* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 17-2 Questions ppt
Role of music in World War II wikipedia , lookup
Military history of Greece during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Kriegsmarine wikipedia , lookup
Technology during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Fascism in Europe wikipedia , lookup
World War II by country wikipedia , lookup
Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Pursuit of Nazi collaborators wikipedia , lookup
Operation Bodyguard wikipedia , lookup
Allied Control Council wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Diplomatic history of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Foreign relations of the Axis powers wikipedia , lookup
Mediterranean and Middle East theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
British propaganda during World War II wikipedia , lookup
Causes of World War II wikipedia , lookup
German evacuation from Central and Eastern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Nazi views on Catholicism wikipedia , lookup
New Order (Nazism) wikipedia , lookup
World War II and American animation wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Mediterranean wikipedia , lookup
Economy of Nazi Germany wikipedia , lookup
Invasion of Normandy wikipedia , lookup
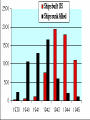
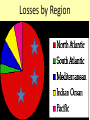
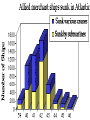
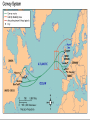
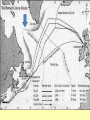
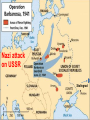
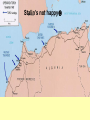
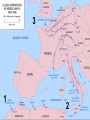
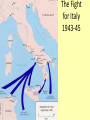
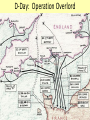
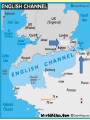
Chapter 17-2 Questions Focus Q • To bring scientists into the war effort, FDR created the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD). How did radar, sonar, DDT, and penicillin help U.S. soldiers? • Page 567 Focus Q: March 7 • Page 574, read “D-day” • Bullet point notes • 1 sentence summary Wading ashore June 6, 1944 Later on June 6, 1944 1. Why defeat Germany first? 1. FDR and Churchill—Dec. 1941—DEFEAT NAZI’S FIRST 2. Hitler and IT greater threat than Japan 3. Stalin needed help badly 4. If Germany defeated, BR and USSR could help us w/Japan 5. Churchill and FDR get along well—quote p. 570 Nazi Tanks invading Poland, 1939 Blitzkrieg 2. How did the US win the war in the Atlantic? • German goal—stop food and war material from BR, USSR 1. Nazi subs along east coast 2. 1st 4 months of 1942, sink 87 US ships 3. by July, wolf packs has sunk 681 Allied ships Nazi Wolf Packs Winning war in Atlantic 1. US building ships fast: 2. early 1943 build 140 Liberty (cargo) ships/month— 3. winning battle of the Atlantic by May 1943—Germans u-boat losses unbearable See overhead Sunk by a German U-boat In the North Atlantic Losses by Region And the answer is ……… US response: 1. Convoys escorted by 2. battleships w/sonar (underwater) drop depth charges and 3. planes w/ radar (surface)—spot uboats Convoy System Ships and planes offer protection from u-boats Mark IX Depth Charge • 200 pounds of Torpex • Design allows for straight descent • Dropped from ships, planes, helicopters • Shock sub by exploding near it Depth Charge Launcher 3. Why was the Battle of Stalingrad a turning point in WW2? How many Soviets died defending Stalingrad? 1. Germans fighting in USSR since June 1941—winter stops them—begin again summer 1942 2. Hitlers tactics—Nazi’s are low on oil Seize oil fields in Caucasus—1 GOAL Capture Stalingrad (Volgograd)—2ND GOAL 3. Once Stalingrad captured, cut supply line for Moscow, the Volga River Nazi attack on USSR Stalingrad Battle of Stalingrad (Volgagrad) 1. Luftwaffe bombs by night—most wooden buildings burned 2. Stalin orders troops to defend no matter the cost 3. By Sept. 1942, 90% of Stalingrad taken 4. November—USSR counterattack 5. Nazi advisors say retreat, Hitler says no 6. Fight into winter—Feb. 1943, 91 K Germans surrender—lose 240 K And the answer is …….. 1. Wars 1st turning point: Germans retreat from now on in the east 2. USSR loses 1.1 M defending city Stalingrad Stalingrad Stalingrad The North African Front: 1942-43 1. during battle for Stalingrad—Stalin wants a western front opened— doesn’t happen 2. Operation Torch instead— Mostly Americans invade N. Africa November 1942 Stalin’s not happy Operation Torch: North Africa 1942-43 1. Ike (Dwight Eisenhower) in command— Nov. 1942, 107 K land @ Casablanca, Oran, Algiers Battle Erwin Rommel, the Desert Fox Afrika Corps surrender May 1943 3 1 2 FDR, Churchill meet at Casablanca 1. accept unconditional surrender only • controversial—may have caused Germany and Japan to fight longer The Fight for Italy 1943-45 The Fight for Italy 1943-45 1. Strangely, Mussolini is taken from power only to have Hitler take control of IT and put him back in power 2. 