* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hinduism
Brahma Sutras wikipedia , lookup
Tamil mythology wikipedia , lookup
2013 Bangladesh anti-Hindu violence wikipedia , lookup
Buddhism and Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
History of Shaktism wikipedia , lookup
Akhil Bharatiya Hindu Mahasabha wikipedia , lookup
Hindu nationalism wikipedia , lookup
Rajan Zed prayer protest wikipedia , lookup
Anti-Hindu sentiment wikipedia , lookup
Classical Hindu law in practice wikipedia , lookup
Indra's Net (book) wikipedia , lookup
California textbook controversy over Hindu history wikipedia , lookup
Women in Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hinduism in Malaysia wikipedia , lookup
Invading the Sacred wikipedia , lookup
Dharmaśāstra wikipedia , lookup
History of Hinduism wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Vedanta wikipedia , lookup
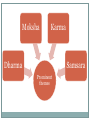
Hinduism BY HUGO, HOLLIE, LAUREN AND FIONA Something you didn’t know! Worlds oldest religion World’s third largest religion It is a way of life (dharma) The word ‘Hindu’ came from the river ‘Sindhu’ In Hinduism, they do not have any system or beliefs just prominent themes. Key Belief’s Truth is Eternal Hindu’s pursue knowledge and understanding of the truth Brahman is truth and reality Brahman is the one true God (Formless, all inclusive and eternal) The Vedas are the ultimate authority Hindu scriptures that contain revelations received by ancient saints Everyone should strive to achieve dharma Described as the right conduct; moral law and duty, anyone who makes dharma central of their lives strive to do the right thing. Individual souls are immortal Believe that the persons soul is neither created or destroyed. Moksha Karma Dharma Samsara Prominent themes Dharma (ethics and duties) Dharma in Hinduism means duty, virtue and morality, it refers to the power in which the universe and society holds. Dharma is seen to acting virtuously, which means it is the same for everyone. Different people have different obligations and duties, dependant on their age, gender and social position. Everyone has their own dharma Flood, G. (2009) Samsara (Rebirth) The soul reincarnates again and again until it becomes perfect and reunites with its source. During this process they believe the soul enters many bodies and holds many forms. The following verse of the Bhagavad gita summarises Samsara is , ‘Just as a man discards worn out cloths and puts on new clothes, the soul discards worn out bodies and wears new ones.’ (2.22) Karma Karma is a word which means action, it refers to the law that every reaction has an equal reaction either immediately or some point in the future. Good actions with dharma will have good reactions or responses and bad actions which go against dharma will have the opposite effect. In Hinduism they believe that karma doesn’t operate in one lifetime but across lifetimes, the results of one action may not be experienced in the present life but in a new life. Flood. G. (2009) Moksha Moksha is the end of death and rebirth cycle and is known as the forth ultimate artha, which means goal. This goal is achieved by overcoming ignorance and desires. It can be achieved by both in life and after death. (BBC 2006) Hindu Celebrations Hindu’s celebrate Diwali, the festival of light. The festival celebrates the victory of good over evil, light over darkness and all over the world it is celebrated differently. In Britain the festival is a time for cleaning the home, wearing new clothes, exchanging gifts, fireworks and decorating buildings. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OK-5GiGhhKU Deities In Hinduism there are a wide variety of deities (god and goddesses) to choose and worship, every Hindu can pray for something different as each deities means something different. Many Hindu’s view their religion with only one supreme deities who is formless and impersonal, all other deities are parts of the one God. In the Hindu faith there is a trinity where the deities is in three people. Brahma: is the creator of all reality Vishnu is the preserver of all of the creations Shiva is the destroyer. Krishna Vishnu Shiva Brahma Reference List BBC. (2006). Moksha .[online] Available: http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/hinduism/belief s/moksha.shtml. [Last accessed 09/10/13]. BBC . (2009). Gurdwara. [online] Available:http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/sikhis m/ritesrituals/gurdwara_1.shtml. [Last accessed 09/10/13] Flood, G. (2009). Hindu concepts. [online] Available at: http://www.bbc.co.uk/religion/religions/hinduism/conce pts/concepts_1.shtml. [Last accessed 09/10/13] Indiavideodotorg. (2009). Diwali Festival of lights. [online] Available at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OK-5GiGhhKU. [Last accessed 17/10/13]