* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Islamic World and Africa
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Salafi jihadism wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in South Africa wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
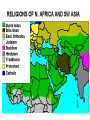
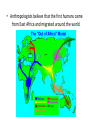
The Islamic World and Africa العالم اإلسالمي وأفريقيا The Rise of Islam • During the 5th century the Byzantine and Persian empires were warring. • The Spice Trade route had originally been an overland route called the Silk Road. Outlined in red • Because of the warfare it was forced to change to a water route that passed by the Arabian peninsula. Outlined in blue The Rise of Islam • Cities that were located along this new trade route became more important. • Two of these cities were Mecca and Medina on the Arabian Peninsula. • It was in this city of Mecca that Mohammad was born in 570 A.D.. Mohammed, the Prophet of Islam • Islam was founded by Mohammed. • A vision convinced Mohammed to convert Arabs from a polytheistic religion (belief in many gods) to a monotheistic religion (belief in a single God) called Allah. • This Allah was the same God worshipped by Jews and Christians. • A follower Islam is called a Muslim. The Hegira • Mohammed became so successful at converting Arabs to Islam that some people became jealous of his growing influence in the city of Mecca. • In 622 A.D., Mohammed’s life was threatened and he was forced to flee to Medina. • This journey was called the Hegira and it marks the starting point of the Muslim calendar. Check the dates Jihad • Mohammed continued to be a popular religious leader in Medina. • Mohammed gathered an army to retake the city of Mecca in a jihad or ‘holy war’. • Two years after a successful jihad, Mohammed became ill and died. • By the time of his death most of the Arabian peninsula had united and converted to Islam. The Quran (Koran) • The Quran is the sacred text of Islam. • It contains the words God gave to Mohammed. • It discusses proper worship, treatment of women, etc. • It contains the fundamental doctrine of Islam – – ‘There is no God but Allah and Mohammed is his prophet” Five Pillars of Faith • Muslims differ from Christians since Muslims worship God directly without a priest. • The pillars establish how a good Muslim should live: – Pray 5 times daily facing east towards Mecca – Fast during Ramadan (holy month) – Make pilgrimage to Mecca Mecca – Charity towards the poor – Faith “There is no God but Allah and Mohammed is his prophet” The Spread of Islam • Islam united different Arab tribes with a common: – language (Arabic) – religion (Islam). • Using the jihad to conquer non-believers they gained new lands. • Only the loss at the Battle of Tours stopped Muslim expansion and the spread of Islam into Europe. Purple is Islamic controlled lands Christians Muslims The Spread of Islam Islam is the dominate religion throughout the : Middle East, Northern Africa, Southeast Asia. As Islam spread so did the ideas, art, literature, science, and math of the Islamic culture. The Caliphates • A caliph was a successor to Mohammed. • After Mohammed’s death the Muslim world split in to two caliphates (or branches): – Shiite, small group who believed the caliph should be a descendent of Mohammed. – Sunni, larger group that didn’t care • These caliphates used the jihad to conquer other nations. • This helped to spread the influence of Islam into other societies. Golden Age of Muslim Culture • Arab Muslims absorbed the cultural achievements of the Greeks, Persians, Jews, and Byzantines. • The empire was located at the crossroads of Europe, Africa, and Asia and they controlled a vast trading area. • The Arabic language became the common language of literature, philosophy and art. • Christians and Jews were treated fairly and given many freedoms because they worshipped the same God as the Muslims. Muslim Cultural Achievements Art • Mohammed forbade making images of God or people. • Islamic art is largely made up of geometric designs, Arabic lettering, flowers, and stars. Muslim Cultural Achievements Architecture • Muslim rulers built beautiful palaces and mosques (churches) . • They were decorated with mosaics, calligraphy and geometrical designs. El Alhambra in Spain The Taj Mahal in India Sankore in Timbuktu Muslim Cultural Achievements • • • • Mathematics Arabs borrowed concept of zero from India. Algebra is an Arabic word for equation. Arabic mathematicians made great advancements in Algebra and Geometry. Developed Arabic numerals, that were adopted by other cultures, including ours. Muslim Cultural Achievements Medicine • Arab doctors discovered blood moves to and from the heart. • Diagnosed many diseases including smallpox and measles. Invasions • The prosperous Islamic Empire attracted invaders from Central Asia in the 11th century. • The Seljuk Turks conquered the empire, but the Seljuk Turks are the ones who converted to the new religion of Islam. Muslims and the Crusades • In the 12th century, Muslims became engaged in a war with Christians over control of the Holy Lands. • For hundreds of years the Christians and Muslims would kill each other over control of the Holy Lands. Muslims and the Crusades • Control of the Holy Lands see-sawed back and forth. • Christians captured the holy city of Jerusalem, but the Muslim warrior Saladin became an Islamic hero by recapturing it. The Kingdoms of Africa • Anthropologists believe that the first humans came from East Africa and migrated around the world. Early East African Kingdoms • Because of their location, the early kingdoms of Kush and Axum were influenced by the Egyptians. • They traded in iron, ivory, valuable wood, and slaves. • Ethiopia developed its own form of Christianity. Gold and Salt Trade • The Sahara Desert of northern Africa has rich salt deposits. • The salt was valuable for flavoring and preserving foods as well as being vital to human survival. • Other areas in West Africa had gold deposits. • A trade of salt for gold would soon develop. Rise of West African Kingdoms • The salt for gold trade led to the development of powerful kingdoms in West Africa. • Kingdoms like : – Ghana – Mali – Songhai Kingdom of Ghana (750 – 1200) • Ghana used superior weapons made of iron to conquer their neighbors. • Caravans brought salt to Ghana and returned with gold. • The kings of Ghana made a fortune in taxing the trade that passed through their kingdoms. • Muslim invaders brought Islam to West Africa Kingdom of Mali (1240 – 1400) • In 1249 the Mali conquered Ghana. • Mali gained control of the valuable salt and gold trade. • The Mali adopted the Ghana religion of Islam. Mansa Musa • Mansa Musa practiced Islam and he made a religious pilgrimage to Mecca in 1324. • He brought back Muslim scholars and architects with him to Mali. • Mansa Musa’s great city of Timbuktu became a center for trade and Islamic learning and culture. Ibn Battuta • Ibn Battuta was an Arab traveler during the 1300s. • He was impressed by the wealth, respect for law, and power of Mansa Musa. • Ibn Battuta’s descriptions of life in Africa and the Middle East gives us a view of what it was like. Green show travels of Ibn Battuta Kingdom of Songhai (1464 – 1600) • In 1464, Sultan Sunni Ali captured the great Mali city of Timbuktu. • The Kingdom of Songhai became the largest of West Africa’s trading kingdoms. • Songhai collapsed when the army of Morocco used gunpowder to defeat them. Other African Kingdoms • Ife and Benin – developed in the rainforests of West Africa. They created great art and they captured slaves and sold them along the coast of the Atlantic Ocean. • Zimbabwe – Gold made this a great trading nation, the area is still rich in gold today. Family Roles in Africa • In traditional African societies the boys and girls are separated from the community and must undergo special ceremonies at puberty. • Marriages were arranged by the family with the groom paying a dowry to the brides family. • Under Islamic religion women were only allowed to run the household while men represented the family outside it. TEKS • Category 1 – 1C – 4 D, E, I, J • Category 3 – 23 A, B – 24 A – 25 D • Category 5 – 27 A