* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Volcanoes - Ms. Mudd`s Science Spot
Mono–Inyo Craters wikipedia , lookup
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Blanco (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Lascar (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
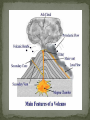
6 th Grade Ms. Mudd Early sailors mistakenly thought glistening calcite crystals inside the tuff rocks were diamonds, leading to the incorrect name. Diamond Head formed when hot magma rising up a conduit hit ocean water, causing large explosions that threw exploded magma particles (tuff) into a broad ring. Over the last 10,000 years, Mt. Shasta has erupted on average once every 800 years. During the 3,500 years the volcano has erupted about once every 300 years. The most recent eruption may have occurred in 1786 A.D. Kohala is the oldest of the subaerial volcanoes that make up the Island Of Hawaii. Kohala is considered to be extinct because it has not erupted for 60,000 years. Element-is a substance that cannot be broken down into other substances. Compound- is a substance made of two or more elements that have been chemically combined. Each substance has a particular set of physical and chemical properties. These properties can be used to identify a substance or to predict how it will behave. Physical Properties- is any characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the composition of the substance. Density, Hardness, Melting Point, Boiling Point Chemical Properties- is any property that produces a change in the composition of matter. Ability to burn, react, or combine with other substances. Viscosity is the resistance of a liquid to flowing. Because liquids differ in viscosity, some liquids flow more easily than others. The greater the viscosity of the liquid, the slower it flows. The lower the viscosity, the more easily a liquid flows. The movement of the particles that make up a liquid determine its viscosity. The greater the friction among particles the higher the viscosity. Mantle rock melt to form magma. Not all types of magma have the same viscosity. The viscosity of magma depends on its silica content and temperature. Magma is a complex mixture, but its major ingredient is silica. The compound silica is made up of particles of the elements oxygen and silicon. Silica is the most abundant material in the Earth’s crust. The content in magma is between 50-70 percent. The amount of silica helps determine its viscosity. The more silica magma contains the higher the viscosity. This magma is light colored, sticky and doesn’t flow very far. When it cools it forms the rock rhyolite, has the same composition as granite. The less silica magma contains, the lower its viscosity. Low silica magma flows steadily and produces dark colored lava. When this kind of lava cools, it forms rocks like basalt. How does temperature affect viscosity? Viscosity increases as temperature decreases. Heated syrup flows easier than cold syrup. The temperature of magma can range from 750-1, 175 degrees C. The hotter the magma the lower it’s viscosity and it flows more rapidly. Cooler types of magma have high viscosity and flow slowly. Pahoehoe is fast moving, hot lava that has low viscosity. The surface looks like a mass of wrinkles or cake batter. Aa has a higher viscosity. When aa hardens, it forms a rough surface consisting of jagged lava chunks. What is an element? What is a compound? What is the difference between a chemical and physical property? Give examples. What is viscosity? The viscosity of magma depends on what two things? Element-is a substance that cannot be broken down into other substances. Compound- is a substance made of two or more elements that have been chemically combined. Physical Properties- is any characteristic of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the composition of the substance. Chemical Properties- is any property that produces a change in the composition of matter. Viscosity is the resistance of a liquid to flowing. The viscosity of magma depends on its silica content and temperature. Beneath a volcano, magma collects in a pocket called a magma chamber. The magma moves up through a pipe, a long tube in the ground that connects the magma chamber to the Earth's surface. Molten rock and gas leave the volcano through an opening called a vent. Most vents are central vents on the top of a volcano, but some vents can be on the sides. A lava flow is the area covered by lava as it pours out of a vent. A crater is a bowl shaped area that may form at the top of a volcano around the central vent. As magma rises to the surface, the pressure of the surrounding rock on the magma decreases. The dissolved gases begin to expand, forming bubbles. As pressure falls within the magma, the size of the gas bubbles increase greatly. These expanding gases exert an enormous force. When a volcano erupts, the force of the expanding gases pushes magma from the chamber through the pipe until it flows or explodes out a vent. Once magma escapes the volcano it becomes lava. A volcano erupts quietly if its magma is low in silica. Low silica magma has low viscosity and flows easily. The gases bubble out gently. The lava oozes quietly out of the vent. Creating either pahoehoe or aa. The Hawaiian Islands were formed from quiet eruptions. A volcano erupts explosively if its magma is high in silica. High silica magma has high viscosity, making it thick and sticky. The high viscosity magma does not flow out of the crater. Instead it builds up and clogs the pipe. The dissolved gases and water vapor cannot escape the thick magma. The trapped gases build up pressure until they explode. An explosive eruption breaks lava into fragments that quickly cool and harden into pieces of different sizes. The smallest pieces are volcanic ash-fine, rocky particles as small as a speck of dust. Pebble sized particles are called cinders. Larger pieces are called bombs. They range in size from baseball to the size of a car. A pyroclastic flow occurs when an explosive eruption hurls out a mixture of hot gases, ash, cinders, and bombs. The activity of a volcano can last less than a decade or 10 million years. Active- is one that is erupting or has shown signs that it may erupt in the near future. Dormant or sleeping- Scientist expect a dormant volcano to awaken in the future and become active. Extinct or dead- the volcano is unlikely to ever erupt again. The time between eruptions may be hundreds or many thousands of years. People living near dormant volcanoes may be unaware of the danger. Dormant volcanoes can become active at any time. 1. What are the main parts of a volcano? 2.Describe the order of parts through which magma travels as it moves to the surface. 3.What are the two main types of eruptions? 4.What do the lava flows made of pahoehoe and aa indicate about the type of volcanic eruption that occurred? 5.What are the three stages of volcanic activity?