* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sex- Linked Traits
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Segmental Duplication on the Human Y Chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
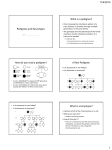
Sex- Linked Traits, and Human Genetics NOTES ch14 Karyotype- Map of all of the chromosomes in a cell Karyotype Has 46 Chromosomes (23 pairs, Last pair is the sex chromosomes XY : Male, XX: Female) Enables scientists / doctor’s to view the chromosomes of a person, plant or animal Detection of abnormalities/ gender Chromosomal defects What is a mutation? __________________________________________ There are two types of mutations that can occur in gamete cells: 1. Gene mutation: affect only one gene. Examples: point and frameshift. 2. Chromosomal mutation: affect the number or structure of chromosomes. Usually involves many, many genes. 5 types of Chromosomal Mutations 1. Deletion 2. Duplication 3. Inversion 4.Translocation 5. Non-disjunction 1.Deletion: Involves the loss of all or part of a chromosome Examples: Cri du Chat syndrome, Angelman’s syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Miller-Dieker syndrome 2.Duplication-Involves the production of extra copies of parts of the chromosome Examples: Fragile X syndrome, Beckwith-Wiedeman syndrome 3.Inversion: Reverses the direction of parts of a chromosome 4.Translocation: When one part of a chromosome breaks off and attaches to another chromosome. Example: Edward’s syndrome 5. Non-disjunction: Means “not coming apart”. When homologous chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis. Results in abnormal numbers of chromosomes. Normal is two of each type of chromosome. Trisomy means a person has an extra copy of a chromosome. Review Question Which parent determines the sex of an offspring? ________________ How? _______________________________________________ Sex linked traits… what are they? those traits that are controlled by genes on the X or Y chromosomes. The Y chromosome is much smaller than the X chromosome and only contains fewer genes. Most sex-linked traits are on the X chromosome. Question: Why is a male more likely to inherit a sexlinked genetic disorder? A male can inherit a recessive trait if the gene for the trait is present on his X chromosome, because Y chromosome cannot hide the trait. A female must have the recessive trait on both X chromosomes for that trait to show Previous Knowledge : What are some sex-linked genetic disorders that you already know? __________________________________________ __________________________________________ ________________________________________. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy SCID- severe combined immune deficiency disorder Colorblindess Hemophilia * Klinefelter’s Syndrome and *Turner’s syndrome caused by chromosome abnormalities of the sex chromosomes but, the genes are not located on the X chromosome. Punnett Squares with Sex-Linked Traits In humans, hemophilia is a sex-linked trait. Having hemophilia is recessive (Xh) to being normal (XH).The heterozygous female is called a carrier. Cross a carrier female with a normal male. __ XHXh __ X __ XHY ___ What are the phenotypic ratios? XH X H Y Xh TRACKING TRAITS AND GENETIC DISORDERS How do we trace traits or genetic diseases through families? Pedigrees! What is a pedigree? A chart that shows relationships within a family that is used to show inheritance of traits. INTERPRETING AND DRAWING PEDIGREES 1. squares represent males, circles represent females 2. shaded shapes represent those family members having the trait being traced (or disease) 3. un-shaded shapes represent family members not affected by trait or disease. 4.½ shaded square or circle indicates a carrier (heterozygous) individual. 5.Horizontal line connecting circle to square indicates a marriage and/ or a generation. 6.Vertical line with a bracket connecting circles or squares to a marriage line indicates siblings (oldest child first) 7. Roman numerals or capital letters indicate generations. Symbols used : do not write Royal disease Human Traits Traits can be autosomal (on a chromosome other than the sex chromosomes) or on the sex chromosomes. Almost all of human traits are polygenic. Human traits are also influenced by the environment. Recessive Autosomal Disorders Inherited by recessive alleles. 1. PKU- cannot process an amino acid 2. Albinism 3.Tay Sachs- lipid build up in brain caused by a single nitrogen base change (A, C, T,G) 4. Cystic Fibrosis – excessive mucous in lungs Dominant Autosomal Disorders Caused by Dominant alleles Examples: 1. Achondroplasia – dwarfism 2. Huntington’s – mental deterioration 3. Hypercholesterolemia- heart disease due to excessive cholesterol 4. Marfan’s syndrome- lanky, cardiovascular issues Codominant disorders Sickle cell disease/ anemia Blood cells are abnormal or sickle-shaped In a heterozygous individual, both normal and sickleshaped are present.