* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Origins of the Cold War
Survey
Document related concepts
Allies of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact wikipedia , lookup
Background of the occupation of the Baltic states wikipedia , lookup
German–Soviet Axis talks wikipedia , lookup
Ursula Kuczynski wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
European theatre of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of the Winter War wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
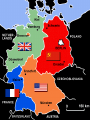
Origins of the Cold War After WWII • Germany & Japan were in Ruins Germans were “…without houses without window panes, without roofs, holes in the asphalt, rubble, rubbish, and rats.” “Tokyo was flattened, and people were living in holes with corrugated roofs.” Postwar Germany July 1945 - Allied leaders met in Potsdam, Germany Potsdam Conference Stalin, Truman, & Attlee Came up with joint occupation of four zones West -- Britain, France & America East -- Soviets • They also divided Austria into zones • Jointly with Russia Berlin with in Eastern patrician Founding of Israel • Zionism: The movement seeking a Jewish homeland in Palestine. Both the US and the Soviet Union recognized the nation of Israel in 1948 • Arabs reacted violently, and set out to reclaim the state for Palestine. • Cold War = the competition for global power and influence between the US and the Soviet Union. • The Cold War (1945-91) was one of perception. Where neither side fully understood the intentions and ambitions of the other. This led to mistrust and military build-ups. United States – U.S. thought that Soviet expansion would continue and spread communism throughout the world. – They saw the Soviet Union as a threat to their way of life; especially after the Soviet Union gained control of Eastern Europe. IRON CURTAIN • In 1946, Winston Churchill gave a speech at Fulton College in Missouri in which he proclaimed that an “Iron Curtain” had fallen across Europe. Truman Doctrine • In March 1947, U.S. president Harry Truman proclaimed the Truman Doctrine. • Reasoning – Threatened by Communist influence in Turkey and Greece – “Two hostile camps” speech •Financial aid “to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation” •Sent $400 million worth of war supplies to Greece and helped push out Communism •The Truman Doctrine marked a new level of American commitment to a Cold War. Marshall Plan • Economic aid to all European countries offered in the European Recovery Program • $17 billion to western Europe • Soviets were refused – The blame for dividing Europe fell on the Soviet union, not the United States. And the Marshall Plan proved crucial to Western Europe’s economic recovery. •George C. Marshall won the Nobel Peace Prize in 1953 Berlin Airlift • The Soviet Union opposed the Marshall Plan • June 24th 1948 Soviets blocked all roads in and out of Berlin cutting off supplies and shipments. • Western leaders over the next 10 months carried more than 2 million tons of food and supplies to the people of West Berlin. Beginning of NATO • After Berlin the US shifts attention from economic recovery military security. North Atlantic Treaty Organization & the Warsaw Pact • Stalin’s aggressive actions accelerated the American effort to use military means to contain Soviet ambitions. • The U.S. joined with Canada, Britain, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg to establish NATO, a mutual defense pact in 1949. • Early critics of the UN insisted that it was doomed to fail because it did not have the power to enforce its own decisions • When West Germany joined NATO in 1955, the Soviet Union countered by creating its own alliance system in eastern Europe– the Warsaw Pact (1955)