* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Respiratory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Myasthenia gravis wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
Ankylosing spondylitis wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
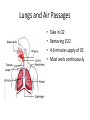
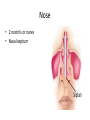
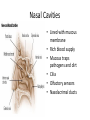
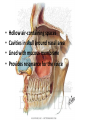
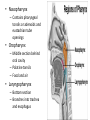
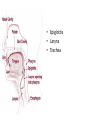
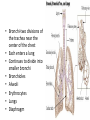
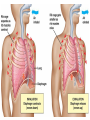
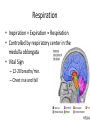
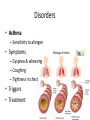
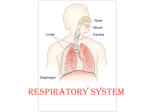
Respiratory System Lungs and Air Passages • • • • Take in O2 Removing CO2 4-6 minute supply of 02 Must work continuously Nose • 2 nostrils or nares • Nasal septum Nasal Cavities • Lined with mucous membrane • Rich blood supply • Mucous traps pathogens and dirt • Cilia • Olfactory sensors • Nasolacrimal ducts • • • • Hollow air-containing spaces Cavities in skull around nasal area Lined with mucous membrane Provides resonance for the voice • Nasopharynx – Contains pharyngeal tonsils or adenoids and eustachian tube openings • Oropharynx – Middle section behind oral cavity – Palatine tonsils – Food and air • Laryngopharynx – Bottom section – Branches into trachea and esophagus • Epiglottis • Larynx • Trachea • Bronchi-two divisions of the trachea near the center of the chest • Each enters a lung • Continues to divide into smaller bronchi • Bronchioles • Alveoli • Erythrocytes • Lungs • Diaphragm Pathway of Air Ventilation • Process of breathing • Respiration – Diaphragm – Intercostal muscles • Two phases – Inspiration – Expiration Respiration • Inspiration + Expiration = Respiration • Controlled by respiratory center in the medulla oblongata • Vital Sign – 12-20 breaths/min. – Chest rise and fall Abnormal Breathing • • • • • • Dysp/nea Ap/nea Tach/yp/nea Brad/yp/nea Orth/op/nea Cyanosis Respiratory Suffixes • • • • • • -ema -osmia -pnea -ptysis -sphyxia -thorax condition smell breathing spitting pulse chest, plural cavity Disorders • Asthma – Sensitivity to allergen • Symptoms – Dyspnea & wheezing – Coughing – Tightness in chest • Triggers • Treatment Disorders • Chronic Bronchitis • Etiological factors – Smoking – Infection • Symptoms – – – – Excessive mucous Wheezing & dyspnea Chest pain Prolonged expiration of air • Treatment – – – – Antibiotics Bronchodilators Respiratory Therapy No cure Disorders • COPD • Any chronic lung disease that results in obstruction of the airways • Smoking is primary cause; allergies and chronic respiration infections are also factors Disorders • Emphysema • Hyperinflation of air sacs • Walls of alveoli deteriorate and lose elasticity – CO2 is trapped – Poor exchange of gases • Causes – Heavy smoking – Prolonged exposure to air pollutants Disorders • Epistaxis (nosebleed) • Occurs when capillaries become congested • Causes – Irritation of mucous membranes (allergies) – Trauma – Vitamin K deficiency – Clotting abnormalities – Hypertension – Dehydration Disorders • Laryngitis • Inflammation of larynx and vocal cords • Frequently occurs with other respiratory infections • Symptoms – Hoarseness or loss of voice – Sore throat – Dysphasia (difficulty swallowing) Disorders • Pleurisy • Inflammation of pleura or membranes of the lungs • Usually occurs with pneumonia or other infections • Symptoms – Sharp stabbing pain while breathing – Capitation or grating sounds in lungs – Dyspnea and fever Disorders • Pneumonia • Inflammation and infection of the alveoli with a build up of fluid or exudates • Usually caused by a bacteria, virus or chemicals • Symptoms – – – – – – Chills Fever Chest pain Productive cough Dyspnea Fatigue Disorders • Tuberculosis • Infectious disease of the lung caused by the bacterium Myobacterium tuberculosis • “TB” • WBC surround invading TB organisms, wall them off creating a nodule “tubercle” – Organisms remain dormant – Can cause an active case later is the body’s resistance is lowered • Symptoms – Fatigue, chest pain, fever, night sweats, wt. loss – Hemoptysis (coughing up blood-tinged sputum)