifiers 2/4 0-10V, PWM, TRIAC Dimmable LED panel (SCR). However, unlike SCRs, which are unidirectional devices (i.e. can conduct current only in one direction), TRIACs are bidirectional and so current can flow through them in either direction. Another difference from SCRs is that TRIACs can be triggered by either a positive or a negative current applied to its gate electrode, whereas SCRs can be triggered only by currents going into the gate. In order to create a triggering current, a positive or negative voltage has to be applied to the gate with respect to the A1 terminal (otherwise known as MT1). Once triggered, the device continues to conduct until the current drops below a certain threshold, called the holding current. The bidirectionality makes TRIAC very convenient switches for AC circuits, also allowing them to control very large power flows with milliampere-scale gate currents. In addition, applying a trigger pulse at a controlled phase angle in an AC cycle allows one to control the percentage of current that flows through the TRIAC to the load (phase control), which is commonly used, for example, in controlling the speed of low-power induction motors, in dimming lamps and in controlling AC heating resistors. 3/4 0-10V, PWM, TRIAC Dimmable LED panel Remark: We focus on LED Lighting, and our products include LED Bulb Light, T8 LED Tube Light,T5 LED Tube Light, LED Panel Light, LED Track Light, LED Down light, LED Ceiling Light, LED Spot Light, LED Flood Light, LED Emergency Lighting, LED Dimmer, etc. [email protected] , Or add Skype Jackchen198 or Call us, Let's talk details. 4/4