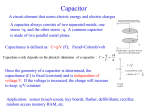
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exercise 2B_ Capacitor(2)
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor discharge ignition wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
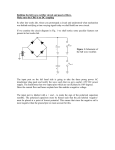
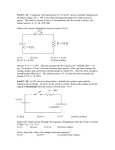
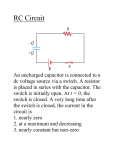
CK Cheung Exercise 2_ Capacitor(1)_0506 89' connected in series to a d.c. voltage supply as shown. At time t = 0, the key K is closed. Which of the following statements is/are true? 26. An isolated spherical conductor of radius r is charged to a potential V. The total electrical energy stored is A. V²/(80 r). B. V²/(40 r). C. V²/(20 r). D. V² (20 r). V² (40 r). E. (1) At any time t the sum of the potential differences across C and R is a constant. (2) The capacitor is almost fully charged after a time t = 5 CR. (3) The final charge on the capacitor does not depend on the position of R in the circuit. 89' 29. 1 1 A In the A. B. C. D. E. B 2 above circuit, the (1), (2) and (3) (1) and (2) only (2) and (3) only (1) only (3) only 85' equivalent resistance between A and B is 43. C1 C2 A. 2/7 . B. 2/5 . C. 2/3 . A charged capacitor C1 is connected to an D. 2 . uncharged capacitor C2 as shown. E. 5 . If E1 = the total enrgy stored in C1 and C2 83' 46. before connection, and E2 = the total energy stored in C1 and C2 R C after connected, K d.c. which of the follwoing is/are correct? (1) A capacitor and a resistor are E1 = E2. (2) After connection, the p.d. across C1 is 1 CK Cheung equal to the p.d. across C2. In the circuit above, the equivalent resistance across XY is (3) After connection, the charges stored in C1 and C2 are in the ratio capacitance of C1 capacitance of C2 A. 0 . . B. 10 . C. 20 . D. 40 . E. 64 . A. (1), (2) and (3) B. (1) and (2) only C. (2) and (3) only D. (1) only 87' E. (3) only 28. A 3 F 86' 32. 4 F C 16 V 1 F 2 B 2 2 F D 2mH A voltage of 1200 V is applied across AB in 2 F the capacitor network shown above. 2 The voltage across CD is found to be 450 V. If after some time, the voltage across CD When a steady state is reached, the current delivered by the battery is suddenly jumps to 600 V, which capacitor(s) A. zero. A. 1 F B. C. D. 4.0 A. 5.0 A. 5.3 A. B. 2 F C. 3 F D. 4 F E. 8.0 A. has been shorted? E. 86' 34. All 4 capacitors have been shorted. Further, can you find the charge stored in each capacitor in the above circuit? 8 8 8 90’ 8 8 X Y 8 8 30. 8 2 CK Cheung A parallel-plate capacitor is connected to a battery as shown. The above figure shows a network of resistors. If a voltage of 100Vis applied across terminals A and B, the potential difference between C and D is 80V. If the voltage is applied across terminals C and D instead. What is the potential difference between A and B ? What will happen if the separation of the plates is increased? capacitance voltage charge A. decreases decreases decreases B. decreases unchanged decreases C. decreases decreases increases A. 80V D. increases unchanged decreases B. 60V E. increases unchanged increases C. 40V D. 20V E. 90’ It cannot be found as the value of R is not known. 33. 2000’ 3 3 23. 3 I 6V In the above circuit, the battery has The figure shows some of the resistors in a negligible internal resistance. network of resistors. The magnitudes and The current I is directions of some of the currents are A. 2/3 A. B. 1 A. C. 4/3 A. D. 2 A. E. 6 A. Also find the equivalent resistance across the battery (1Ω) marked as shown. Find the magnitude and direction of the current passing through the resistor R. 2001’ 21. A. 0.2A from right to left B. 0.2A from left to right C. 0.4A from right to left D. 0.4A from left to right E. It cannot be determined as the value of R is not given. 3 CK Cheung 81’IIB(4) Revision on R-C circuit 81’ IIB 4. A student is asked to perform an experiment to demonstrate that the charge on a capacitor is proportional to the p.d. across its terminals. The circuit to be used is shown in Figure 2. A 10 V C S to oscilloscope y-input; timebase off; y-sensitivity set to d.c. 2 V/cm Figure 2 The principle of the experiment is to close switch S and charge the capacitor linearly by continuously adjusting the variable resistor to keep the current in the circuit constant at its initial value. The p.d. across the capacitor will therefore increase linearly with time, and a graph of the deflection of the oscilloscope spot in the y-direction against time will be a straight line. (a) The student decides that it would be most convenient to start with the variable resistor set to its maximum value of 100 k and to use an ammeter which he can maintain at full scale deflection when the switch is closed. What should be the full scale deflection of the meter? (b) Having selected his meter, the student considers the deflection of the oscilloscope spot. He decides that he will be able to time a deflection rate of 0.1 cm/s satisfactorily. What value of C should he choose? (c) What will be the value of the variable resistor 10 s after closing the switch S? (8 marks) 4








![Sample_hold[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008409180_1-2fb82fc5da018796019cca115ccc7534-150x150.png)





![1. Higher Electricity Questions [pps 1MB]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000880994_1-e0ea32a764888f59c0d1abf8ef2ca31b-150x150.png)