* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inherited Traits
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
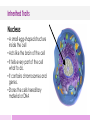
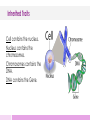
Inherited Traits Presented by Kesler Science Essential Questions: 1. What are inherited traits? 2. How are traits governed by the genetic material found in the genes within chromosomes in the cell nucleus? Inherited Traits Heredity The transfer of traits from one generation to another generation. Inherited Traits Gregor Mendel • Known as the “father of modern genetics” • Born in 1822 • A monk, in Austria Mendel discovered the basic principles of heredity through experiments with pea plants. Inherited Traits Inherited Traits • A characteristic or features of one organism that are inherited (passed from parent to offspring). • In humans • Freckles, eye/hair color, dimples • In animals • Eye/hair color, hair texture, face shape • In plants • Leaf shape, plant height, flower color Inherited Traits Dominant Traits • Traits that hide other traits when passed on to offspring. • Shows its specific trait even if only one parent passed the gene to the child. • When a child inherits dominant brown-hair gene from dad, the child will have brown hair. Inherited Traits Recessive Traits • Traits that get hidden by dominant traits. • Shows its specific trait when both parents pass the gene to the child. • When a child inherits recessive blue-eye gene from both mom and dad, the child will have blue eyes. Quick Action – Inherited Traits • Stand up and find a partner to work with. • Using this diagram make a list for each of you of the dominant traits you have. • Think about your parents, who did you get each dominant trait from? Quick Action – INB Template Title INB Template 1. 2. 3. 4. Cut out the Template on the solid lines Glue narrow tab into notebook Folds like a fan Write notes under vocabulary Inherited Traits How are traits passed? • When organisms reproduce, traits are passed from parent to offspring. • It all begins in the organisms’ cells. • Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. • Cells contain the body’s hereditary material and can make copies of themselves. Inherited Traits Nucleus • A small egg-shaped structure inside the cell • Acts like the brain of the cell • It tells every part of the cell what to do. • It contains chromosomes and genes. • Stores the cells hereditary material or DNA Inherited Traits Chromosomes • Thread-like structures that are found in the nucleus of a cell that contains all DNA. • Each chromosome is made of protein and a single molecule of DNA. • Comes in matching sets of two • Human cell nucleus contains 46 chromosomes or 23 pairs. • Half of these chromosomes come from one parent and half come from the other parent. Inherited Traits DNA • Molecule that carries the genetic instructions for all living organisms. • Short for deoxyribonucleic acid • Contains the specific instructions that make each type of living creature unique. • Determines how the cells in a body will function Inherited Traits Genes • Genes determine traits. • A stretch of DNA on a chromosome with instructions for one trait. • Like chromosomes, genes also come in pairs. • Each parent has two copies of each of their genes. • Each parent passes along just one copy to make up the genes of the offspring. Quick Action – Inherited Traits • Stand up and find a partner to work with. • Make a Venn diagram for the similarities and differences between DNA and genes. Quick Action – Inherited Traits Write About 1. Make a list in order from largest to smallest of the 4 cell parts you just learned about. 2. Think it through. Which one is inside the other? 3. Make a quick sketch in your notebook showing this order. Inherited Traits Cell contains the nucleus. Nucleus contains the chromosomes. Chromosomes contains the DNA. DNA contains the Gene. Inherited Traits Acquired Traits • Physical characteristic of an organism • Not passed down to offspring genetically • Is a learned trait • Is a product of the environment’s influence on the organism Check for Understanding Can you… 1. Recognize inherited traits? 2. Explain how genetic material found in genes governs inherited traits?