* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download function - City Tech OpenLab
Survey
Document related concepts
Monad (functional programming) wikipedia , lookup
Algorithm characterizations wikipedia , lookup
Functional programming wikipedia , lookup
Name mangling wikipedia , lookup
Falcon (programming language) wikipedia , lookup
Recursion (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Abstraction (computer science) wikipedia , lookup
Dirac delta function wikipedia , lookup
Parameter (computer programming) wikipedia , lookup
APL syntax and symbols wikipedia , lookup
Function object wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
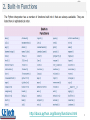
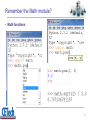
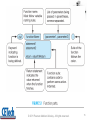
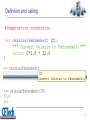
Functions, Procedures, and Abstraction Dr. José M. Reyes Álamo Status of Assignment and Quizzes Past Due • RA1_ComputerConcepts Pending • RA4_PythonCh3Ch6 • RA2_PythonCh1Ch2 • RA5_PythonCh8Ch10 • RA3_PythonCh5Ch7 • Labs • Quiz1 – Lab1 – Lab2 – Lab3 – Lab4 2 Outline • Functions • Built-in functions • User defined functions • Abstraction • Reusability • Parameters and arguments • Returning values • Variables Scope 3 Functions Functions • From mathematics, a functions perform some operation and returns a result. • Functions hide the details of and operation, to make it easy to use by others –e.g. sqrt() for computing the square root. 5 Function • In the context of programming, a function is a named sequence of statements that performs a computation. • When you define a function, you specify the name and the sequence of statements. • You can invoke the function by name. 6 Built in functions Python provides built-in functions • Type conversion functions 8 A big list of built-in functions http://docs.python.org/library/functions.html 9 Remember the Math module? • Math functions 10 Lots of Python modules available • Built-in modules – The Python Standard Library: http://docs.python.org/library/ • Other modules – PyPI - the Python Package Index http://pypi.python.org/pypi – The Python Package Index is a repository of software for the Python programming language. – There are currently 24018 packages there. 11 User defined functions Mathematical notation • Consider a function which converts temperatures from Celsius to temperatures in Fahrenheit: – Formula: F = 1.8 *C + 32.0 – Functional notation: F = celsisus2Fahrenheit(C) where celsius2Fahrenheit(C) = 1.8*C + 32.0 13 Function definition • Math: –f(C) = 1.8*C + 32.0 • Python: • Terminology: parameter “C” 14 © 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 15 Definition and calling 16 Triple quoted string in function • A triple quoted string just after the def is called a docstring • docstring is documentation of the function’s purpose, to be used by other tools to tell the user what the function is used for. 17 Abstraction Abstraction 19 19 Abstraction 1. The ability of dealing with ideas rather than events. 2. Something that exists only as an idea. 20 20 Abstraction in computing • A programmer would use abstraction to define general purpose functions. • Abstraction is one of the most important techniques in software engineering as it is used to reduce complexity. 21 21 Reusability Why have functions? • Support divide-and-conquer strategy • Abstraction of an operation • Reuse: once written, use again • Sharing: if tested, others can use • Security: if well tested, then secure for reuse • Simplify code: more readable 23 How to write a function • Does one thing. If it does too many things, it should be broken down into multiple functions (refactored). • Readable. You should be able to read it as well as others. • Reusable. If it performs its task well, you can reuse. 24 More on functions • Complete. A function should check for all the cases where it might be invoked. Check for potential errors. • Not too long. As it does one thing, code is usually succinct. 25 Parameters and arguments Parameters vs argument • A parameter is the variable which is part of the function's definition. – Inside the function, the arguments are assigned to the parameters. • An argument is an expression, value, or literal used when calling the method. 27 celsius=25 val=25* 1.8 + 32 = 77.0 © 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. 28 Returning values Return Statement • The return statement indicates the value that is returned by the function. • The return statement is optional. If there is no return statement, the function is often called a procedure. • Procedures are often used to perform duties such as printing output or storing a file 30 Multiple returns in a function • A function can have multiple return statements, but only one will execute. • The first return statement found, executes and ends the function. • Multiple return statements can make your code confusing, therefore should be used carefully. 31 Multiple return statements example 32 Variables scope Local variables • When you create a variable inside a function, it is local, which means that it only exists inside the function. For example: • This function takes two arguments, concatenates them, and prints the result twice. Here is an example that uses it: 34 Local values • When cat_twice terminates, the variable cat is destroyed. If we try to print it, we get an exception: • Parameters are also local. For example, outside cat_twice, there is no such thing as part1 or part2. 35 Summary • Function: – Named sequence of statements that performs a computation • Built in functions: – Python provides built-in functions and modules. Lots of extra modules available • User defined functions: – It is also possible to add new functions. A function definition specifies the name of a new function and the sequence of statements that execute when the function is called. • Abstraction: – The ability of dealing with ideas rather than objects or events. 36 Summary • Reusability: – Functions can be re-used in another program. • Parameters and arguments: – A parameter is the variable which is part of the function’s definition. An argument is the value or expression used when calling the method. • Returning values: – The return statement indicates the value returned by the function. A function with no return statements is often called a procedure. • Variables Scope: – Parameters and variables created inside a function are local, which means that they only exists inside the function 37 Status of Assignment and Quizzes Past Due • RA1_ComputerConcepts Pending • RA4_PythonCh3Ch6 • RA2_PythonCh1Ch2 • RA5_PythonCh8Ch10 • RA3_PythonCh5Ch7 • Labs • Quiz1 – Lab1 – Lab2 – Lab3 – Lab4 38