* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 9 Study Guide
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Lunar effect wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
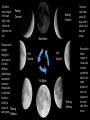
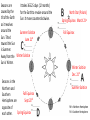
Unit 9 Study Guide The Moon does not give off its own light, it only reflects the light from the Sun. Waxing Crescent The amount of sunlight hitting the moon causes it to look different – called phases. You need to memorize these phases in order and be able to identify a picture of Waxing each phase. Gibbous Waning Crescent New Moon Last Quarter First Quarter Full Moon Waning Gibbous The lunar cycle takes about 28 days…that’s about 3 to 4 days per phase. Because the Moon rotates on its axis and revolves around the Earth in the same amount of time, we always see the same side of the moon. The Earth is tilted on its Axis at an angle of 23.5 degrees. The Earth rotates on its Axis every 24 hours. It is day on the part of the Earth that the Sun’s light is hitting, and night on the other side of the Earth. Seasons are It takes 365.25 days (12 months) caused by the for the Earth to revolve around the tilt of the Earth Sun. It moves counterclockwise. as it revolves around the Summer Solstice Sun. Tilted June 21st toward the Sun is Summer. Away from the Winter Solstice Sun is Winter. B North Star (Polaris) Spring Equinox March 21st Fall Equinox C Seasons in the Northern and Fall Equinox Southern Sept 23rd Hemisphere are opposite of Spring Equinox each other. Winter Solstice Dec. 21st A Summer Solstice D NH = Northern Hemisphere SH = Southern Hemisphere A Solar Eclipse can ONLY happen during the position of a New Moon. A Lunar Eclipse can ONLY happen during the position of a Full Moon. These diagrams show the position of the Earth, Moon, and Sun when there is a Full Moon and a New Moon. The bulge on the Earth shows the high tide caused by the pull of the Moon’s gravity on Earth’s water. It is low tide where it is not bulging. When the Sun, Earth, and Moon are at right angles to each other, a Neap Tide occurs. When the Sun, Earth, and Moon are in a straight line, a Spring Tide occurs.