* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review for Astronomy Exam 1
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
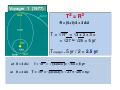
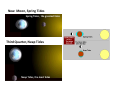
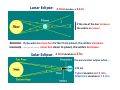
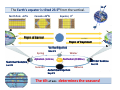
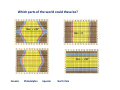
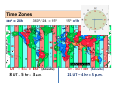
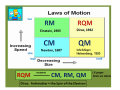
Review for Astronomy Exam 1 • Note that a Review emphasizes the main concepts and is not to replace your e-text and notes in class. • Do not expect a review to cover everything or include much on critical thinking. edited by Michael J. Ruiz for website posting prepared by Lyubov Nichols 1 mm = 0.001 m = 10-3 m 1 cm = 10 mm = 0.01m = 10-2 m 1 m = 100 cm = 1000 mm 1 km = 1000 m =105 cm 1 m = 3.28 ft 1Ȧ = 0.1 nm 1 nm = 10 Ȧ 1 pc = 3.3 ly 100 cm = 1000 mm = 103 mm 100 m = 100,000 mm = 105mm 6560 Ȧ = 656 nm 410 nm = 4100 Ȧ 100 pc = 330 ly Quark: 10-16 m Quasar: 1026 m away Sense of Scale • Solar System – 80 AU across • Our Galaxy 100,000 ly across • Earth – Star (Proxima Centauri, 4 ly) 3 ly away (approx.) • Andromeda Galaxy (2.5 Mly) 3 million ly (approx.) • Local Group of Galaxies – 10 million ly across • Quasars – 10 billion ly away From Quark to Quasar there is 42 (16 + 26 ) powers of ten in distance 16 26 Quark ----------------- Arm (1 m) ----------------- The reaches of the Universe Sun -27 Moon -13 Venus - 4 Sirius -1.5 You can see 2000 stars with the naked eye. The faintest star + 25 Magnitude vs Luminosity (intensity) Hipparchus: 1 2 3 4 5 6 m Weber-Fechner law: 2.5 x 2.5 x 2.5 x 2.5 x 2.5 L 6.25 x 6.25 x 2.5 40 x 2.5 = 100 A star 6 times more intense than +5 mag star will have mag ____ A star 2 mag dimmer in brightness will be measured __________ A star 15 times less intense will be measured ________________ A star 40 times less intense than -10 mag star will have mag ____ The standard distance for Absolute Magnitude is 10 pc = 33 ly Precession 13,000yr (Ursa Minor) 26,000 yr (Lyra) Cosmic “Clock” Cosmic “Day” is 26,000 yr.; Cosmic “Hour” is 2000 yr. Polaris North Celestial Pole is drifting toward Polaris The Vernal Equinox is leaving Pisces to enter the “Age of Aquarius”. “Age “ changes every 2000 years ( 26,000/12 = 2150 yr) (26000/13 = 2000 yr) Vega Greek Ancient Astronomers Thales: the Universe is made of Water Heraclitus: the Universe is made of Fire Empedocles: the Universe is made of Water, Air, Fire, Earth Aristotle: the Universe has 8 crystalline spheres (Moon, Mercury, Venus, Sun, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Stars) he added a fifth element “quintessence” to his cosmological system Ptolemaic model of the Universe: the epicycle, a little circle that the planet follows as it proceeds around the Earth on a larger circle. Eratosthenes: Earth was discovered to be round. 130 CE Bright stars are usually designated by a Greek letter: α, β, γ, δ, ... (α Lyrae in Lyra is Vega) Arab Astronomers • Alhazen (1000 CE) • Arab astronomers named the stars. • Egyptian divided the sky into regions called constellations. Anasazi Sun Dagger (New Mexico) Stonehenge in England Bighorn Medicine Wheel THE BIG FIVE Copernicus Heliocentric model of the Universe ● First Observatory Tycho Brahe ● Tycho’s Supernovae (1572) ● 30 Years of Observations Galileo Galilei ● Laws of Terrestrial Motion ● Moons of Jupiter ● Rings of Saturn ● Phases of Venus ● Craters on the Moon ● Sunspots KEPLER’S LAWS of Planetary Motion • Law of Ellipses - The planets orbit the Sun in elliptical orbits with the Sun at one focus. • Law of Areas - A line drawn from a planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times. • Law of Periods - T x T = R x R x R Planets far from the Sun T2 = R3 take longer to orbit the Sun The planet's year