* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math Glossary - Waioneke School
Survey
Document related concepts
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Elementary arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Math Glossary of Terms
•
Term
The list below explains the meaning of some of the key terms used in
the math:
Meaning
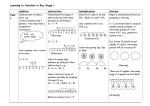
Additive is a term used to describe a range of strategies for solving
Additive
problems which involve using addition and subtraction to split up and
rejoin numbers.
Advanced Counting is a stage of the Number Framework. It describes
children who are able to solve problems by 'counting on' from a number
Advanced
other than 1. For example, to solve 5 + 3 they would start at 5, and count
Counting
on 6, 7, 8 to find the answer. These children are also likely to be able to
skip count (2, 4, 6, 8...) to solve multiplication problems such as 2 x 4.
A series of steps that can be followed mechanically to find a solution. For
Algorithm
example, there are standard algorithms that are used for addition,
subtraction, multiplication and division.
The sums (additions) and products (multiplications) of all pairs of whole
Basic facts
numbers from 0 to 9.
Common factor A whole number that divides exactly into two or more other numbers
Counting from A strategy for adding or subtracting groups of objects by counting each
one
object, one at a time.
Counting on is a strategy used to solve addition problems. It involves
Counting on
counting from a number other than 1. For example, to solve 5 + 3 they
would start at 5, and count on 6, 7, 8 to find the answer.
The denominator is the bottom number in a fraction. For example in the
Denominator
fraction 3/4 the denominator is 4. The top number is called the numerator.
Equivalent
Fractions that represent the same value, such as 1/4 and 2/8.
fractions
Knowledge describes information that a child should be able to recall
without needing to work it out. The addition and multiplication basic facts
Knowledge
are examples of knowledge that children should learn. Knowing which
numbers are smaller or larger than others is also an example of knowledge.
Mental strategy An in-the-head process that the learner chooses to use to solve a problem.
Multiplicative is a term used to describe a range of strategies for solving
Multiplicative problems which involve using multiplication and division to split up and
rejoin numbers.
Number facts are items of knowledge that children should be able to recall
Number Facts
instantly, such as the addition and subtraction basic facts.
The Number Framework is a model describing the various knowledge and
Number
strategies that children learn in the development of numeracy. Click for
Framework
more information about the Number Framework?.
A number line is a way of recording information. It is a line which
represents the all the numbers between one number and another.
Number line
Sometimes it may be labelled with the numbers, and sometimes those that
are not involved in the recording are not shown.
Number sequence refers to the order of numbers from smallest to largest.
Number
The activities grouped under number sequence in this part of the site also
Sequence
include activities related to identifying numbers - reading and writing
them.
Numeracy refers to an ability to handle numbers and other mathematical
Numeracy
concepts. The Numeracy Project aims to help children become beter at
understanding and solving problems involving numbers.
The numerator is the top number in a fraction. For example in the fraction
Numerator
3/4 the numerator is 3. The bottom number is called the denominator.
Partitioning means 'breaking up'. Partitioning strategies for maths involve
using either subtraction or division to break numbers up into smaller
Partitioning
numbers to help solve problems. For example, to solve 18 + 5, a child
might split the 5 into 2 and 3, because they know 18 + 2 = 20. They can
then add the 3 on to find the answer, 23.
Place value describes the value of the place of a digit in a number. For
Place Value
example, the 4 in 47 is in the tens place, giving it a total value of 4 x 10, or
40.
A problem in maths refers to a question to be answered. This could be as
Problem
simple as 3 + 2, or a complicated word problem, which requires several
steps to solve.
Proportional is a term used to describe a range of strategies for solving
Proportional
problems which involve using a range of operations to solve problems,
often involving fractions, percentages, decimals, or ratios.
A judgment about an answer based on the learner asking: “Keeping in
Reasonableness
mind everything I know about the problem, does the answer make sense?”
Adding the same number multiple times in order to find the answer to a
Repeated
multiplication problem, for example, finding the answer to 3 x 4 by saying
addition
4 + 4 + 4 = 12
A ratio describes the relationship between quantities. The ratio of 2:3
means the whole is made up of 2 parts of one thing and 3 parts of another.
Ratio
For example, if there were four apples and three bananas in the fruit bowl
the fruit could be described as apples and bananas in the ratio 4:3.
Skip counting is counting in amounts other than ones. The most common
Skip counting amounts to skip count in are 2 (2, 4, 6…), 5 (5, 10, 15…), or 10 (10, 20,
30…). Skip counting is often an efficient strategy to solve problems.
A strategy is a way of working out the answer to a problem, or part of a
Strategy
problem. There are many different strategies that can be learned, and often
more than one is suitable for solving a given problem.
The numbers from 13 to 19 are often referred to as teen numbers. Some
Teen numbers
children confuse them with the ty numbers (20, 30, 40…).
The multiples of ten up to 90 (20, 30, 40…) are often called the ty
Ty numbers
numbers. Some children confuse them with the teen numbers (13, 14,
15...).
Unit fraction
Any fraction that has a numerator of 1, for example, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8.
All numbers in the set {0, 1, 2, 3 ...}. This set excludes all negative and all
Whole numbers
fractional numbers.
Perimeter The boundary of a shape.
Also, the distance measured around a shape.
• A man walks around the perimeter of a lake.
• The perimeter of a 4 cm by 5 cm rectangle is 18 cm.
Whole number A number from the set {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, ...}.
• 12 is a whole number.
3.8 is not a whole number.
Counting number A number from the set {1, 2, 3, 4, ...}.
• 12 is a counting number.
• 0, –1 and 4.1 are not counting numbers.
Sum The result of adding two or more numbers together.
• The sum of 3, 4 and 5 is 12.
• The sum of the first 10 counting numbers is 55.
Product The result of multiplying two or more numbers together.
• The product of 3, 4 and 5 is 60.
• The product of 2 with any whole number is always even.
Multiple A multiple of a number is the product of that number with
a whole number.
• 12 is a multiple of 3 (since 12 = 3 × 4).
• 100 is a multiple of 20 (since 100 = 20 × 5).
• 24 is not a multiple of 9.
Divisible A whole number is divisible by another number if the first
is a multiple of the second.
• 12 is divisible by 3.
• 100 is divisible by 20.
• 24 is not divisible by 9.
Factor If a whole number is divisible by another whole number, the
second is a factor of the first.
• 3 is a factor of 12.
• 20 is a factor of 100.
• 9 is not a factor of 24.
• The number 28 has 6 factors (namely 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, 28).
Prime number A whole number greater than 1 whose only factors
are 1 and the number itself.
• The first ten prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23,
29
•