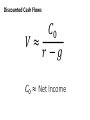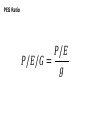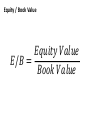* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Relative value
Survey
Document related concepts
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
International Financial Reporting Standards wikipedia , lookup
Financial crisis wikipedia , lookup
Private equity in the 1980s wikipedia , lookup
Short (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Leveraged buyout wikipedia , lookup
Market sentiment wikipedia , lookup
Investment fund wikipedia , lookup
Black–Scholes model wikipedia , lookup
Efficient-market hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Stock market wikipedia , lookup
2010 Flash Crash wikipedia , lookup
Derivative (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Stock exchange wikipedia , lookup
Hedge (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
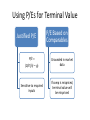
How do we value companies? Intrinsic value • The value of a company to you is wrong • We assume it will become right • Stock vs. other assets Relative value • Other companies are valued differently • If our company is an outlier, it will tend to change to normal over time • Stock vs. stock Discounted Cash Flows Annual FCF for that year Estimated future Free Cash Flows Discounted Cash Flows 𝐶0 𝑉≈ 𝑟−𝑔 𝐶0 ≈ Net Income PE Ratio Annual FCF for that year Estimated future Free Cash Flows PE Ratio 𝑉≈ 𝐶0 𝑟−𝑔 𝑉 𝑃/𝐸 = 𝑁𝐼 𝑝 𝑃/𝐸 = 𝐸𝑃𝑆 ≈ 𝑁𝐼 𝑑 Price-to-Earnings Multiple Rationales & Drawbacks Rationales Drawbacks EPS is driver of value Zero, negative, or very small earnings Widely used Permanent vs. transitory earnings Related to stock returns Management discretion for earnings Price-to-Earnings Multiple Definitions Trailing P/E Uses last year’s earnings Preferred when forecasted earnings are not available Forward P/E Uses next year’s earnings Preferred when trailing earnings are not reflective of future PEG Ratio 𝑃/𝐸 𝑃/𝐸/𝐺 = 𝑔 Issues in Calculating EPS EPS Dilution Underlying Earnings Normalized Earnings Differences in Accounting Methods Method of Comparables Benchmark Value of the Multiple Choices Industry peers Industry or sector index Broad market index Firm’s historical values Method of Comparables Using Peer Company Multiples Law of one price Risk and earnings growth adjustments PEG limitations: Assumes linear relationship Does not account for risk Does not account for growth duration Using P/Es for Terminal Value Justified P/E P/E = (D/E)/(r – g) Sensitive to required inputs P/E Based on Comparables Grounded in market data If comp is mispriced, terminal value will be mispriced Enterprise Value EV = + market value of common stock + market value of preferred equity + market value of debt + minority interest - cash and investments EBITDA EV/EBITDA 𝐸𝑛𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑠𝑒 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝐸𝐵𝐼𝑇𝐷𝐴 Enterprise Value/EBITDA Multiple Rationales & Drawbacks Rationales Drawbacks Useful for comparing firms of different leverage Exaggerates cash flow Useful for comparing firms of different capital utilization Usually positive FCFF more strongly grounded Issues in Using Enterprise Value Multiples EV = Market Value of Stock + Debt – Cash – Investments Justified EV/EBITDA • Positively related to FCFF growth • Positively related to ROIC • Negatively related to WACC Comparables May Utilize TIC Other EV Multiples • • • • EV/FCFF EV/EBITA EV/EBIT EV/S Equity / Book Value 𝐸𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑡𝑦 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 𝐸/𝐵 = 𝐵𝑜𝑜𝑘 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒 Price-to-Book Value Multiple Rationales Book Value Is Usually Positive More Stable than EPS Appropriate for Financial Firms Appropriate for Firms that Will Terminate Can explain stock returns Price-to-Book Value Multiple Drawbacks Does Not Recognize Nonphysical Assets Misleading when Asset Levels Vary Can Be Misleading Due to Accounting Practices Less Useful when Asset Age Differs Can Be Distorted Historically by Repurchases Adjustments to Book Value Intangible Assets Inventory Accounting Off-BalanceSheet Items Fair Value Price-to-Cash-Flow Multiple Rationales Cash Flow Less Easily Manipulated Ratio More Stable Than P/E Ratio Addresses Quality of Earnings Issue with P/E Ratio Can Explain Stock Returns Price-to-Cash-Flow Multiple Drawbacks Cash Flow Can Be Distorted FCFE More Volatile and More Frequently Negative Cash Flow Increasingly Managed by Firms Cross-Country Comparisons US GAAP vs. IFRS • Net income higher under IFRS • Shareholder's equity lower under IFRS • ROE higher under IFRS Valuation Multiples Inflation • P/CFO & P/FCFE most comparable • P/B, P/E, & EBITDA multiples least comparable • Higher inflation Lower justified price multiples • Higher pass-through rates Higher justified price multiples