* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 7: The Origins and Spread of Islam
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Violence in the Quran wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Muhammad and the Bible wikipedia , lookup
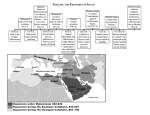
Chapter 7: The Origins and Spread of Islam Guiding Question: How did Islam originate and spread? Name: Due Date: Period: Vocabulary Complete the chart below for the vocabulary terms for this chapter. Term Definition Islam The religious faith of Muslim; also the civilization based on the Islamic religion and the groups of countries where Islam is the main religion Muhammad A man born around 540 CE who taught the faith of Islam Polytheism The belief in more than one god Prophet A person who speaks or interprets the words of God Monotheism The belief in a single God Muslim A follower of the Islamic faith Boycott A refusal to do business with an organization or group Siege A military action in which a place is surrounded and cut off to force those inside to surrender Picture that helps you remember the term Section 7.2: Arabia in the 6th Century 1. Describe Makkah during Muhammad’s birth. Possible Answer: During the time of Muhammad’s birth, Makkah was a prosperous desert trading city on the Arabian Peninsula where many merchants had become wealthy. Makkah was also a religious center, and pilgrims from all over Arabia came to worship at the Ka’bah 2. Why was the Ka’bah built and how was it being used during the time of Muhammad’s birth? Why? The Ka’bah was built by Abraham, for God, centuries before Muhammad’s birth. In Muhammad’s time, most Arabs were polytheists and the Ka’bah housed statues of many different gods. ***For sections 3-6: • Read the section • Complete the questions • Find the words/terms around the room that match the section of the reading and write the English translation Section 7.3: Muhammad’s Early Life 1. Muhammad was born around 570 CE. Muhammad was sent away to live with a clan, but then returned to his birth city and grew up. How was Muhammad viewed by others as an adolescent and young man? As an adolescent, Muhammad was seen as a trustworthy and honest man by others. 2. Walk around the room and find the four words or terms that best match the part of the story you just heard. Write the English translation of the Arabic words here. You can try to write the Arabic words as well if you want. Birth, orphan, trader, marriage Section 7.4: The Call to Prophethood 1. What happened to Muhammad around 610 when he went to meditate in a cave? Around 610, Muhammad went to meditate in a cave and received the call to be a prophet (messenger of Allah) from the angel, Gabriel. 2. What does the word Muslim mean? The word Muslim means “those who surrender to God.” 3. What is one things that Muslims did right away in an attempt to create a just society? In an attempt to create a just society, Muslims granted more rights to women and ensured their equality before God. 4. What is contained in the Qur’an? The messages from Gabriel were written down by Muhammad’s followers and recorded in the Qur’an. 5. Walk around the room and find the four words or terms that best match the part of the story you just heard. Write the English translation of the Arabic words here. You can try to write the Arabic words as well if you want. Cave, Gabriel, Allah, Qur’an Section 7.5: Muhammad’s Teachings Meet with Rejection 1. What did Muhammad teach when he preached to the Makkans? Muhammad taught that people must worship one God, that all believers in God were equal, and that the rich should share their wealth with the poor. He urged Makkans to take care of orphans and the poor, and to improve the status of women. 2. Why did most Makkans reject Muhammad’s teachings? Makkan leaders rejected Muhammad’s teachings because they did not want to share their wealth, and they feared that if Muhammad became too powerful he would seize political power. 3. Why is Jerusalem a holy city for Muslims? Jerusalem is a holy city for Muslims because it is the site of Muhammad’s Night Journey where he met and prayed with earlier prophets, such as Abraham, Moses, and Jesus, before being guided through the seven levels of heaven and meeting God (Allah). 4. Walk around the room and find the four words or terms that best match the part of the story you just heard. Write the English translation of the Arabic words here. You can try to write the Arabic words as well if you want. Reject, Followers, Boycott, Night Journey Section 7.6: From the Migration to Madinah to the End of his Life 1. On the timeline below, place each of the following events. Make sure you include the date for each event. One example is done for you. • Makkans make a truce with the Muslims • Muhammad develops a new Muslim community in Madinah • Muhammad delivers his Last Sermon • Fighting breaks out between the Muslims and Makkans • Muhammad and his followers leave on the hijrah • Muhammad’s army captures Makkah: he rededicates the Ka’bah to Allah 622 C.E. Muhammad and his followers leave on the hijrah 624 C.E. Fighting breaks out between the Muslims and Makkans 628 C.E. Makkans make a truce with the Muslims 632 C.E. Muhammad delivers his Last Sermon 600 CE 622- 628 CE Muhammad develops a new Muslim community in Madinah 650 CE 630 C.E. Muhammad’s army captures Makkah; he rededicates the Ka’bah to Allah 619 C.E. Muhammad’s uncle Abu Talib dies and Muslims come under more attacks in Makkah 2. Walk around the room and find the four words or terms that best match the part of the story you just heard. Write the English translation of the Arabic words here. You can try to write the Arabic words as well if you want. Madinah, People of the Book, Battles, Last Sermon Section 7.7: The Four Caliphs 1. List the accomplishments or events that occurred under each of the first four caliphs. Caliph Abu Bakr Caliph Umar Completed the unification of Arabia so that Islam could spread beyond the peninsula Continued to expand the empire through conquest Used military force to reunite the community when they tried to break away Spread religion, allowed Muslim to gain new lands, resources, and goods Caliph Uthman Unite Muslims Oversaw official edition of Qur’an Caliph Ali ibn Abi Talib Some Muslims challenged his rule, which led to a civil war People not happy with him because he ruled unfairly and he was killed Set up governments and tax systems in new provinces of Iraq, Persia, eastern Mediterranean, North Africa Section 7.8: The Umayyad Dynasty 1. Explain the reason for the schism after Ali’s death. What two branches emerged? After Ali’s death, there was a disagreement about who should claim the caliphate. Most Muslims, called Sunnis, wanted Mu’awiyah, the leader of the Umayyads. A smaller group of Muslims, called the Shi’ah, thought that the caliph should only be a direct descended from Muhammad. The schism still exists. 2. What are examples of the ways that Muslim lands took on more elements of Arab culture? Some of the ways that Muslim lands took on more elements of Arab culture are through the introduction of Arabic language, Arabs taking over as top officials, and the use of new Arab coins. 3. Why was Muslim expansion into Spain significant? Muslim expansion into Spain was significant because they had expanded into Europe. Additionally, the city of Cordoba became a center of learning where Muslim, Jewish, and Christian scholars could share ideas and make advances in culture. Section 7.7 & 7.8 1. Complete the map below by adding labels for Tours, Jerusalem, and Damascus. Then color in the key and the corresponding regions. Use three colors.