* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download project_7 - Homework Market
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
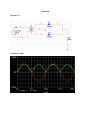
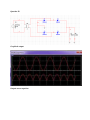
Diode Rectifiers Introduction A rectifier diode gives electrical current stream access one and only bearing and is essentially utilized for power supply operation. Rectifier diodes can deal with higher current stream than standard diodes and are for the most part utilized as a part of request to change AC current into direct current. They are outlined as discrete parts or as incorporated circuits and are typically created from silicon and described by a genuinely expansive P-N-intersection surface. These outcomes in high capacitance under turn around predisposition conditions. In high-voltage supplies, two rectifier diodes or more might be associated in arrangement keeping in mind the end goal to expand the peak inverse voltage (PIV) rating of the blend. Consider the figure beneath. A Full Wave Rectifier is a circuit, which changes an AC voltage into a throbbing dc voltage utilizing both half cycles of the connected voltage. It utilizes two diodes of which one behaviors amid one half cycle while alternate behaviors amid the other half cycle of the connected air conditioning voltage. Amid the positive half cycle of the source voltage, diode D1 gets to be forward biased and D2 gets to be reverse biased. Henceforth D1 behaviors and D2 stays OFF. The heap current moves through D1 and the voltage drop crosswise over RL will be equivalent to the information voltage. Amid the negative half cycle of the info voltage, diode D1 gets to be invert one-sided and D2 gets to be forward one-sided. Thus D1 stays OFF and D2 conducts. The heap current moves through D2 and the voltage drop crosswise over RL will be equivalent to the info voltage. Some of the important parameters of rectifiers are shown below. Ripple Factor The ripple factor for a Full Wave Rectifier is given by The average voltage or the dc voltage available across the load resistance is RMS value of the voltage at the load resistance is Efficiency Efficiency, h is the ratio of dc output power to ac input power The maximum efficiency of a Full Wave Rectifier is 81.2%. Transformer Utilization Factor Transformer Utilization Factor, TUF can be used to determine the rating of a transformer secondary. It is determined by considering the primary and the secondary winding separately and it gives a value of 0.693. Form Factor Form factor is defined as the ratio of the rms value of the output voltage to the average value of the output voltage. Peak Factor Peak factor is defined as the ratio of the peak value of the output voltage to the rms value of the output voltage. Peak inverse voltage for Full Wave Rectifier is 2Vm because the entire secondary voltage appears across the non-conducting diode. This concludes the explanation of the various factors associated with Full Wave Rectifier. Calculations and Analysis Question 23 a. The circuit is a center tapped full wave rectifier b. Calculating the total peak voltage, we have; c. Calculating the peak voltage on the ½ of the secondary part we have; d. Plotting the voltage waveform e. Peak voltage across each diode f. PIV of each diode Question 28 Question 30 Question 33 Question 34 Simulation Question 23 Graphical output Question 28 Graphical output Output across capacitor Conclusion In conclusion, a rectifier circuit utilizes the unidirectional property of diodes to change the voltage from Ac to Dc. The circuit allows current only in the forward biased direction and thus the effects as shown above. The capacitors at the output are used to reduce the rippling of the rectified wave as shown in the Multism simulation. It is thus clear that the experiment was a success since the objectives were made.