* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 35 – Review Questions
Crystal radio wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
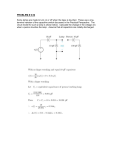
Ch. 35 – Review Questions 1. Are all the electrons flowing in a circuit provided by the battery? No, both the battery and the wires in the circuit provide the electrons. 2. Why must there be no gaps in an electric circuit for it to carry current? Gaps prevent the flow of electrons. 3. Distinguish between a series circuit and parallel circuit. A series circuit provides a single pathway for current. A parallel circuit provides multiple pathways for current. 4. If three lamps are connected in series to a 6-volt battery, how many volts are impressed across each lamp? Each lamp would have a voltage drop of 2 volts, each sharing a third of the battery’s voltage. 5. If one of three lamps blows out when connected in series, what happens to the current in the other two? The other bulbs would not light because the circuit is no longer complete. 6. If three lamps are connected in parallel to a 6-volt battery, how many volts are impressed across each lamp? Each lamp would have a voltage drop of 6 volts. 7. If one of three lamps blows out when connected in parallel, what happens to the current in the other two? The current would continue in the other two lamps. 8. a. In which case will there be more current in each of the three lamps – if they are connected to the same battery in series or in parallel? There will be more current in the lamps if they are connected in parallel. b. In which case will there be more voltage across each lamp? There will be more voltage across each lamp in parallel. 9. What happens to the total circuit resistance when more devices are added to a series circuit? To a parallel circuit? Circuit resistance increases when more devices are added in series. Circuit resistance decreases when more devices are added in parallel. 10. What is the equivalent resistance of a pair of 8-ohm resistors in series? In parallel? In series, the equivalent resistance is 16 ohms. In parallel, the equivalent resistance is 4 ohms. 11. Why does the total circuit resistance decrease when more devices are added to a parallel circuit? There are more pathways for current to flow. 12. What does it mean when you say that lines in a home are overloaded? Lines are overloaded when there is too much current flowing in them. 13. What is the function of a fuse or circuit breaker in a circuit? A fuse or circuit breaker will shut down the circuit if it becomes overloaded. 14. Why will too many electric devices operating at one time often blow a fuse or trip a circuit breaker? Home circuits are wired in parallel. As more devices are turned on, the current increases. 15. What is meant by a short circuit? A short circuit is when wires are crossed in a way that bypasses normal circuit resistance. The very low resistance leads to very high current.