* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 53. The Beginnings of Islam
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
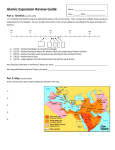
World History Detective* Book 1 Medieval Civilizations 53. The Beginnings of Islam A 'Muhammad was born in Makkah (formerly Mecca in English) in 570. 2He married a wealthy merchant and prospered in business. 3ln 610, he retreated to meditate in a cave, and there, according to Islamic beliefs, he received his first revelation (communication) from the angel Gabriel. 4 Gabriel told him he was the messenger of God. B 5Three years later, the prophet (Muhammad) began sharing the revelations he received. 6He believed his mission was to restore the worship of one God, whose name was Allah in Arabic. 7He called on people to turn from their sins and live good lives. 8The new religion was called Islam, which means submission to God. 9lts followers are called Muslims, meaning one who submits to God. C 10At the time of Muhammad's revelations, Jews and Christians also lived in Arabia. 11According to Muhammad, Allah was the same God who spoke to Abraham and Jesus, and he (Muhammad) was God's last great prophet, so Islam was the true religion. D 12!n Makkah, Muhammad preached about believing in Allah, prayer, seeking forgiveness, and taking care of the needy. "He was persecuted and mocked and his followers were attacked. 14 Because of this persecution Muhammad left Makkah for Medina in 622. 15ln Arabic, this journey is called the Hijra and is designated the first year of the Islamic calendar. 16 ln Medina, Muhammad built an army of his ew believers and led raids against Makkah's caravans. 17He eventually conquered and converted Makkah to Islam. 18When Muhammad or an Islamic leader conquered a territory, he instituted laws that reflected Islamic beliefs. 19One of the laws dealt with marriage. 20The Koran allows for men to have up to four wives. 21Muhammad had eleven wives himself. F 22The Koran is the Muslim holy book just as the Bible is the holy book for Christians. 23Muhammad believed he received revelations from 610-632, the year of his death. 24The Koran is the central religious text of Islam, which Muslims consider the word of God. 25Muslims believe that God spoke the words in the Koran to the angel Gabriel, and then Gabriel told them word for word to Muhammad who wrote them directly into the Koran. 26The other source for Islamic thought and authority is the Sunnah. 27The Sunnah contains the words and actions of Muhammad himself, and it is used as a guide on how to live as a true Muslim and how to correctly interpret the Koran. ^^**^ww***^r'*^'!3^l***1™*'^lBBBMBBB(>|MMMBnss* paradise. 39Once conquered, most Arabs had to convert. 40Muslims allowed Jews and Christians to practice their faith privately if they paid ay'/'zya (special tax). 28 G To be a good Muslim, you are to follow the five pillars. Muslims must: 1. 29Profess there is no God but Allah, and Muhammad is his prophet. 2. 30Pray five times a day. 3. 31Give to the community. 4. 32Fast during the holy month of Ramadan (the ninth month of the Muslim calendar). 33 Make a pilgrimage to Mecca. "FT"" 34A little more than 100 years after Muhammad's death, Islam had spread from the Arabian Peninsula to parts of Africa and Europe. 35 How did Islam spread so quickly? 36lslam's belief in one God attracted many followers. "Muslim warriors believed that spreading Islam was part of a holy war. 3BWarriors who died were promised 220 I 41Muslims believe that heaven is a reward for those who do good and that hell is a place of punishment for evildoers. 42Muslim places of worship are called mosques. 43lslam has no hierarchy, like the Catholic Church, but men who lead the faithful in prayer in mosques are called imams. © 2012 The Critical Thinking Co.™ • www.CriticalThinking.com • 800-458-4849