* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Two Worlds of Christendom
Survey
Document related concepts
Medieval technology wikipedia , lookup
Post-classical history wikipedia , lookup
Early Muslim conquests wikipedia , lookup
Muslim conquest of the Maghreb wikipedia , lookup
Migration Period wikipedia , lookup
Late Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
European science in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Early Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 13th century wikipedia , lookup
Italy in the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
High Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Christianity in the 9th century wikipedia , lookup
History of Christianity during the Middle Ages wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
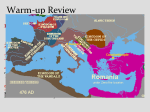
Two Worlds of Christendom Chapter 16 I. Quest for Political Order • Political challenges in the west led to invaders • Byzantine Empire – Economically sound capital – Architecturally wealthy • Caesorpapism -Secular lord but also played a role in church affairs • Justinian & Theodora (Byzantine emperor & wife) -Hagia Sophia-important Christian architecture -Justinian’s CodeCodification of Roman Law Influenced civil law codes of Europe, US, Japan II. Muslim Conquest & Byzantine Revival • Muslim Conquest -Byzantine under Muslim rule for a time - “Greek fire” helps keep Muslims away • Theme System - Response to Islamic rulers - Province is under a general’s authority - Civil & military responsibility - Free peasants recruited - Received allotments for service III. Rise of the Franks • Germanic Kingdoms arise in Roman areas - adopted Christianity - adapt Roman Laws • Franks -Military & Political Power in W. Europe - Adoption of Christianity led to popularity -Charles Martelstops Muslim invasiondid not sack further west III. Rise of the Franks • Charlemagne - re-establish centralized imperial rule - Intelligent • Charlemagne’s Administration - Traveled through horseback no elaborate bureaucracy relied on deputies - Miss dominicienvoys that reviewed accounts of local authorities III. Rise of the Franks • Charlemagne as Emperor - 8000cepope proclaims him emperor, may not have been planned IV. Age of Vikings • Louis the Pious - Surviving son of Charlemagne—>Lost control of local authorities ended the empire -Louis’ sons split the empire between them warred against each other • Invasion -Magyars, Vikings (Norse people) -Attacked settlements, cities, and monasteries IV. Age of Vikings • Devolution of Political Authority - Since Carolingians had no real protection regional and local protection - Made it difficult for true imperial rule V. Two Economies of Early Medieval Europe • Byzantine Peasantry -Sprouted from theme systemprovided large agricultural surpluses • Manufacturing - Supported by agriculture - Glassware, linen, woolen textiles, gems, jewelry • Silk -major contribution to economy V. Two Economies of Early Medieval Europe • Byzantine Trade - Constantinople clearinghouse for W. Eurasia -Traded w/Muslim counterparts -Bezant standard currency in Mediterranean basin • Heavy Plows - took more energy but provided greater agricultural production - Cleared lands for more cultivation V. Two Economies of Early Medieval Europe • Trade in Western Christendom - Local markets & fairs - Christian merchants • Norse Merchant Mariners - Medieval Merchantscargoes fish, furs, wine, honey - silver used for minting coins VI. Social Development of Two Worlds of Christendom • Byzantium: Urban Society - most urbanized society, main area, everything in “ the city” • City Life – – – – – – Various forms of city centers Women were highly protected Artisans lived above their shops Gov’t official lived in apartments Poor in tenaments EVERYONE still wanted to be a part of the CITY VI. Social Development of Two Worlds of Christendom • Attractions - Baths - Taverns - Restaurants - Social Gatherings • Western Europe: Rural Society - agriculture enough for locals, but not enough to support larger populations VI. Social Development of Two Worlds of Christendom • The Question of Feudalism - a political and social order of medieval Europe? - supposed hierarchy: Lordsvassalsretainers (lands for military service)Peasantry - more complex than what was thought • Peasants - provide agriculture • Population - Population decline due to economic disease and political turmoil - 36 mil. In 200ce – 26 mil. In 600ce VII. Popes and Patriarchs • The Papacy - Roman empire collapsed but papacy survives as spiritual authority - 1st close ties w/Byzantine, later more independent, focus on the west • Pope Gregory I - Independent course of Roman Church - Papal primacypope supreme authority for ALL Christians - Enhance Christianity in everyday lives. VII. Popes and Patriarchs • Patriarchs - part of the state - caesorpapism now creates tension • Iconoclasm - Byzantine practice - the ridding of icons (sculptures, images) - created tension VII. Monks & Missionaries • Asceticism - holiness rather than world success - celibacy, fasting, prayer • St. Basil (Byzantine) & St. Benedict (Italy) - reformers - regulations for monasteries - practice mild for of ascetism - gave up their lives, lived in smaller community VII. Monks & Missionaries • Monasticism & Society - Social Services counsel, relief efforts, medical, inns, education • Missionaries VII. Two Churches • Constantinople and Rome are at odds with each other • Religious Rivalry - Ritual and Doctrinal differences • Schism - Patriarch vs. Popesbattled their positions - Patriarch autonomy of Christian Jurisdiction - Popeprimal papacy - East and West go separate ways excommunicationnot properly Christian - 1054 West known as Roman Catholic Church, East known as Eastern Orthodox