* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Management Process Today
Operations research wikipedia , lookup
Project management wikipedia , lookup
Managerialism wikipedia , lookup
Workers' self-management wikipedia , lookup
Operations management wikipedia , lookup
Management consulting wikipedia , lookup
International Council of Management Consulting Institutes wikipedia , lookup
Environmental resource management wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable management wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem-based management wikipedia , lookup
Public service motivation wikipedia , lookup
Strategic management wikipedia , lookup
Vitality curve wikipedia , lookup
High-commitment management wikipedia , lookup
Opportunity management wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
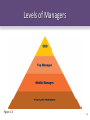
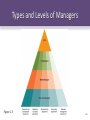
The Management Process Today Chapter One McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright © 2011 by the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives LO1 Describe what management is, why management is important, what managers do, and how managers use organizational resources efficiently and effectively to achieve organizational goals LO2 Distinguish among planning, organizing, leading, and controlling (the four managerial functions), and explain how managers’ ability to handle each one can affect organizational performance LO3 Understand the three levels of management and the tasks and responsibilities of managers at different levels in the organizational hierarchy 1-2 Learning Objectives LO4 Distinguish between three kinds of managerial skills, and explain why managers are divided into different departments to perform tasks more efficiently and effectively LO5 Discuss some major changes in management practices today that have occurred as a result of globalization and the use of advanced information technology (IT) LO6 Discuss the challenges managers face in today’s increasingly competitive global environment 1-3 What is Management? • Management – The planning, organizing, leading, and controlling of human and other resources to achieve organizational goals effectively and efficiently 1-4 What is Management? • Organizations – Collections of people who work together and coordinate their actions to achieve a wide variety of goals 1-5 What is Management? • Managers – The people responsible for supervising the use of an organization’s resources to meet its goals – Resources include people, skills, know-how, machinery, raw materials, computers and IT, and financial capital 1-6 Achieving High Performance • Organizational Performance – A measure of how efficiently and effectively managers use organizational resources to satisfy customers and achieve goals 1-7 Efficiency, Effectiveness, and Performance in an Organization Figure 1.1 1-8 Organizational Performance • Efficiency • Effectiveness – A measure of how – A measure of the well or productively appropriateness of resources are used to the goals an achieve a goal organization is pursuing and the degree to which they are achieved. 1-9 Why study management? • The more effective and efficient use an organization can make of resources, the greater the relative wellbeing of people • Almost all of us encounter managers because most people have jobs and bosses • Understanding management is one important path toward obtaining a satisfying career 1-10 Four Tasks of Management Figure 1.2 1-11 Planning • Planning – Process of identifying and selecting appropriate goals and courses of action 1-12 Steps in the Planning Process 1. Deciding which goals to pursue 2. Deciding what strategies to adopt to attain those goals 3. Deciding how to allocate organizational resources 1-13 Planning • Strategy – Cluster of decisions about what goals to pursue, what actions to take, and how to use resources to achieve goals 1-14 Organizing • Organizing – Structuring working relationships so organizational members interact and cooperate to achieve organizational goals. 1-15 Organizing • Organizational Structure – A formal system of task and reporting relationships that coordinates and motivates organizational members so that they work together to achieve organizational goals 1-16 Leading • Leading – Articulating a clear vision! Energizing and enabling organizational members so they understand the part they play (share) in attaining organizational goals. 1-17 Controlling • Controlling – Evaluating how well an organization is achieving its goals and taking action to maintain or improve performance – The outcome of the control process is the ability to measure performance accurately and regulate efficiency and effectiveness 1-18 Question? What is a group of people who work together and possess similar skills or use the same knowledge, tools, or techniques? A. Organization B. Department C. Team D. Presentation Group 1-19 Levels and Skills of Managers • Department – A group of people who work together and possess similar skills or use the same knowledge, tools, or techniques to perform their jobs 1-20 Levels of Management • First-Line Managers – Responsible for the daily supervision of nonmanagerial employees • Middle Managers – Supervise first-line managers and are responsible for finding the best way to use resources to achieve organizational goals 1-21 Levels of Management • Top Managers – Establish organizational goals, decide how departments should interact, and monitor the performance of middle managers • CEO – Chief Executive Officer; the company’s most senior and important manager. All other top managers report to CEO or COO. 1-22 Levels of Managers Figure 1.3 1-23 Relative Amount of Time That Managers Spend on the Four Managerial Tasks Figure 1.4 1-24 Levels of Managers • Top-management team – Group composed of the CEO, COO, and the heads of the most important departments 1-25 Question? A. B. C. D. Which management skill is the ability to understand, alter, lead, and control the behavior of other individuals and groups? Conceptual Human Technical Technological 1-26 Managerial Skills • Conceptual skills – The ability to analyze and diagnose a situation and distinguish between cause and effect. • Human skills – The ability to understand, alter, lead, and control the behavior of other individuals and groups. • Technical skills – The specific knowledge and techniques required to perform an organizational role. 1-27 Question? What is the specific set of abilities that allows one manager to perform at a higher level than another manager? A. Skill-sets B. Competencies C. Skill traits 1-28 Technical Skills • Core competency – Specific set of skills, abilities, and experiences that allows one organization to outperform its competitors 1-29 Types and Levels of Managers Figure 1.5 1-30 Recent Changes in Management Practices • Restructuring – downsizing an organization by eliminating the jobs of large numbers of top, middle, or first-line managers and non-managerial employees 1-31 Recent Changes in Management Practices • Outsourcing – Contracting with another company, usually in a low cost country abroad, to perform an activity the company previously performed itself – Increases efficiency because it lowers operating costs, freeing up money and resources that can be used in more effective ways 1-32 Empowerment and Self-Managed Teams • Empowerment – Expansion of employees’ knowledge, tasks, and decision-making responsibilities 1-33 Empowerment and Self-Managed Teams • Self-managed team – A group of employees with the responsibility of: organizing, controlling and supervising their own activities and for monitoring the quality of the goods and services they provide 1-34 Challenges for Management in a Global Environment • Rise of Global Organizations. • Building a Competitive Advantage • Maintaining Ethical and Socially Responsible Standards • Managing a Diverse Workforce • Utilizing IT and ECommerce • Practicing Global Crisis Management 1-35 Challenges for Management in a Global Environment • Global organizations – Organizations that operate and compete in more than one country 1-36 Building Competitive Advantage • Competitive advantage – Ability of one organization to outperform other organizations because it produces desired goods or services more efficiently and effectively than they do 1-37 Building Blocks of Competitive Advantage Figure 1.6 1-38 Building a Competitive Advantage • Innovation – Process of creating new or improved goods and services or developing better ways to produce or provide them 1-39 Practicing Global Crisis Management Crisis management involves making important choices about how to: 1. Create teams to facilitate rapid decision making and communication 2. Establish the organizational chain of command 3. Recruit and select the right people 4. Develop bargaining and negotiating strategies to manage conflicts 1-40