depends on the distance from the Sun. Voyager 1 (1977) T2 = R3 R = (5+1)/2 = 3 AU T = √ R3 = √3 x 3 x 3 = = √27 ≈ √25 = 5 yr Tvoyager = 5 yr / 2 = 2.5 yr at R = 4 AU at R = 3 AU T = √R3 = √ (4x4x4 )= √ 64 = 8 yr T = √R3 = √(3x3x3) = √ 27 ≈ √25 = 5yr Isaac Newton Laws of Motion I. A body experiencing no force continues at rest or at constant speed in a line. ɑ = F/m II. F = mɑ A small mass will undergo a greater change in motion than a larger mass. III. Action – Reaction Universal Law of Gravitation Inverse Square Law F ~ 1/r2 r = 9 AU F = 100 N 3 times less, at r = 3 AU F = ? F = 100 x (3)2 = 900 N r = 20 AU F = 100 N 2 times more If at at at F=? F = 100 / (2)2 = 25 N at r = 15 AU F = 100N 5 times less at r = 3 AU F = ? F = 100 x (5)2 = 2500 N r = 40 AU New Moon, Spring Tides Spring Tides , the greatest tides Third Quarter, Neap Tides Neap Tides, the least tides Lunar Eclipse: A total duration is 5-6 hr. If the size of the Sun increases the umbra decreases. If you were to move Sun farther from planet, the umbra increases. ..................... move Sun closer to planet, the umbra decreases. Solar Eclipse: A total duration is 2 hr. The annual solar eclipse when … 270 km Typical duration is 2-3 min. Maximum duration is 7.5 min The Sun moves about one degree from west to east with respect to the 'fixed' stars. Tsol = 24 hr 10=4min Tsid= 23 hr 56min The Solar Day is the time it takes the Earth to rotate once with respect to the Sun The Sidereal Day is the time it takes the Earth to rotate once with respect to the fixed stars. Sidereal Day is 4 minutes shorter than Solar Day (1/360) x 24 h x (60 min/h) = 4 min 360 days ……. 4min 180 days ……. 8 min 90 days ………16 min 60 days ……… 24 min 30 days ……… 48 min 23.50 The Earth's equator is tilted 23.50 from the vertical. North Pole +900N Canada +450N Equator, 00 N Tropic of Cancer Tropic of Capricorn S Vernal Equinox Spring Mar 21 Aphelion (1.02 AU) Winter Perihelion (0.98 AU) Summer Solstice Jun 21 Winter Solstice Dec 21 Summer Autumn Autumnal Equinox Sep 21 The tilt of axis determines the seasons! Which parts of the world could these be? Dec. = +450 Dec. = 0 Dec. = +900 Canada Philadelphia Equator North Pole Time Zones 3600 = 24h 3600 / 24 = 150 UT - 5 hr = EST (Asheville) 8 UT – 5 hr = 3 a.m. 150 =1h UT - 4 hr = EDT (Asheville) 21 UT – 4 hr = 5 p.m. Distance from lens to F = f. Image stays real, inverted, and gets larger for object distances > f. Image stays real, inverted, and gets smaller for distances > f. What happens when the object is at 2f, i.e., twice the focal distance from the lens? Image stays virtual, upright, and gets smaller for object distances less than f. Image stays virtual, upright, and gets larger for object distances less than f. . 400nm 450 nm shorter wavelength (λ) higher frequency (f) greater energy (E) 500 nm 550 nm E210 nm > 600 nm 650 nm E410 nm E410 nm > E656 nm Electromagnetic radiation is energy composed of rapidly varying electric and magnetic fields. speed c = 300,000 km/s 700 nm longer λ lower f lower E The Theory of Special Relativity (1905): ● The Laws of Physics are the same in all Inertial Frames ● The Speed of Light is the same in all Inertial Frames c = 300,000 km/s ( uniform motion cannot be detected) Albert Einstein E = mc2 m = E/C2 = (1017 J)/(300,000,000 m/s)2 ~ (1017 J)/(1017 m/s) = 1 kg ~ means approximately One megaton of TNT is equivalent to the energy released from 1kg. ɑ = 9.8 m/s2 General Theory of Relativity (1915) Gravity is the result of the curved fabric of the spacetime. ↑ The principle of equivalence is the foundation of general relativity.






















![TEXT: With all wisdom and insight [God] has made known to us the](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/007747874_1-3985d0fda67639394a1af03e474bc0a9-150x150.png)






