* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Engineering Electromagnetic
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electron mobility wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatic generator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Electromigration wikipedia , lookup
Photoelectric effect wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Static electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
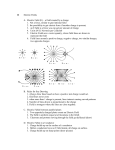
Engineering Electromegnetic Engineering Electromagnetic SUB : Engineering Electromagnetic Topic : Conductors Department : Electronics and communication Name : Parmar Taruna M. Enroll No : 130430111110 Guided By, j .m bhoot A conductor is something which allows electricity to flow through. Exam.: Scissors, Paper clip, Aluminum foil,Iron,Steel,Copper. In Conductors Valence electronics are present. When an electric field is applied ,then these electrons start moving which constitute an electric current. Conductors are the materials which allow the current to flow very easily. Fig. Energy band diagram for conductors This is due to the large number of free electrons present in conductors. Look at the energy band diagram of conductor show fig. for metals like copper , alumina, etc. There is no “forbidden gap” present between the valence and conductors bands. Therefor even at room temperature , a large number of free electrons are present and available for conduction. When a charge Q is placed in an electric field E, it experiences a force Gives by F=QE. If this charge is an electrons, then Q=-e so that F=-e E . Due to negative sign of elections charge it is clear that the force acting on the electron is in opposite direction to that of eclectic field intensity E. If there is no opposition or resistance to the motion of electron, then the velocity of electron will increase indefinitely with the time t provided the electron field E is constant. Lets us now consider a conductor placed in a static electric field , as show fig. the free electrons in the conductor moves opposite to the direction line of electric field . Thus a negative surface charge forms on the boundary accompanied by an equal amount of positive surface charge show in fig. ,since the conductor as a whole is neutral. Fig : Effect of Field Conductor * Imagine that you have a solid metal ball or sphere and you place charge inside of it. * How fast this charge arrives at the surface can be calculated using the term relaxation time . * Time taken by charges to travel to the surface is represented by relaxation time. Using the relations, In electrostatic fields, following principle are applicable to conductors: Within a Conductor, charge or change density(pv c/ m3) is zero and a surface charge density (ps c/m3) is present on the other surface of the conductor. The tangential component of external electrical field intensity as well as electric flux density is zero. The conductor surface is an equipotential surface. The normal component of electric flux density is equal to surface charge density on the conductor surface. * References 1.www.wikipedia.in 2.www.google.com 3.www.yahoo.com