* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 4
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
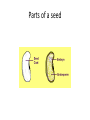
Chapter 4 Plants 5th Grade Science Plants • Plants make their own _____. This process is food called ___________ photosynthesis and takes place in their leaves __________. cells • Leaves are _______ made of _____ and organs tissues _________. • Layers of similar _______ make up the cells tissues _______ in the leaf. • Plant tissues are very similar to animal tissues. Photosynthesis • _______________ is the process that plants Photosynthesis use to make sugar for food. chloroplasts • Photosynthesis happens in the ___________ which are located in plant cells. Carbon dioxide • In photosynthesis ____________ and ________ are used to make _________ and water sugar ____________. oxygen • ___________ supplies the energy needed for Sunlight photosynthesis. Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis • Carbon dioxide + water → oxygen + sugar • The plant gets water from the _______ and soil stomata carbon dioxide through the ________ which are small pores on the underside of leaves. • Once the plant makes the sugar it is transported to all of the ______ in the plants cells including the roots. Sugar • Plants use some of the sugar immediately as _______ to continue the process of energy photosynthesis ____________ during the day. • Some sugar is _______ to use at night. stored • Thousands of sugars combine in plant cells to form ________. cellulose • ________ is a chemical that makes up the Cellulose strong _______ Cell walls of plants. Chlorophyll • Inside of the chloroplasts are structures that look like plates called __________. chlorophyll pigment • Chlorophyll contains a ________ that gives the plant its color. • The function of the chlorophyll is to absorb _________from the sun in the chloroplast. energy • __________ gives the cell energy to make Sunlight sugar from ___________ Carbon dioxide and ________. water Stems support • Stems provide ________ for the plant and hold the leaves and flowers. Vascular • __________ plants have stems have a transport system just like the _____________ Circulatory system in the human body. • The tissues in plant stems that transport xylem materials are __________ and ________. phloem Xylem and Phloem Xylem • ________ - are tissues that carry materials from the roots to the leaves. roots – The _______ soak up the water from the soil. _______ Phloem - are tissues in the shape of tubes that carry sugar away from the leaves. water -The sugar from plants is dissolved in _______. bark Dead -In trees, phloem is made below the ____. phloem makes the bark. Roots Roots • ___________ - anchor the plant into the ground and hold it in place as it grows. • Root systems: Taproot – ___________ - a large root that grows straight food down. Taproots may store _______ for the plant. Small roots may grow sideways out of the main taproot. Fibrous root systems - many roots grow out in all – ________________ directions. Root Tip • Roots grow longer because of special _________ near the root tip. tissues Root Tip • At the __________, cells quickly divide and form new cells. cells • The new ______ push the root further into the ground. absorb • Roots also _______ water for the plant. Functions of Roots anchor store • Roots _________ a plant and may _______ food. water minerals • Roots absorb ______ and ________ or ___________ from the soil. nutrients • The materials that are taken in from the soil are used in the processes of ___________, photosynthesis growth maintenance reproduction ________, ____________, and ____________ Parts of a Plant Parts of a Flower stamen • _______ - male part of a flower • __________ - a grainy yellow powder is made pollen in the stamen. stamens • A single flower may have many_________. • ________ - female part of a flower. pistil pistil • _______ often has a wide bottom an a narrow neck pistil • A single flower may have more than one ____. Flowers • _______________ - do not have both a stamen Imperfect Flowers and a pistil. Perfect Flowers • _______________ - flowers with both male and female parts. Composite Flowers • _______________ - one flower unit is made up of hundreds of tiny flowers Pollination - the moving of pollen from the stamen • ________ to the pistil. Pollination – ____________ - can involve the stamen and pistil of the same plant or two different plants Pollination • Pollination takes place in different ways. • _______ or ______ can move pollen. wind water • ________, _____, or ________ moving from insects bats birds plant to plant can transport pollen. • Some plant species are only pollinated in one way while others can be pollinated in different ways. Pollination of a Pea Plant pollen • 1. Pollen sticks to the _________ at the end pistil of the ________. pistil • 2. Pollen tubes grow down the _______ to the __________. Egg cell • 3. _________ from the pollen move down the Sperm tubes. Fertilization • 4. ___________ combines the DNA of both plants Pollination / Parts of a flower Seeds • A seed is made of three main parts: – ____________ Seed coat embryo – ____________ endosperm – ____________ The __________ is a covering that protects the new Seed coat plant and stores food. embryo The __________ is the new plant contained in the seed coat. The __________ endosperm is a stash of food stored in the seed coat Parts of a seed Monocots / Dicots embryo • An _________ has structures called _________ Seed leaves or __________. cotyledons • ___________ - seeds that have one cotyledon Monocots – example: corn Dicots • __________ - seeds that have more than one cotyledon – example: beans Compare and Contrast Spreading Seeds • Some plants ______ their seeds on the ground drop and the seeds begin to grow. • _________ are helpful in scattering seeds. animals • The seeds of berries pass through the Digestive system _______________ of animals and are eliminated as waste. temperature and • Outside conditions such as _________ __________ must be right before the plant moisture can begin to grow. Spores mosses ferns • __________ and ________ are plants that do not produce flowers. Two parts • The life cycle of these plant have _______: fertilization – ____________ – ____________fern and mosses use _______ reproduction spores to reproduce. spore A plant ________ is a single plant cell that can develop into a new plant. Differences between spores and seeds • • • • Spores do not have a multicellular _________ embryo Spores are not made by __________ fertilization Both spores and seeds have____________ Stored food Reproducing without sperm cells and egg cells: Asexual – _________ reproduction – there is only one parent – The offspring are identical to the parent Runners Budding – ___________ and ____________ Runners and Budding Runners • ________growing new plants from stems or roots of the plant. Example: strawberries • __________buds form on the plant and drop Budding off to grow as separate plants. Life Cycle of a Moss plant • Page 109 How Do Plants Grow? DNA • A plants growth depends on ______ and its ___________ Environmental conditions • ____________ - when a seed sprouts Germination roots downward • _______ will grow out of a seed __________ • ________ will grow out of a seed _________ stems upward DNA • _________ - genetic information that instructs the plant on how to grow and in what conditions Tropisms • ___________ - ways in which the plant Tropisms changes direction to get what it needs environmental • Tropisms often occur when the ___________ conditions change. cells • _____will grow faster on one side of the plant causing the plant to bend in a certain direction. • _____________ - kind of chemical that affects Growth hormone plant growth. Growth Hormone in Plants • Growth hormones in plants cause more cells to grow in the plant. • The hormone may make the plant grow larger • Plants make their own growth hormone.