* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download End of the Cold War
Survey
Document related concepts
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
War in Vietnam (1954–59) wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Canada in the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Cuban Missile Crisis wikipedia , lookup
North Vietnam wikipedia , lookup
Role of the United States in the Vietnam War wikipedia , lookup
Operation Cyclone wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Crisis of 1961 wikipedia , lookup
Sino-Vietnamese War wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1947–1953) wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
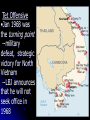
John F Kennedy’s Containment Flexible Response •Policy of containment does not change, just the means •ICBM buildup, Green Berets, Peace Corps, Alliance for Progress •“Race to the Moon” Cold War under Kennedy •Bay of Pigs (April 1961)—Plan to take out Castro fails, US—weak •Berlin Wall (August 1961)—Khrushchev asks Kennedy to remove U.S. troops from Berlin, Kennedy refuses --Khrushchev has the East Germans build a wall around West Berlin --lack of strong response is a further sign of JFK’s weakness --the wall will be a symbol of the Cold War until 1989 Cuban Missile Crisis (October 1962) --Soviets start to build missile sites in Cuba --Kennedy issues ultimatum to Khrushchev to remove the missiles and sets up a naval blockade of Cuba --VERY TENSE, U.S. forces set on highest alert, prepare for invasion --Closest the two sides came to war --Khrushchev agrees to withdraw missiles if US withdraws missiles from Turkey --cooling of direct confrontation between the two sides, still have rivalry over Third World Countries Vietnam (1950-1975) “Containment’s Crisis” --French tried to re-colonize Indochina and needed help, Truman sent aid (1950) --by 1954 we are financing 78% of the war --1954 Geneva Accords split country along 17th Parallel, allow for free elections in 3 years, US stops elections --Eisenhower and Kennedy continue involvement (Domino Theory) North Vietnam --Ho Chi Minh “we hold these truths” --Communist --Father of the country South Vietnam --Ngo Dinh Diem --Democracy --unpopular --Diem assassinated in a military coup d’etat 1963 --Kennedy will take care of this once he returns from Dallas Lyndon Johnson’s Containment •Gulf of Tonkin Resolution (1964) --not a Declaration of War, does not feel he needs one --as war progresses, casualties increase, protests start --North Vietnamese see this and they use it to their advantage --N Vietnam uses the “will” of the U.S. citizens to help their cause Tet Offensive •Jan 1968 was the turning point --military defeat, strategic victory for North Vietnam --LBJ announces that he will not seek office in 1968 July 20, 1969 Moon Landing US puts the first man on the Moon “One small step for man, One Giant leap for Mankind”—Neil Armstrong Richard Nixon Détente •Saw Vietnam as a mistake •We focused on stopping Communism rather than focusing on the people of the country and what they wanted •Why would it be better to support a government that is popular with the people as opposed to focusing on Communism? •Détente—permanent thawing of cold war tensions through negotiations and bringing other nations in to help deter USSR •Nixon goes to China (February 1972) --example of supporting popular governments AND gaining allies to balance the Soviet strength --Nixon goes to China and meets with Mao, HUGE STEP --wake-up for USSR, China had been a traditional ally East meets West Mao Zedong shakes hands with Richard Nixon SALT I (May 1972) --Summit meeting as both sides discuss limiting the amount of nuclear missiles, warheads and submarines --Leonid Brezhnev agreed to push North Vietnam to the negotiating table --Short-term agreement Nixon and Vietnam •Vietnamization—fighting to be done by the Vietnamese, reduction in number of US troops --Public finds out that Nixon was secretly bombing Cambodia, leads to further chain of events that lead to his resignation --April 1975 Vietnam falls •War Powers Act (1973) --During the Cold War, Presidents sent troops without congressional authorization. Cite examples --Resolution stated President must tell Congress he is sending troops