* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download White Blood Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
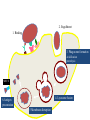
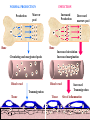
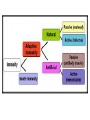
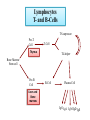
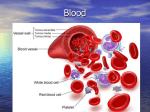
White Blood Cells Prepared by Dr. Hamad ALAssaf [email protected] 2015 Leukocytes / White Blood Cells Granulocytes (65%) - neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils - formed in bone marrow Monocytes (5%) - tissue macrophages - formed in bone marrow Lymphocytes (30%) - formed in lymph tissue - life span: hours to years Leukocytes Classification • Granulocytes – Neutrophils – Eosinophils – Basophils Non- Granulocytes - Monocytes - Lymphocytes • Polymorphonuclear – Neutrophils – Eosinophils – Basophils Mononuclear - Monocytes - Lymphocytes • Phagocytes – Neutrophils, monocytes – Macrophages, eosinophils Non-phagocytes - Lymphocytes - Basophils Phagocytic Cells 1- Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils - non-dividing, short-lived (6 hours to a few days) - dominant number in bloodstream 2- Monocytes/Macrophages - long-lived cells (months) - do not circulate - present in tissue, particularly in lungs, spleen, liver, lymph nodes - tissue macrophage system Actions of Phagocytic Cells 1. Margination 2. Diapedesis 3. Ameboid Motion 4. Chemotaxis 5. Phagocytosis Actions of Phagocytic Cells Phagocytosis 2. Engulfment 1. Binding 3. Phagosome formation Acidification proteolysis MHC II 4. Lysosome fusion 6-Antigen presentation 5 Membrane disruption Cell-mediated Response to Inflammation 1. Tissue macrophages: - already present in tissue 2. Neutrophil invasion: - margination, diapedesis, chemotaxis - stimulation of bone marrow to release stored leukocytes, 4-5 hours 3. Macrophage proliferation: - invasion by circulating monocytes (several hours to increase size) 4. Stimulation of granulocyte and monocyte production: - growth factors produced by tissue macrophages (TNF, IL-1, Cell stimulating factor) NORMAL PRODUCTION Production INFECTION Increased Production Marrow pool Bone Decreased marrow pool Bone Circulating and marginated pools Blood vessel Increased circulation Increased margination Blood vessel Transmigration Tissue Tissue Increased Transmigration Site of inflammation Granulocytes • EOSINOPHILS: - ~ 2% of total white blood cells - active against parasites, skin diseases, chronic infections - phagocytic and immunomodulatory, decrease inflammation - life span 5 days • BASOPHILS: ~ 0.5% of total white blood cells - basophils similar to mast cells - release primarily histamine, some bradykinin - release due to binding of IgE - Life span a few hours to a few days Important terms • Leukopenia : decrease in the number of white blood cells. example: bone marrow suppression • Leukocytosis : increase in the number of white blood cells. example : bacterial infections • Leukemia : (cancerous) uncontrolled production of white blood cells Neutropenia Neutropenia: decreased number of neutrophils due to: Decreased production Increased neutrophil destruction (chronic infections) Agranulocytosis: severe neutropenia due to: production failure due to irradiation exposure to chemicals drugs Immunity It is a special defense mechanism which is mobilized when the body is invaded by a foreign organism. Immunity Innate = (present since birth) - ability to resist damaging organisms and toxins - skin, gastric acids, tissue neutrophils and macrophages, complement Acquired = (developed by exposure to specific invading agents). - humoral ----> circulating antibodies - cellular ----> activated cells Sequence - Dormant lymphocytes - Invasion of body by foreign antigen - Phagocytosis by macrophages - Presentation of antigen to lymphocytes Antigen An antigen: is a substance that can induce an immune response when introduced into an immunocompetent host and that can react with the antibody produced from that response. Lymphocytes T- and B-Cells T8-supressor Pre-T Cell T-Cell Thymus T4-helper Bone Marrow Stem cell Pre-B Cell B-Cell Plasma Cell Liver and Bone marrow IgG IgA IgM IgD IgE T-cells Cytotoxic Cells kill infected cells Helper Cells ( CD-4 cells) activate macrophages and B-cells Suppressor Cells regulate activity