* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapt. 13 - Northern Renaissance
Survey
Document related concepts
Waddesdon Bequest wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance philosophy wikipedia , lookup
Northern Mannerism wikipedia , lookup
Dutch Renaissance and Golden Age literature wikipedia , lookup
French Renaissance literature wikipedia , lookup
Early Netherlandish painting wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance in Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance Revival architecture wikipedia , lookup
Renaissance music wikipedia , lookup
Art in early modern Scotland wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
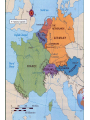
Northern Renaissance Agenda: 1. Northern Renaissance discussion 2. Historical thinking skills activity: Contextualization using thematic approaches HW: outline: “Politics and the State in the Renaissance” (p. 441- 446) Printing Press c. 1440 Gutenburg’s Bible was the first European book printed using moveable type- the printing press Printing encouraged scholarly research and increase desire of public to gain knowledge (access to works of the past) Lay piety Ideas of the Renaissance and Reformation could not have spread like they did without the printing press Allowed Europe to compete with China who had invented printing much earlier Johannes Gutenburg The Northern Renaissance • Printing press carried the spirit of the Renaissance to : –France –England –Germany –Netherlands Northern Renaissance • Great artists had significant impact on scholars and students in Italy • Royal Courts- paintings were show of grandeur –French hired Italian artists Sir Thomas More • English statesmen • Wrote Utopia 1516 – Greek for “nowhere” – Describes ideal peaceful society – Criticism of society, politics, religion – Later opposed the King's separation from the Catholic Church and refused to accept him as Supreme Head of the Church of England; held at the Tower of London and executed for treason Desiderius Erasmus • Catholic priest from Rotterdam • Believed church was greedy, corrupt, narrow-minded • Translated New Testament to Latin • Wrote The Praise of Folly (1509)– Satire that criticized scholars, clergy, etc. for narrow-mindedness using examples from Greek and Roman mythology In Praise of Folly “ Now, indeed, the Stoics think themselves very close to the gods; but give me a person who is Stoic three or four or even six hundred times over and see if he, though not putting aside his beard, an insignia of wisdom (but also common to the goat), will not surely put off his gravity, smooth his frowning brow, abandon his rockbound principles, and for a few minutes be silly and act the fool” Northern Renaissance Art • Center- Flanders, Netherlands (Dutch trade brings in money, patrons) • Religious themes, symbols • Life in towns and countryside • Use of light and shadow • Interest in classical themes • Oil-painting Northern Renaissance Artists • Jan Van Eyck (Dutch, 1390 – 1441) • Albrecht Durer (German, 1471 - 1528) – Court painter to Holy Roman Emperors – Woodcuts (Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse) • Hans Holbein the Younger (German, 1497-1543) – Portrait painter, Painted for Henry VIII (England) • Pieter Brueghel (Flemish, 1525-1569) – Realistic scenes with detail – Every day farm workers, townspeople • Rembrandt van Rijn (Dutch, 1606 - 1669)- light and shadow Possible Self Portrait (Man in Red Turban) Jan van Eyck Arnolfini Portrait, Jan Van Eyck http://www.oneonta.edu/faculty/farberas/a rth/Images/ARTH_214images/van_eyck/arn olfini/painting.jpg Ghent Altarpiece (Adoration of the Mystic Lamb), Jan van Eyck Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse, Albrecht Durer Portrait of Sir Thomas More By Hans Holbein Portrait of Erasmus By Hans Holbein Henry VIII By Holbein Pieter Bruegel’s The Tower of Babel Peasant Wedding, Pieter Brueghel Self Portrait, by Rembrandt Abraham and Isaac By Rembrandt Madonna and Child, Michelangelo Bruges, Belgium Northern Renaissance Architecture City Center, Ghent, Belgium (late 15th, early 16th century) Royal Palace, Amsterdam, 1665 Historical Thinking Skills – Contextualization using Thematic Approaches Historical thinking involves the ability to connect historical events and processes to specific circumstances of time and place as well as broader regional, national, or global processes. Use the themes of AP European history to practice contextualization. Northern Renaissance – The Supreme Art: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xql4qDfOJI