into action and then must remove them within 60-90 days unless congress grants their approval --emphasizes that Presidents MUST discuss troops commitment with congress Jimmy Carter Détente Détente continued --Emphasis on Moral foreign policy, especially on human rights --negotiation rather than confrontation Events under Carter •Camp David Accords (1977) --Israel and Egypt Yom Kippur War 1973 --Henry Kissinger attempted Shuttle Diplomacy --US supported Israel, USSR supported Egypt --Carter gets Anwar Sadat and Menachem Begin to negotiate face-to-face --Ends disputes between these nations, Carter’s high point as President •SALT II (June 1979) --replaces SALT I with a long-term agreement --never ratified, both sides agreed to the outline limits •Afghanistan (December 1979) --Soviets invade to support the Marxist dictatorship in Afghanistan --ends era of Détente --U.S. sent millions of dollars worth of guns and food to Afghanistan to aid the mujahidin/freedom fighters and refugees Iranian Hostage Crisis (November 1979) --Started when the people revolted against the Shah, who was supported by the U.S. --Iranian students seized the American Embassy, captured 60 Americans and held them hostage for 444 days --Carter received blamed for allowing this to happen, which coupled with his economic difficulties, hurt his Presidency --Carter asks USSR to withdraw from Afghanistan, they refuse --Carter leads a boycott of the 1980 Summer Olympic games which are held in Moscow, 64 nations in all will boycott --Soviets and their allies will boycott the 1984 Summer Games in Los Angeles 1980 Final Medal Standings Nation Gold Silver Bronze Total U.S.S.R. 80 70 47 197 GDR 47 36 43 126 Bulgaria 8 16 16 40 Cuba 8 7 5 20 Italy 8 3 4 15 What are examples of Cold War détente in the 1970’s? What are examples of continued tensions between the US and USSR? Reagan’s Dilemma You are a member of President Reagan’s National Security Team. Based on the state of affairs between the United States and the U.S.S.R. in 1981, you must advise him on the following in relation to his Cold War Policy, and the potential reaction from the U.S.S.R. 1. How do you plan on reversing Soviet Expansion? 2. How do you attempt to convince the Soviets to ease their strict political and economic controls over their people? 3. Are you going to intensify or thaw the arms race? Why or Why not? Ronald Reagan Containment •Confrontation --Return to the old idea of challenging the Soviets --Renewal of the Arms Race, Dramatic increase in defense spending (B1 bomber, Strategic Defensive Initiative) --”peaceful coexistence” to the “evil empire” Cold War 1959 Cold War 1982 Mikhail Gorbachev --elected President of the USSR in May 1985 -- Soviet economy was stagnate, falling behind the Western democracies --Gorbachev sought to change the system so it would work more efficiently and more democratically. --Two key phrases: "glasnost" (openness) and "perestroika" (restructuring) -- Perestroika sent shock waves throughout the USSR and other Soviet Bloc nations --Gorbachev wants to shift resources from the military to the civilian sector of the economy. -- He also began to argue in favor of an end to the arms race with the West --meets with Reagan in November 1988 to discuss reduction. --Gorbachev’s plans and ideals create problems for him in the Soviet Union Who in the USSR, would be against these changes? “Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall.” End of the Cold War •May 1988-Soviet Troops start to withdraw from Afghanistan •March 1989—Hungary allows free elections, Gorbachev will not stop the elections •June 1989—Poland allows free elections •October —East Germany celebrates 50th anniversary, two days later 70,000 protesters demand an end to the regime •November—Berlin Wall is torn down •November, December 1989— Free elections held in Bulgaria, Romania and Czechoslovakia Changes in the Soviet Union •August 1991 •Military places Gorbachev under house arrest •attempts a coup d’etat •December 1991 •Boris Yeltsin, President of the Russian Republic, occupies the Parliament building defying the Coup • Army backs down •December 1991 •Republics of Russia, Belarus and Ukraine starting the path to completely dissolving the Soviet Union Who ended the Cold War? Who ended the Cold War?