18 months to win in IT— 3. 25 K Allied casualties, 30 K Axis 4. April 28, 1945 Mussolini found, shot, body hung in Milan Just hangin’ around Mussolini After being shot, beaten Tuskegee Airman: 99th Pursuit Squadron 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. They escort bombers to their targets 15 K combat missions destroy 261 German planes 66 Tuskegee Airmen killed 32 downed, captured NO US BOMBERS LOST under their escort Other Heroes in Combat 141st all-Mexican unit • one of the most decorated of the war 442nd all-Japanese • many volunteer to get out of internment camps • most decorated unit in US history Anything unique here? D-Day: Operation Overlord June 6, 1944 1. 3 M US, BR, Canadian troops 2. Invade Normandy region of France 133 K soldiers 1200 ships 4100 landing crafts 10 K paratroopers 10 K planes D-Day: Operation Overlord Wading ashore June 6, 1944 Normandy Invasion (June 1944) 1. US fakes like they will attack at Calais— 150 miles N—map p. 575 2. planning this attack for 2 years— 3. bomb supply routes (RR, roads, bridges) for a 45 days before attack 4. June 5 original date, weather forces it back 1 day 5. Largest land-air-sea assault in army history See map p. 575 Why do you think Hitler would have expected an attack at Calais? It is shortest distance across the English Channel The Allies Gain Ground 1. Land 1 M troops in a month, 567 K tons of supplies, 170 K vehicles 2. Paris liberated August 25, 1944 3. Sept. 1944, FR, Belgium, Luxembourg, and most of Holland freed 4. FDR and Harry Truman elected in 1944, 4th term What battle was Hitler’s last offensive? How long did it last? • The Battle of the Bulge—last German offensive • Oct. 1944—Allies take first German town • Allies ignored intelligence that warned of such an attack What battle was Hitler’s last offensive? How long did it last? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Dec. 16 surprise counterattack by Nazis 8 GER tank divisions break through on an 80-mile front get 60 miles into Allied territory Try to break through near Antwerp, Belgium One month battle—Nazis lose 120 K, 600 tanks, 1600 planes 7. Hitler retreats after this Why call it the Battle of the Bulge? What did the Soviets find at Majdanek? 1. Soviets find concentration camps 1st— Majdanek—find Nazis trying to bury and burn the evidence 2. Find 1000 “living corpses”, world’s largest crematorium, 800 K shoes 3. APV p. 576 200 K die here When was V-E Day? What does it stand for? 1. April 25, 1945 USSR storms Berlin 2. April 29, Hitler marries Eva Braun, next day commits suicide, their bodies burned May 8, 1945—V-E Day Victory in Europe Who did Hitler blame (and for what) at the end of his life? • Hitler blamed the Jews for starting the war and his generals for losing it Who becomes president after FDR? FDR dies of a stroke on April 12, 1945 • Harry Truman becomes president D-Day was the code name for the Allied invasion of 1. Italy 2. France 3. Japan 4. North Africa Which problem was targeted by the Office of Price Administration? A inflation B recession C depression D unemployment The Battle of the Bulge was significant because if marked the 1. last German offensive 2. liberation of the death camps 3. Allies’ first victory in a land battle 4. Axis powers’ last loss in a land battle •During WW2, this poster was used primarily to During WW2, this poster was used primarily to 1. 2. 3. 4. contain communism create jobs for the unemployed get financial support for the war convince women to fill vacant factory jobs What situation does the following quote describe, “My family will have to get along without sugar and flour this week?” 1. destruction of crops during wartime 2. need for importing food products 3. food rationing to support a war effort 4. limitation of food production through farm subsidies World War II in Europe and North Africa Map Quiz (You need your map and a blank sheet of paper) 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) What happened in the Atlantic Ocean before the United States was even in the war? World War II began when Germany invaded . Who was the leader of Germany’s “Afrika Korps”? Did he win or lose his battle in Africa in 1943? After defeating the Axis Powers in Africa, where did the Allies head next? What three Allied victories took place in Italy, according to your map? 6) When did the Allies invade France and what was this day called? 7) Which city marked the furthest point east that the German army advanced (and lost)? 8) How long did it take Germany to surrender after D-Day? 9) How many Allied victories did you shade in on your map? 10) Which two Allied countries met in the middle of Germany at the end of the war (1945)?